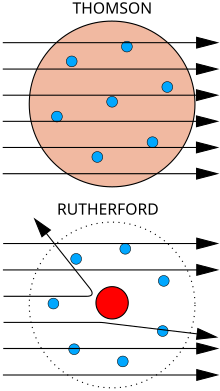
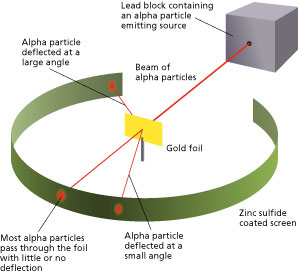
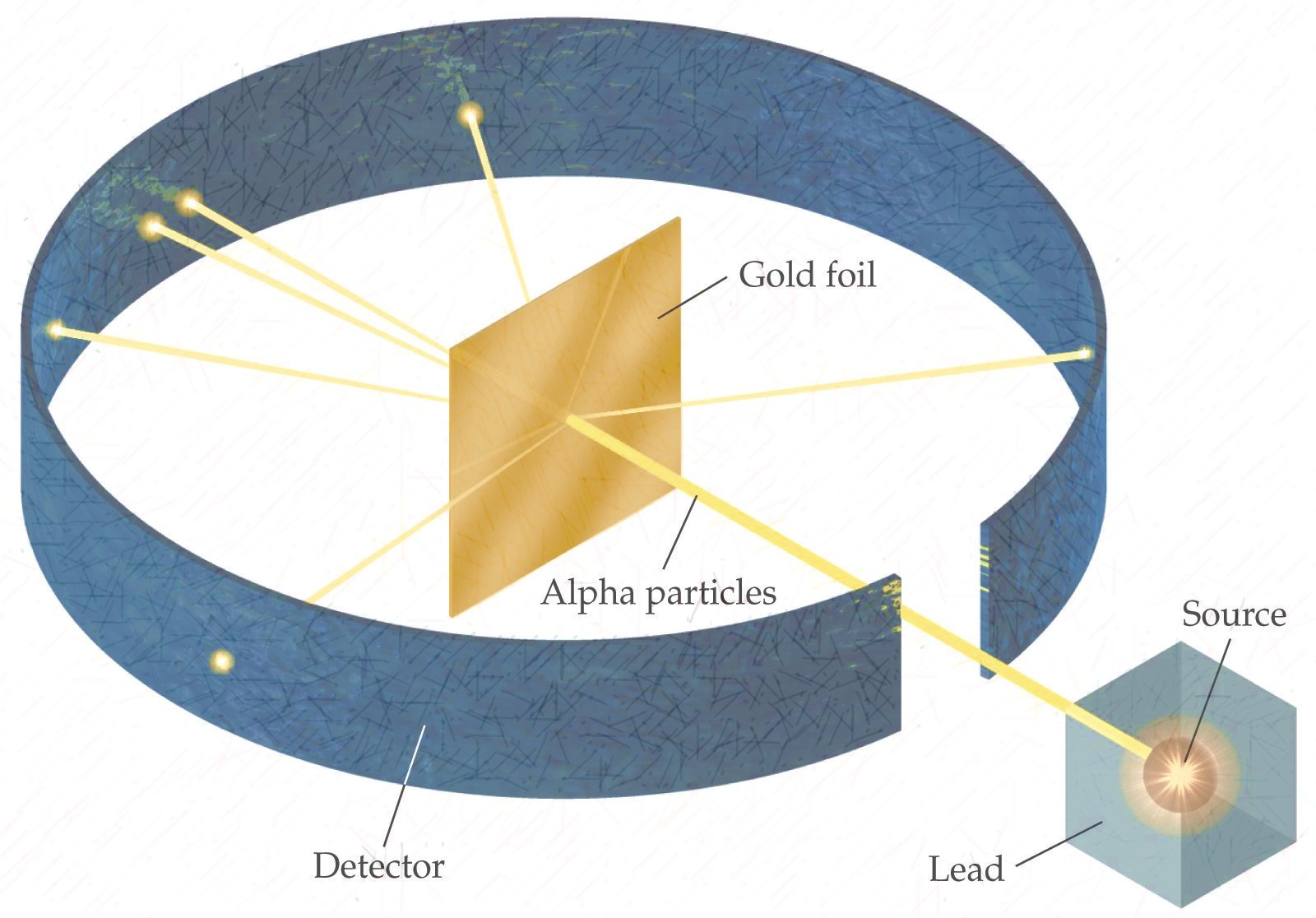
The gold foil experiment, also known as the Rutherford experiment, was a series of experiments conducted by physicist Ernest Rutherford in 1911. These experiments were designed to investigate the structure of the atom, which at the time was believed to be a solid, indivisible sphere.
Rutherford and his team bombarded a thin sheet of gold foil with alpha particles, which are positively charged particles emitted by certain types of radioactive decay. They then used a detector to measure the deflection of the alpha particles as they passed through the foil.
To their surprise, they found that most of the alpha particles passed straight through the foil without being deflected at all. However, a small percentage of the alpha particles were deflected at large angles, suggesting that there was something in the gold foil that was able to exert a significant force on the particles.
Rutherford was able to explain this result by proposing that the atom was not a solid sphere, but rather was composed of a small, dense nucleus at its center, surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The alpha particles were able to pass through the cloud of electrons without being deflected, but when they encountered the dense nucleus, they were deflected due to the strong electric force exerted by the positively charged nucleus.
The gold foil experiment was a groundbreaking achievement that helped to revolutionize our understanding of the structure of the atom. It provided the first experimental evidence for the existence of the atomic nucleus and helped to lay the foundation for the development of modern atomic theory.
Ernest Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment: Physics Lab
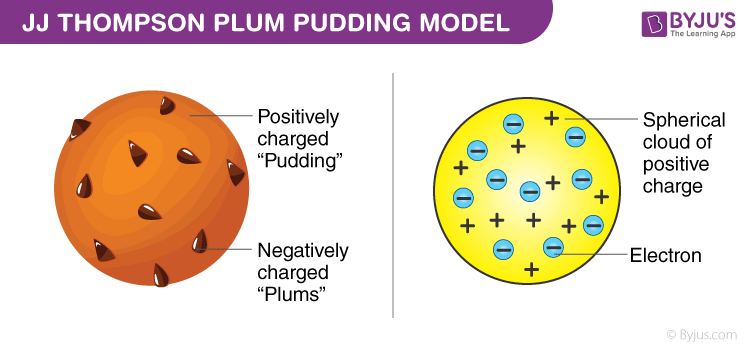
Categories Post navigation The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society. Democritus imagined this by performing a thought experiment where a piece of the matter was cut in half continuously, and each subsequent half was then cut in half. It was a very poor and inefficient way of producing energy, and anyone who looked for a source of power in the transformation of the atoms was talking moonshine. Rutherford reasoned that if Thomson's plum pudding model was correct, then when an α-particle hit a thin foil of gold, the particle should pass through with only the tiniest of deflections.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment

Thomson hypothesized that positively charged alpha particles would almost exclusively follow a straight path when fired through an atom. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that atoms are mostly empty space, with the positive charge concentrated in a nucleus. From the beginning of his research with alpha particles to his discovery of the atomic nucleus, Rutherford made many contributions to the microscopic world of the atom. Like the plum pudding model, since the positive charge of atoms was evenly distributed and too small as compared to that of the alpha particles, the deflection of the particulate matter was predicted to be less than a small fraction of a degree. The way in which the positive particles bounced off the thin foil indicated that the majority of the mass of an atom was concentrated in one small region. Even more shocking, around 1 in 10,000 α-particles were reflected directly back from the gold foil.
Ernest Rutherford
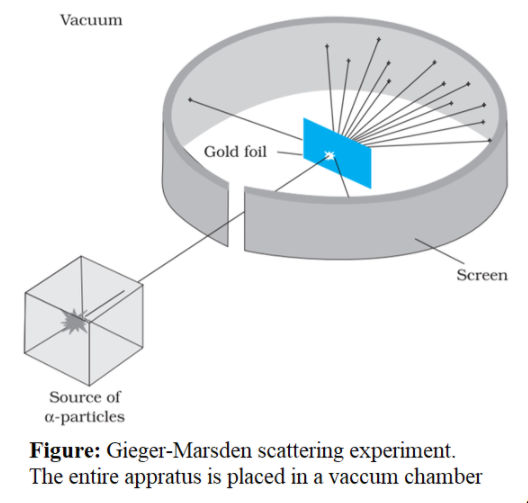
The result, however, was that the positive particles were repelled off of the gold foil by nearly 180 degrees in a very small region of the atom, while most of the remaining particles were not deflected at all but rather passed right through the atom. Geiger and Marsden didn't know what the positive charge of the nucleus of their metals were they had only just discovered the nucleus existed at all , but they assumed it was proportional to the atomic weight, so they tested whether the scattering was proportional to the atomic weight squared. Alpha particles are energetic nuclei of helium usually about 6 MeV. Although much of his theory is still true today, one point was disproved by Ernest Rutherford. The Rutherford gold foil experiment falsified Thomson's hypothesis by demonstrating that atoms scattered the alpha particles. Alpha particles are positively charged particles with a mass of about four times that of a hydrogen atom and are found in radioactive natural substances.
Gold Foil Experiment
Thomson measured the mass and charge of the cathode rays by influencing them with an electromagnet and measuring how much the rays were deflected. When alpha particles, which are heavy energetic radiation, were bombarded on the gold foil, it was expected that the beam would penetrate the foil with slight divergence and with a reduction in speed. In fact, most of the matter isempty space. Next, he set out to determine the relative size of the nucleus compared to the rest of the atom. The idea that atoms could not be subdivided into smaller units was later falsified by the physicist J.