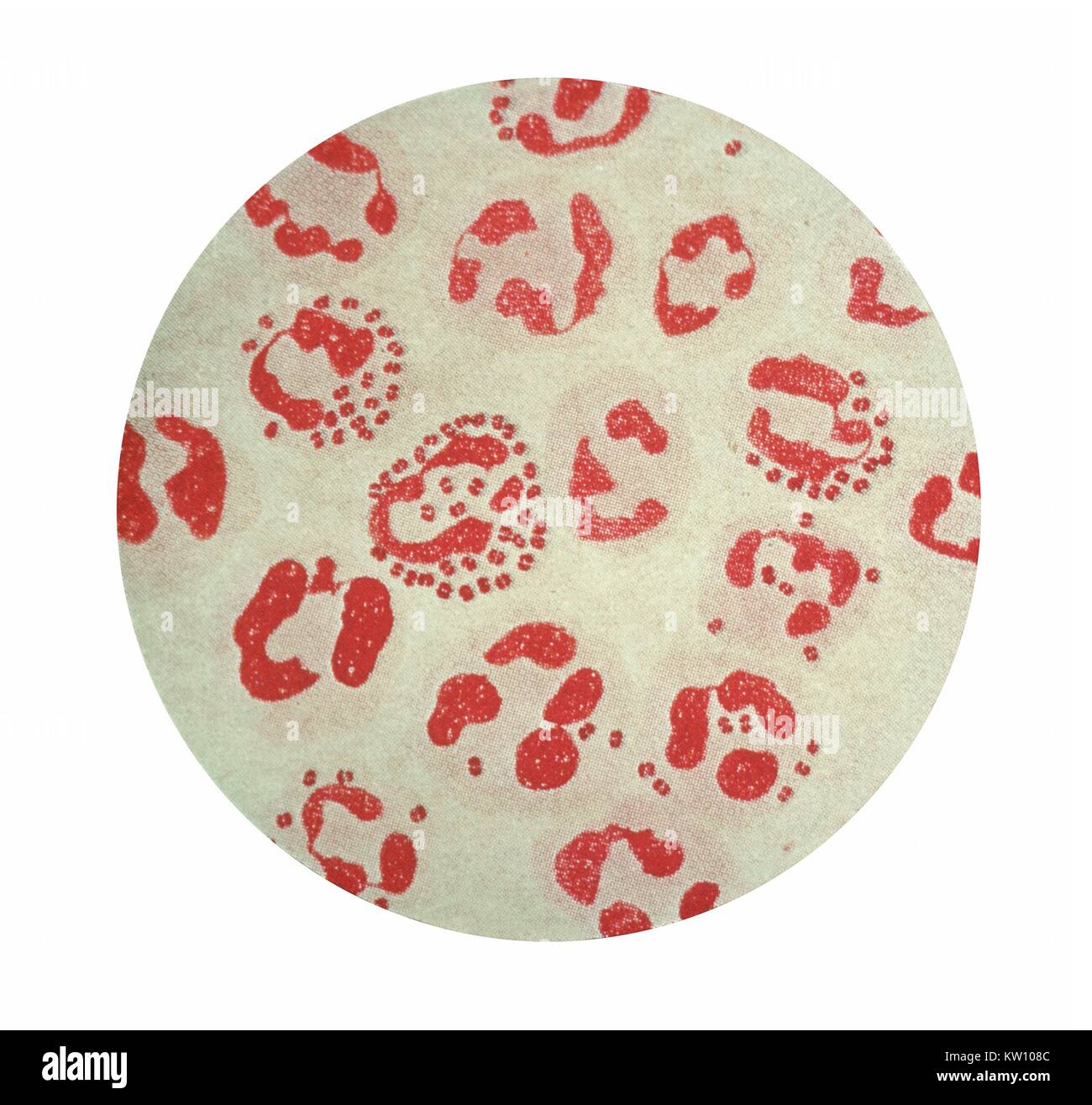
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is a gram-negative diplococcus, meaning it is a bacterium that appears as pairs of cells when viewed under a microscope. The cells are round or oval in shape and are surrounded by a thin, outer membrane.
One of the key features of N. gonorrhoeae is its ability to invade and colonize the mucosal surfaces of the reproductive tract. It is able to do this because of its unique cell surface structure. The outer membrane of the bacterium is composed of lipooligosaccharides, which allow it to evade the host immune system and attach to host cells.
In addition to its outer membrane, N. gonorrhoeae has a number of other surface proteins that allow it to survive and thrive in the host environment. For example, it has pili, which are short, hair-like projections that help the bacterium adhere to surfaces and move around. It also has a capsule, which is a layer of polysaccharides that surrounds the cell and helps protect it from the host immune system.
N. gonorrhoeae also has several enzymes that allow it to survive in the host environment. One of these is an enzyme called penicillinase, which breaks down the antibiotics penicillin and ampicillin. This allows the bacterium to resist treatment with these drugs, making it more difficult to treat.
In conclusion, the morphology of N. gonorrhoeae plays a crucial role in its ability to cause infection and evade the host immune system. Its unique cell surface structure, including its outer membrane, pili, capsule, and enzymes, allow it to colonize mucosal surfaces and survive in the host environment.
Gonorrhea

It is Gram-negative and oxidase-positive. Culture growing colonies of bacteria in order to isolate and identify them and Gram-stain staining of bacterial cell walls to reveal morphology can also be used to detect the presence of N. In addition, in strains that cause systemic infection, LOS binds sialic acid from the serum forming a microcapsule of sialylated LOS, which allows the gonococci to resist the host immune response and serum bactericidal reaction. A doctor can test for gonorrhea with a urine sample. Chris Bignell and Magnus Unemo ORAN, J. Retrieved 25 April 2022. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University.
Morphology & Culture Characteristics of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
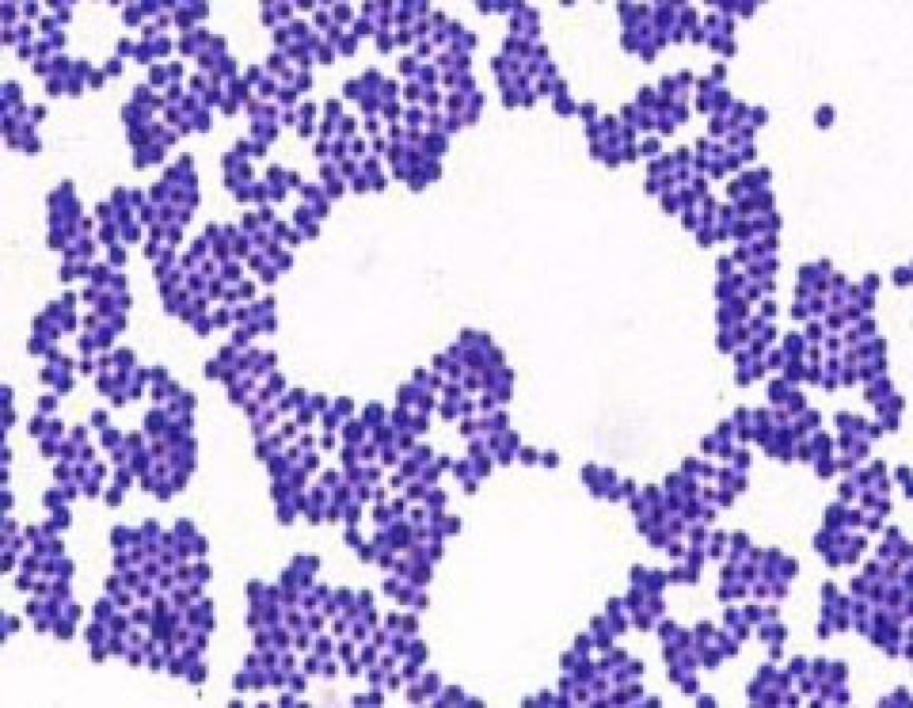

MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 2012 , 61, 590-594. I also known as Por is equivalent to the ompC and ompF porins of E. Neisseria sicca is a gram-negative diplococcus found as nor- mal human oral and upper respiratory tract flora; it is considered one of the commensal Neisseria species. Size— The size of Neisseria gonorrhoeae is about 0. The bacterium is able to form two transferrin receptors Tbp1 and Tbp2 and one lactoferrin receptor Lbp in its outer membrane, which are stimulated under low-iron conditions, and are able to directly extract iron from transferrin and lactoferrin. Review of medical microbiology and immunology Thirteenthed.
Does Neisseria gonorrhea show up on Gram stain?

Urogenital gonorrhea can be diagnosed by testing urine, urethral for men , or endocervical or vaginal for women specimens using nucleic acid amplification testing NAAT 19. Higher order taxa Domain: Bacteria Phylum: Probacteria Class: Beta Probacteria Order: Neisseriales Family: Neisseriaceae Species Neisseria Gonorrhoeae NCBI: Description and significance Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a gram-negative coccus, or bacteria whose overall shape is spherical. Transmission of gonorrhea: mucus membrane infection due to vaginal, oral or anal sexual contact. In some cases, they may also swab the urethra, anus, throat, or cervix to get a more reliable result. The main pathogenicity of the Neisseria gonorrhea stems from the surface pili by following mechanisms: Mediate attachment to the surface of the urethra, fallopian tubes, and endocervix Preventing phagocytosis by neutrophils Opa proteins opacity-associated protein are surface proteins that help gonococcus binds to receptors on immune cells Most Popular Search.