The golden ratio, also known as the golden section or the divine proportion, is a mathematical concept that has captivated the minds of artists, architects, and mathematicians for centuries. The ratio, denoted by the Greek letter phi (φ), is approximately equal to 1.618 and is found in many natural and man-made objects.
The golden ratio can be described as the ratio of the smaller part of a whole to the larger part, or the ratio of the larger part to the whole. In mathematical terms, this can be expressed as a+b is to a as a is to b, or a/b = (a+b)/a.
One of the earliest known references to the golden ratio can be found in the writings of the ancient Greeks. The mathematician Euclid described the golden ratio as "the most beautiful of all proportions" in his work "Elements." The golden ratio also appears in the work of the ancient Greek sculptor Phidias, who used it to create aesthetically pleasing works of art.
The golden ratio has been used throughout history in a variety of contexts. In art, the golden ratio has been used to create compositions that are aesthetically pleasing to the eye. Architects have used the golden ratio to design buildings that are harmonious and pleasing to look at. The golden ratio has also been used in the design of websites and other digital media, as it is thought to be aesthetically pleasing to the human eye.
One of the most famous examples of the use of the golden ratio can be found in the design of the Parthenon in Athens. The Parthenon is considered to be a prime example of classical architecture, and its design incorporates the golden ratio in many ways. The length and width of the temple, as well as the height of the columns, all follow the golden ratio.
The golden ratio has also been found to occur in nature. The spiral patterns found in seashells and pinecones, for example, are believed to be based on the golden ratio. The human body also exhibits the golden ratio, with the ratio of the length of the hand to the length of the arm being approximately equal to the golden ratio.
Despite its widespread use and recognition, the golden ratio has also been the subject of some controversy. Some have argued that the golden ratio is overrated and that its importance has been exaggerated. Others have claimed that the golden ratio is not as common in nature as some believe.
In conclusion, the golden ratio is a mathematical concept that has fascinated people for centuries. It has been used in art, architecture, and design to create aesthetically pleasing compositions and has been found in a variety of natural objects. While it has been the subject of some controversy, the golden ratio remains an important and widely recognized concept.
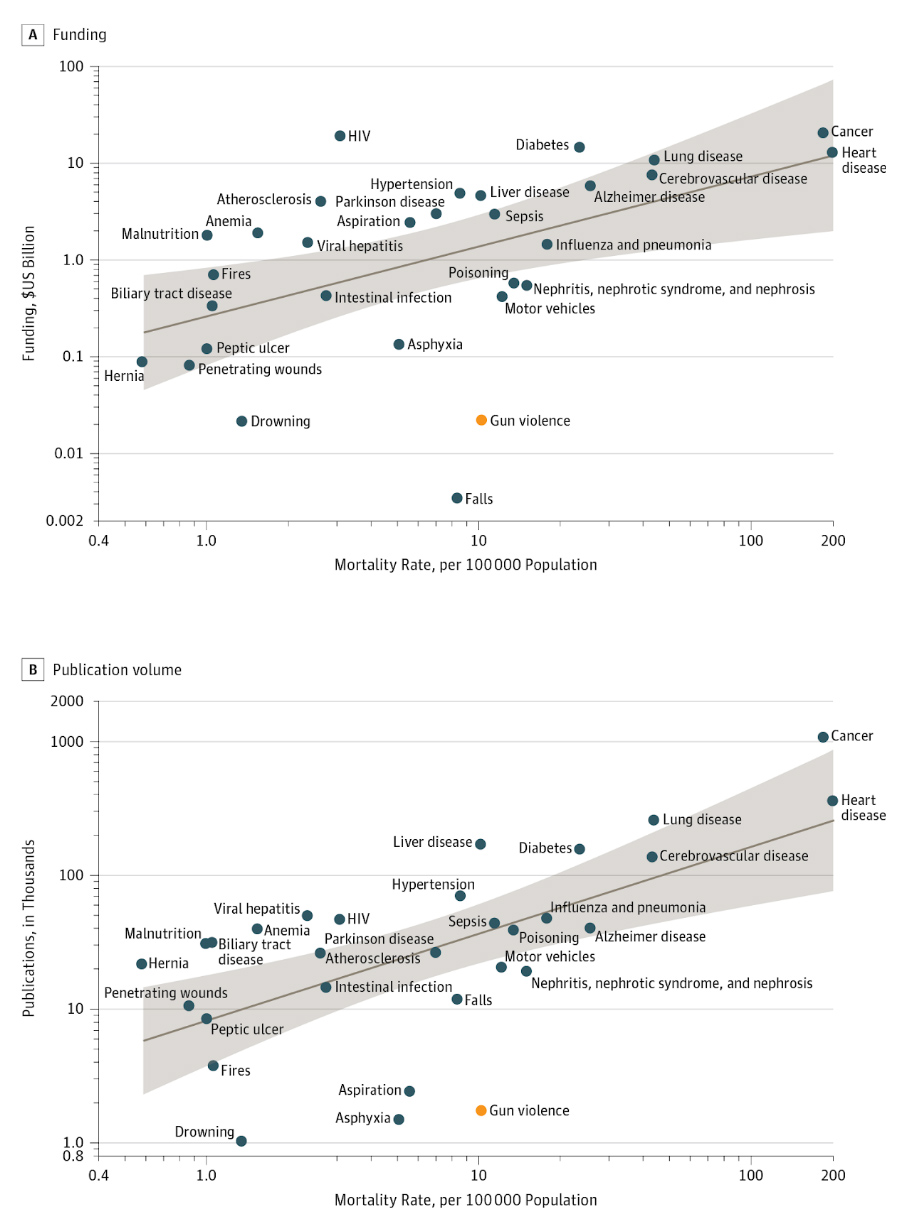
Gun control is a controversial and divisive issue in the United States and other countries around the world. The right to bear arms is protected by the Second Amendment of the United States Constitution, and this right has been fiercely defended by gun rights advocates for centuries. However, the high rates of gun violence in the United States, particularly mass shootings, have led to calls for stricter gun control laws.
There is a significant body of research on the topic of gun control, and the results of this research are often used to inform policy decisions and shape public opinion on the issue. Many studies have focused on the effectiveness of different types of gun control laws, such as background check requirements, age limits, and bans on certain types of firearms. Other research has examined the relationship between gun ownership and gun violence, as well as the impact of cultural and societal factors on gun violence rates.
One of the main arguments made by gun control advocates is that stricter gun laws can reduce gun violence and save lives. Studies have found that countries with stricter gun laws tend to have lower rates of gun violence, and that states in the United States with stricter gun laws also have lower rates of gun violence. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Public Health found that states with stricter gun laws had significantly lower rates of gun homicides and suicides.
However, gun rights advocates argue that stricter gun laws are not the solution to gun violence, and that they can even be counterproductive. They argue that responsible gun owners who follow the law are not the problem, and that stricter gun laws will not deter criminals from obtaining guns illegally. Some research has supported this view, with studies finding that gun control laws have had little or no impact on gun violence rates.
Ultimately, the debate over gun control is complex and multifaceted, and there is no simple answer to the question of whether stricter gun laws are the solution to gun violence. While research suggests that stricter gun laws can be effective in reducing gun violence, it is important to consider the potential unintended consequences of such laws, as well as the cultural and societal factors that contribute to gun violence. It is also important to recognize that addressing gun violence requires a multifaceted approach that involves not only policy changes, but also efforts to address the root causes of violence and promote community-based solutions.