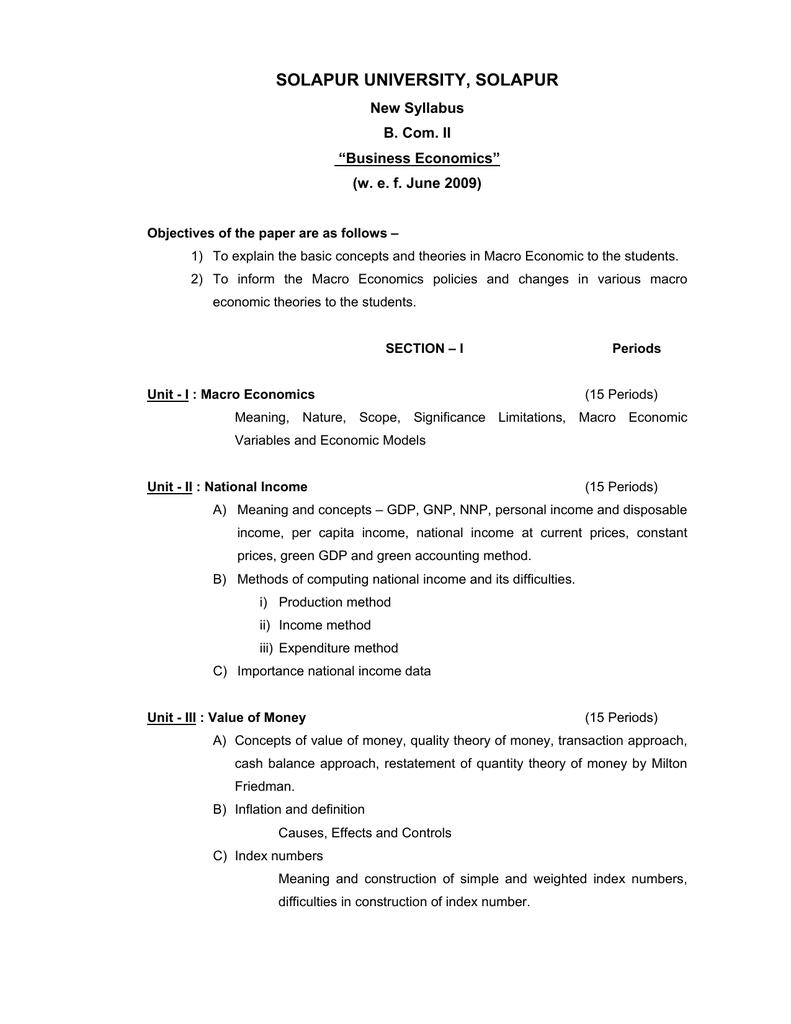
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a measure of the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders in a given year. It is often used as a measure of the size and strength of an economy, as well as a way to compare the economic performance of different countries. GDP can be calculated in various ways, but one common method is to add up the value of all final goods and services produced in a year, taking into account the prices at which they were sold.
There are several advantages to using GDP as a measure of economic performance. One of the main advantages is that it provides a comprehensive measure of economic activity. GDP takes into account a wide range of economic activities, including consumer spending, business investment, government spending, and exports. This makes it an effective tool for understanding the overall health of an economy.
Another advantage of GDP is that it is relatively easy to calculate. Since it is based on the value of goods and services produced within a country's borders, it is relatively straightforward to measure and compare across different countries. This makes it an important tool for policymakers and analysts who need to make informed decisions about economic policy and the direction of an economy.
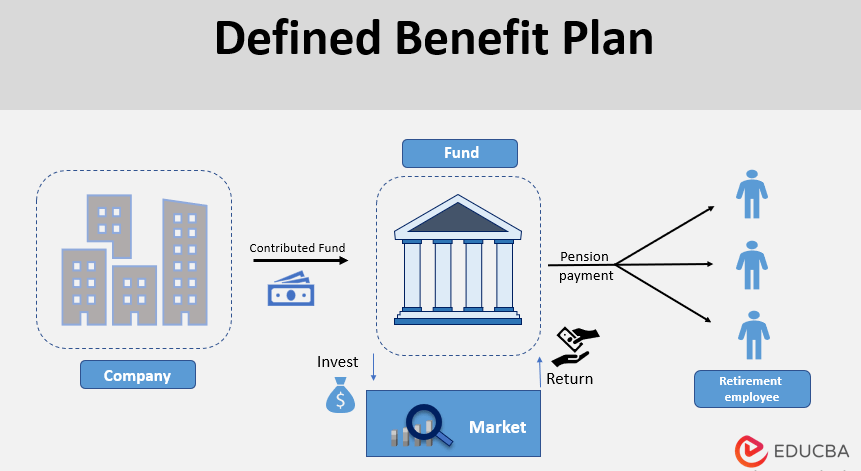
However, there are also several disadvantages to using GDP as a measure of economic performance. One of the main disadvantages is that it does not take into account the value of goods and services that are produced outside a country's borders. For example, if a company based in one country produces goods that are sold to consumers in another country, the value of those goods is not included in the GDP of the producing country. This means that GDP can underestimate the economic activity of countries that are heavily dependent on exports.
Another disadvantage of GDP is that it does not take into account the distribution of income or wealth within a country. For example, if GDP is increasing but the majority of the population is not seeing any benefits from this increase, it may not be an accurate measure of economic well-being.
Finally, GDP does not take into account the negative externalities of economic activity, such as pollution or other forms of environmental degradation. This means that GDP can overstate the true economic value of certain activities that have negative impacts on society or the environment.
Overall, GDP is a useful measure of economic performance, but it is important to recognize its limitations. It is best used as one tool among many when trying to understand the complex economic dynamics of a country or region.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gross-national-income-4020738-ADD-FINAL-v3-467160175f3a4947adfc2ff802927356.jpg)