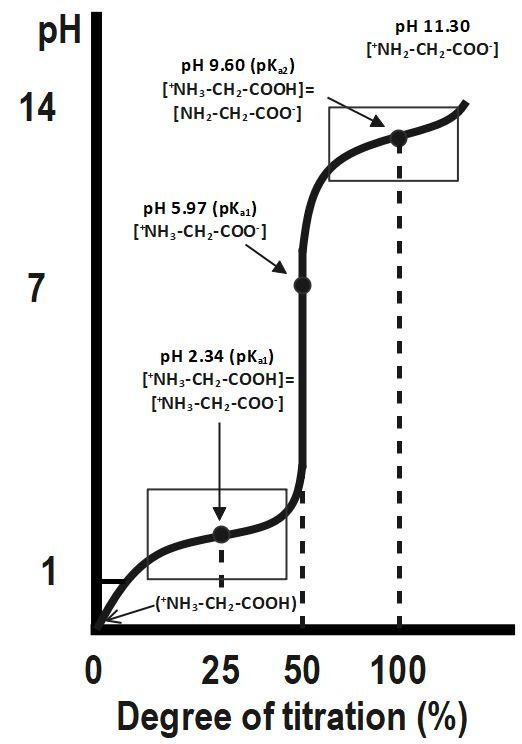
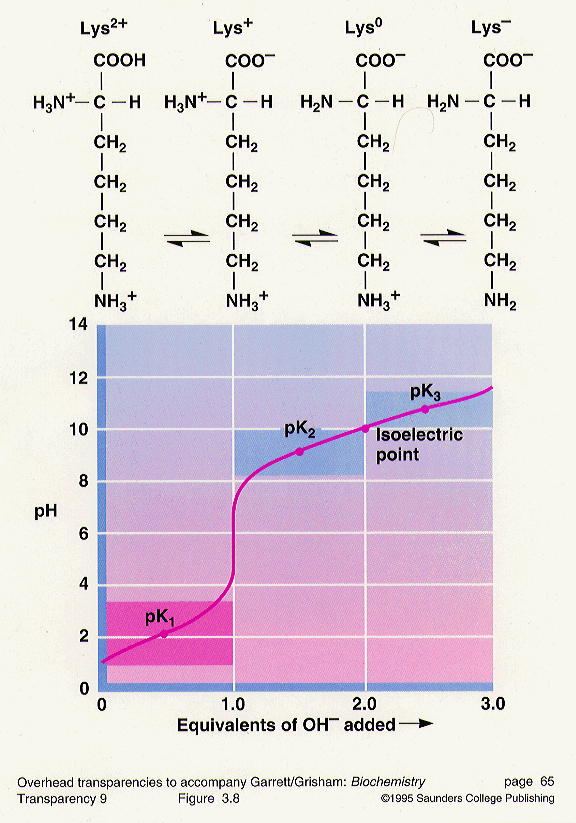
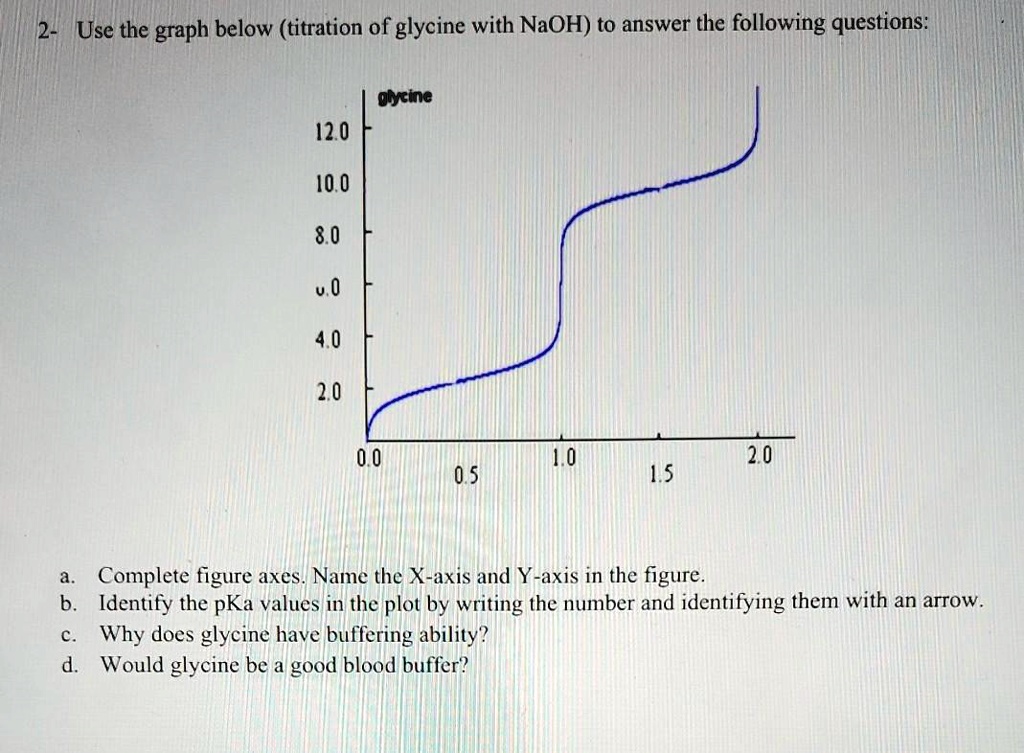
Glycine hydrochloride is a compound that can be titrated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to determine the concentration of the glycine hydrochloride solution. Titration is a common laboratory technique used to determine the concentration of a solution by reacting it with a known concentration of another solution. In this case, the glycine hydrochloride solution is titrated with a standardized NaOH solution to determine the concentration of the glycine hydrochloride.
The titration process begins by preparing a standard NaOH solution of known concentration. This solution is typically prepared by weighing out a precise amount of NaOH and dissolving it in distilled water to make a specific volume. The concentration of the NaOH solution is typically expressed in units of moles per liter (M).
The glycine hydrochloride solution is then placed in a titration flask, along with a suitable indicator. The indicator is a substance that changes color when it reacts with the glycine hydrochloride or the NaOH solution. The most common indicator for this type of titration is phenolphthalein, which turns pink in the presence of a basic solution such as NaOH.
Next, the NaOH solution is slowly added to the glycine hydrochloride solution using a burette, which is a calibrated glass tube with a stopcock that allows precise measurements of the volume of the solution being added. The NaOH solution is added drop by drop until the endpoint of the titration is reached. The endpoint is the point at which the indicator changes color, indicating that the reaction between the glycine hydrochloride and the NaOH is complete.
Once the endpoint is reached, the volume of the NaOH solution that was required to reach the endpoint is recorded. This volume, along with the concentration of the NaOH solution and the molar mass of the glycine hydrochloride, can be used to calculate the concentration of the glycine hydrochloride solution.
Titration of glycine hydrochloride with NaOH is a useful technique for determining the concentration of glycine hydrochloride solutions, as well as for determining the purity of the glycine hydrochloride. It is important to use accurate measurements and carefully follow the titration procedure to ensure accurate results.