The Gibbs model of reflection is a widely used framework in the field of nursing and healthcare. It was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 as a way for individuals to analyze and reflect on their experiences in order to improve their practice and facilitate learning.
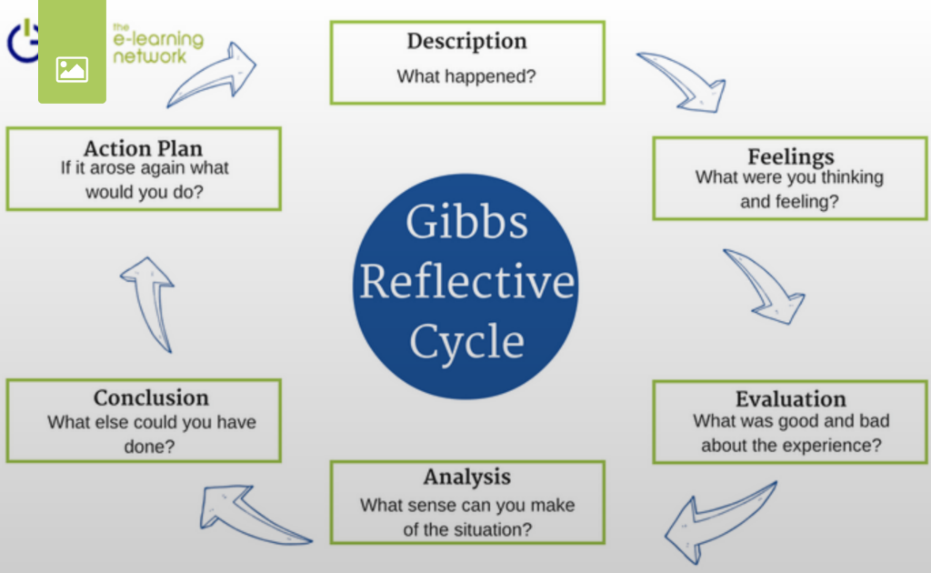
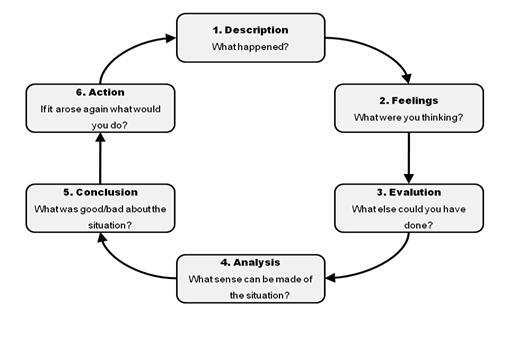
The model consists of six stages: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan. These stages are designed to help the individual reflect on a specific experience or situation in a structured and systematic way.
In the first stage, the individual provides a description of the experience or situation that they are reflecting on. This includes the details of what happened, who was involved, and where and when it took place.
The second stage involves identifying and describing the feelings that the individual experienced during the experience or situation. This can include both positive and negative emotions, as well as any physical sensations that were present.
The third stage involves evaluating the experience or situation. This can include considering the outcomes and consequences of the event, as well as any successes or challenges that were encountered.
The fourth stage involves analyzing the experience or situation in order to identify any patterns or themes that emerge. This can include considering factors such as the individual's own actions, the actions of others, and any external influences that may have impacted the event.
The fifth stage involves drawing a conclusion about the experience or situation, based on the information gathered in the previous stages. This can include identifying any lessons learned or areas for improvement.
Finally, in the sixth stage, the individual develops an action plan for how they can apply the lessons learned from the experience or situation in the future. This can include setting goals and identifying strategies for achieving those goals.
Overall, the Gibbs model of reflection is a valuable tool for nurses and other healthcare professionals to reflect on their practice and identify areas for improvement. By going through the six stages of the model, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their experiences and use that understanding to make positive changes in their practice.