Gut acidifiers are substances that are added to the feed of poultry to lower the pH of the gut and create a more acidic environment. The use of gut acidifiers in poultry production has gained popularity in recent years due to the potential benefits they offer for the health and performance of the birds.
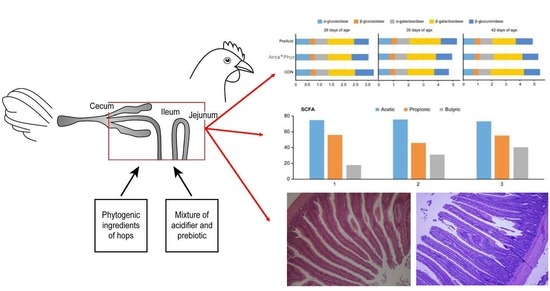
One of the main reasons for using gut acidifiers in poultry is to improve the digestion of feed and increase nutrient absorption. The pH of the gut plays a critical role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, and an optimal pH can improve the utilization of feed by the birds. Acidifiers can also help to reduce the risk of bacterial infections in the gut by creating an environment that is inhospitable to harmful bacteria.
Another benefit of gut acidifiers is their ability to reduce the incidence of necrotic enteritis, a common and often deadly disease in poultry caused by the bacteria Clostridium perfringens. Necrotic enteritis is a serious problem in the poultry industry, as it can lead to significant losses in production and animal welfare. Gut acidifiers have been shown to be effective at reducing the severity of necrotic enteritis by inhibiting the growth of C. perfringens and other harmful bacteria in the gut.
Gut acidifiers can also improve the overall performance of poultry by increasing feed conversion efficiency, growth rate, and carcass yield. These effects are likely due to the improved digestion and nutrient absorption that result from the use of acidifiers.
There are several different types of gut acidifiers that are used in poultry production, including organic acids, buffered acids, and inorganic acids. The most common types of acidifiers are organic acids, such as propionic acid and formic acid, which are derived from natural sources. Buffered acids, such as sodium diacetate, are also commonly used and are often preferred due to their ability to maintain a consistent pH in the gut. Inorganic acids, such as sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, are less commonly used due to their potential to cause irritation and damage to the gut lining.
The use of gut acidifiers in poultry production has been controversial due to concerns about their potential negative effects on animal health and welfare. Some research has suggested that high levels of acidifiers can cause irritation and damage to the gut lining, leading to impaired digestion and nutrient absorption. In addition, there is evidence to suggest that gut acidifiers may alter the gut microbiome and negatively impact the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Overall, the use of gut acidifiers in poultry production can offer numerous benefits, including improved digestion and nutrient absorption, reduced risk of bacterial infections, and improved performance. However, it is important to use these products responsibly and in accordance with established guidelines to minimize the potential negative effects on animal health and welfare.