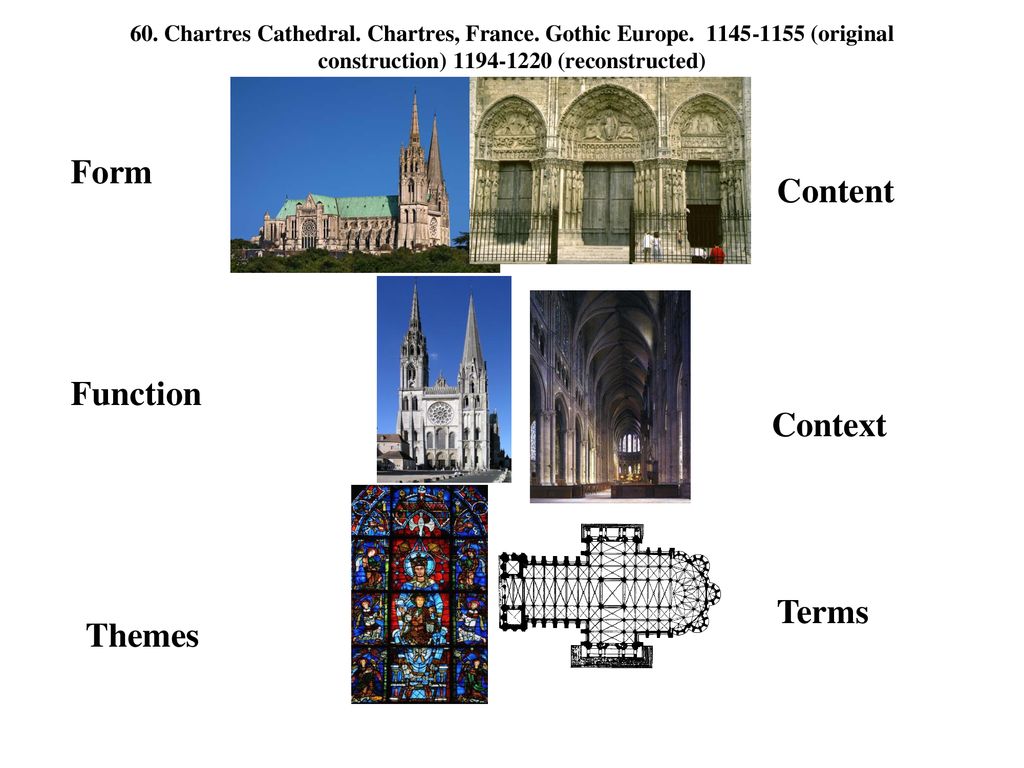
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished in Europe during the High and Late Middle Ages. It is characterized by the use of pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, as well as by elaborate ornamentation and intricate stone carving. Gothic architecture emerged in the 12th century and became the dominant architectural style in Europe until the 16th century.
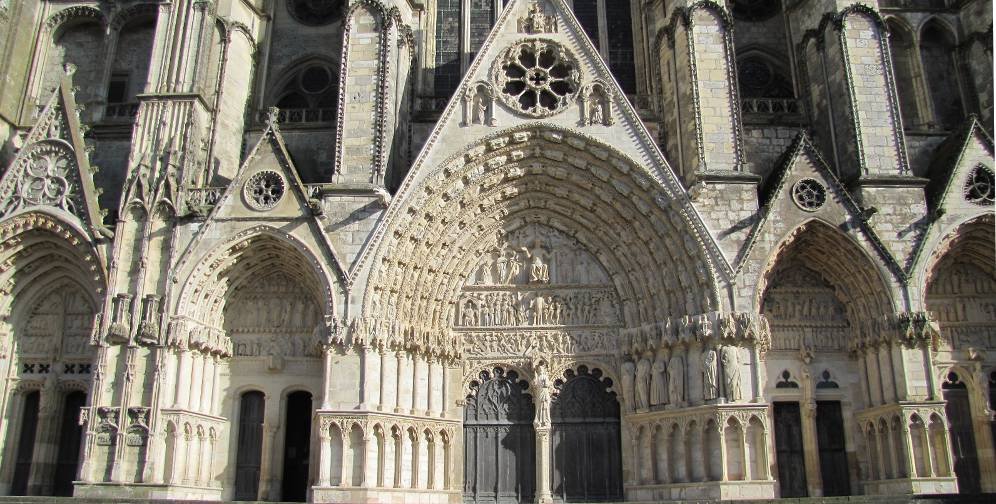
One of the key features of Gothic architecture is the pointed arch. This type of arch is characterized by its sharp, pointed shape, which allows it to support greater weight than a rounded arch. Pointed arches were used extensively in Gothic architecture, and were used to create doorways, windows, and other openings in buildings.
Ribbed vaults are another key feature of Gothic architecture. These vaults are made up of a series of arched ribs that support the weight of the ceiling. Ribbed vaults were often used in Gothic churches and cathedrals, and allowed for the creation of large, open interior spaces.
Flying buttresses are another characteristic feature of Gothic architecture. These are external supports that are used to help bear the weight of the building. Flying buttresses are typically found on the exterior of Gothic buildings, and are composed of arches that extend from the ground to the top of the building.
Gothic architecture is also known for its elaborate ornamentation and intricate stone carving. This includes the use of decorative elements such as gargoyles, which were used to decorate the exterior of buildings. Gothic buildings were also often adorned with intricate stone carvings, including figures of saints and other religious figures, as well as geometric patterns and other decorative elements.
In summary, Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that is characterized by the use of pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, as well as by elaborate ornamentation and intricate stone carving. It was a dominant architectural style in Europe during the High and Late Middle Ages, and is known for its grand and impressive buildings, such as churches and cathedrals.
Gothic Architecture (TERMS) Flashcards
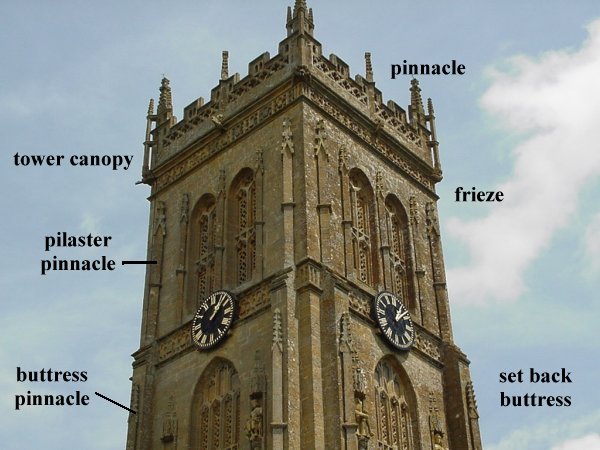
The Pointed Arch A modern example of the characteristic pointed arch. Wall buttresses of high projection, and flying buttresses Complex Gothic buttresses supported the high vaults and the walls pierced with windows 5 Windows Round arches, sometimes paired Pointed arches, often with tracery Gothic windows varied from simple lancet form to ornate flamboyant patterns 6 Piers and columns Cylindrical columns, rectangular piers Cylindrical and clustered columns, complex piers Columns and piers developed increasing complexity during the Gothic era 7 Gallery arcades Two openings under an arch, paired. The term Rayonnant was used to describe the French High Gothic architecture between 1240 and 1350. A portion of the choir collapsed in 1284, causing alarm in all of the cities with very tall cathedrals. Shutter Dogs: The metal attachments which hold shutters in an open position against the face of a building. Canopies are often built over entrances to shelter people from rain or to provide them with shade. One common ornament of flamboyant in France is the arc-en-accolade, an arch over a window topped by a pinnacle, which was itself topped with flamboyant building include the west façade of In England, ornamental rib-vaulting and tracery of Decorated Gothic co-existed with, and then gave way to, the perpendicular style from the 1320s, with straightened, orthogonal tracery topped with Perpendicular Gothic was unknown in continental Europe and unlike earlier styles had no equivalent in Scotland or Ireland.
Glossary of Architectural Terms

A popular example of this style is the Sainte-Chappelle 1242-1248 , located in Paris, which King Louis IX commissioned to hold his numerous holy relics. What is Gothic Architecture? It refers to the aesthetic of unfinished concrete after being removed from formwork. These stone, arched structures extended from the upper portion of walls to piers of great mass in order to redistribute the weight of the heavy roof. Canterbury Cathedral Canterbury Cathedral, Canterbury, Kent. A notable example of this style during the gothic period applied in religious gothic architecture is the Church of St. But, without citing many authorities, such as The Elements of Architecture,.
The Origins and Evolution of Gothic Architecture

The Changing Scottish Landscape, 1500—1800. The large clerestory windows often used tracery, a decorative type of stone support, and detailed Biblical stories Pointed Arches were another critical feature of gothic architecture to be both decorative and practical. These ceilings are another feature of gothic architecture. Stone castles and cathedrals were rudimentary — dark, cold, and damp. The Romans always concealed their Butments, whereas the Normans thought them ornamental.