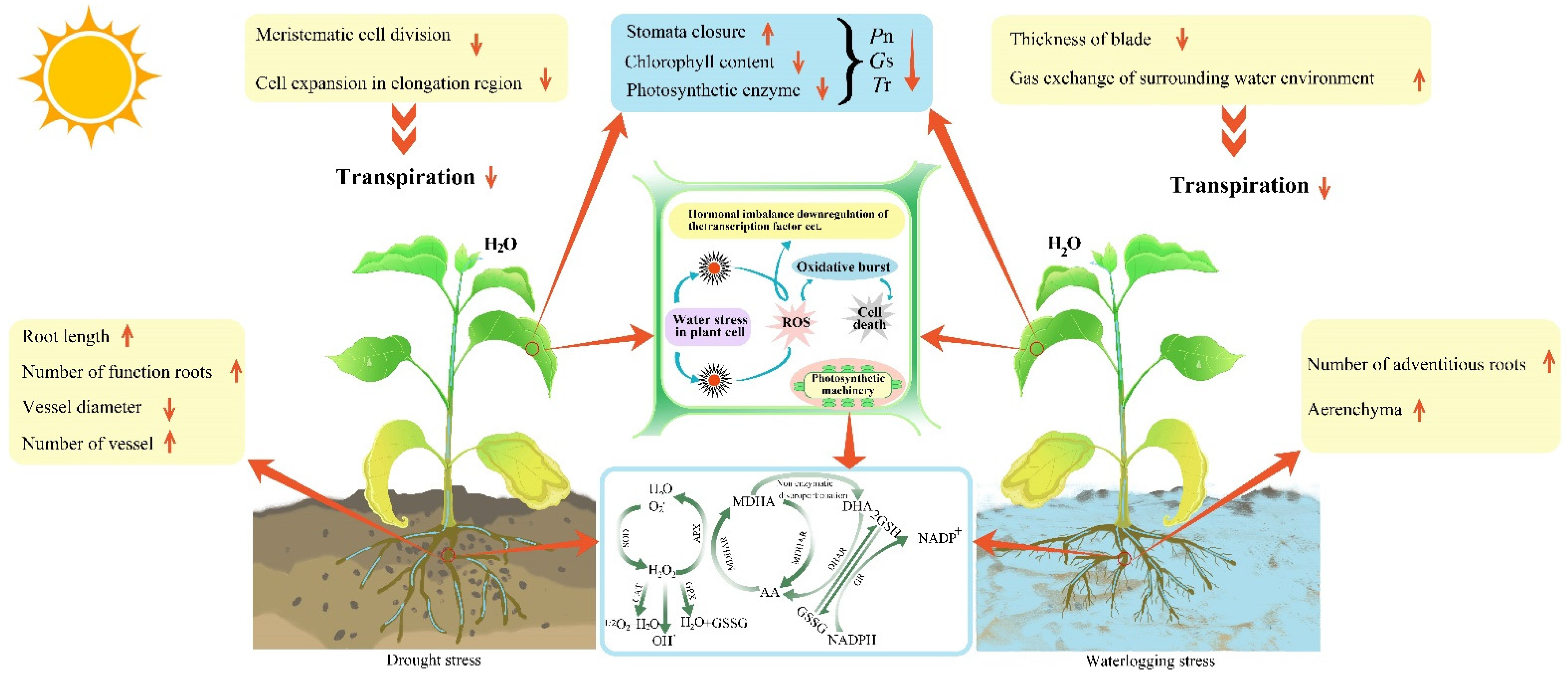
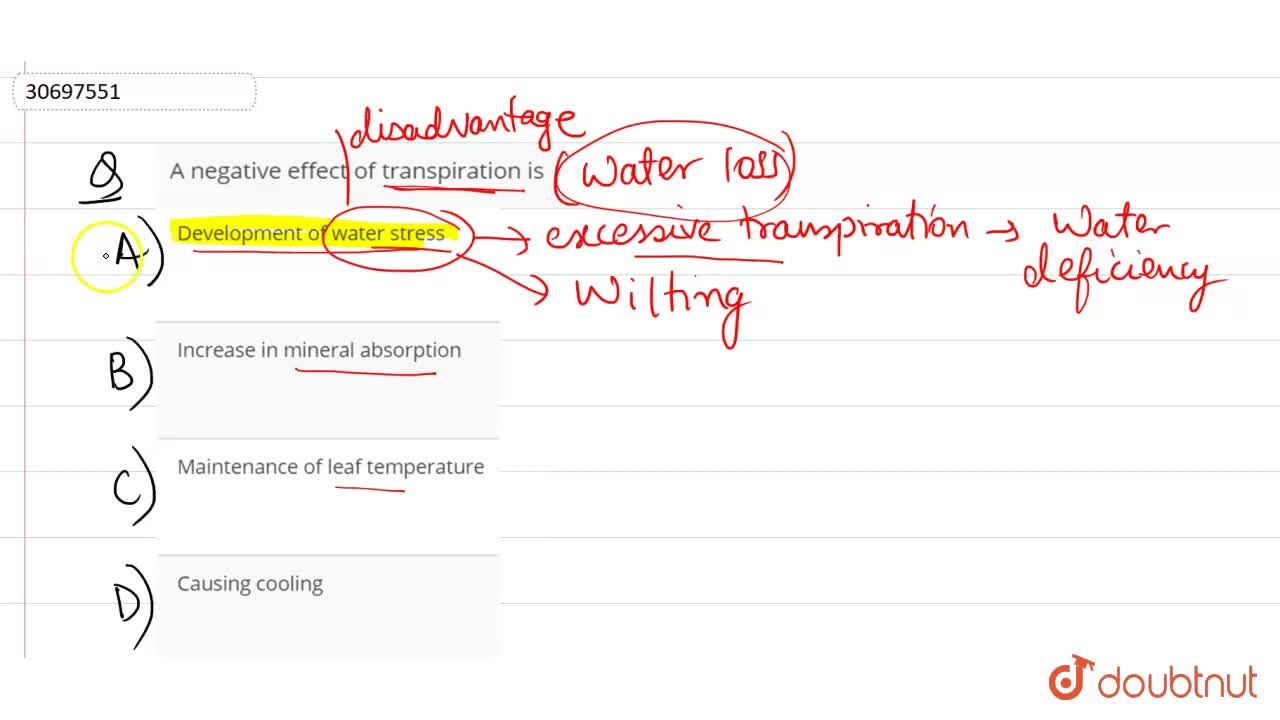
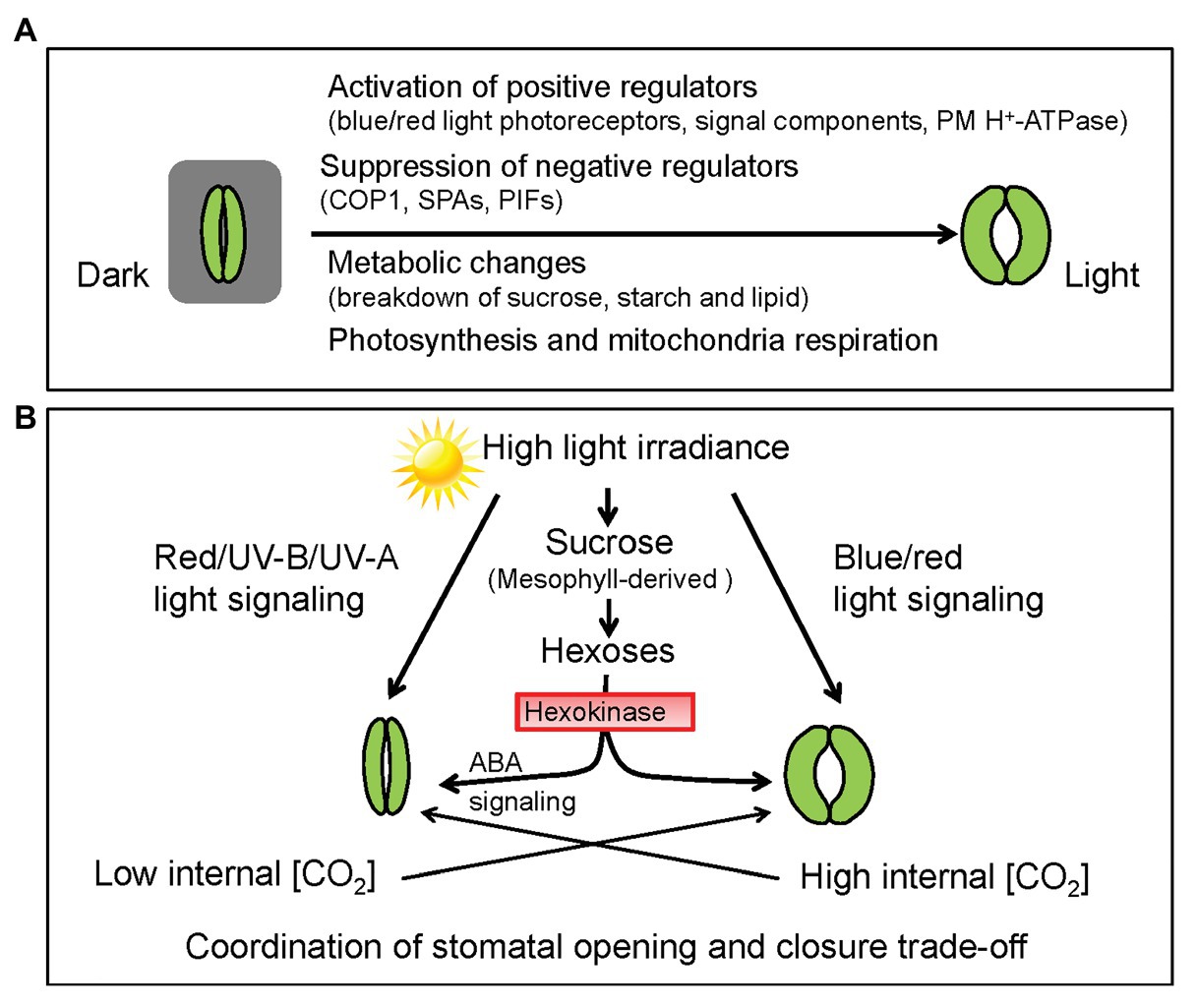
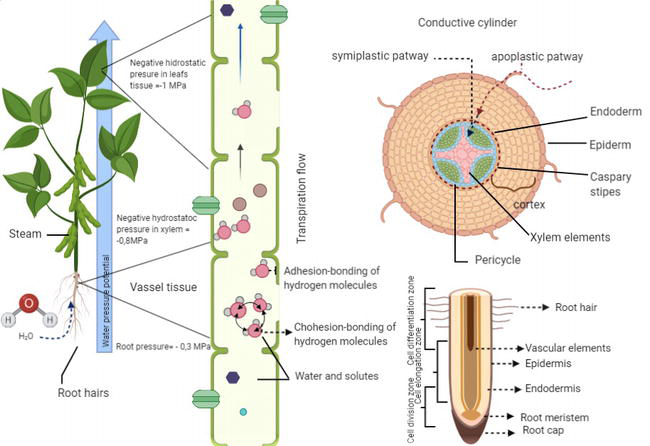
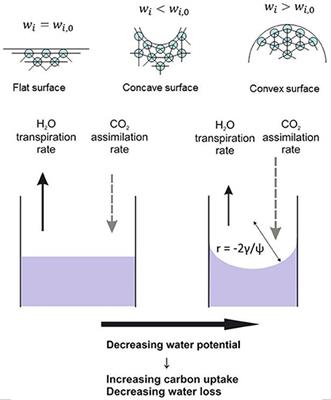
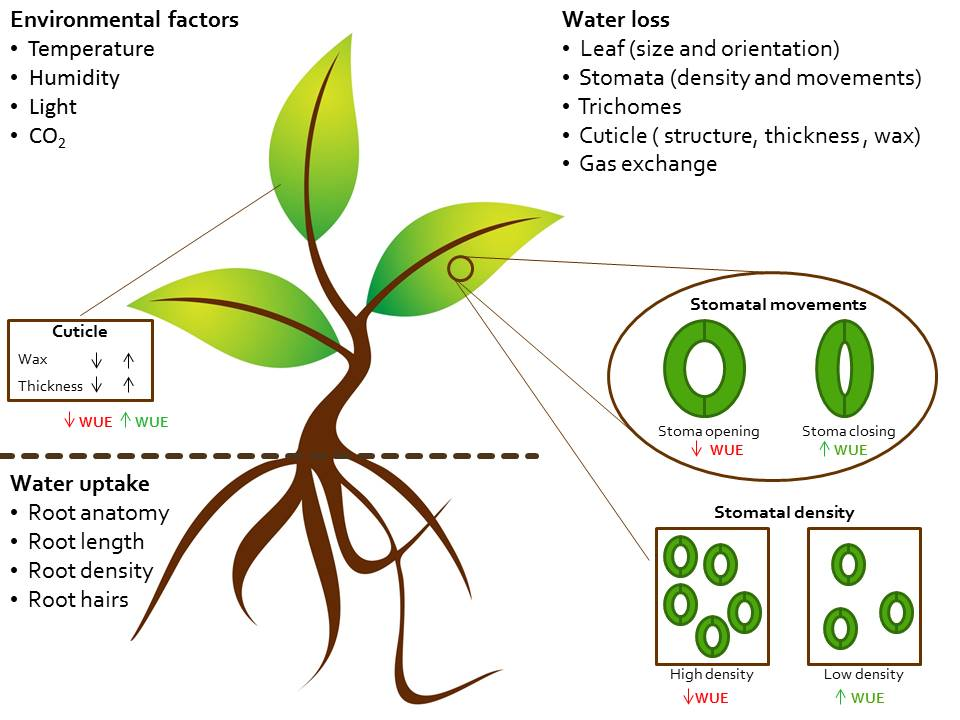
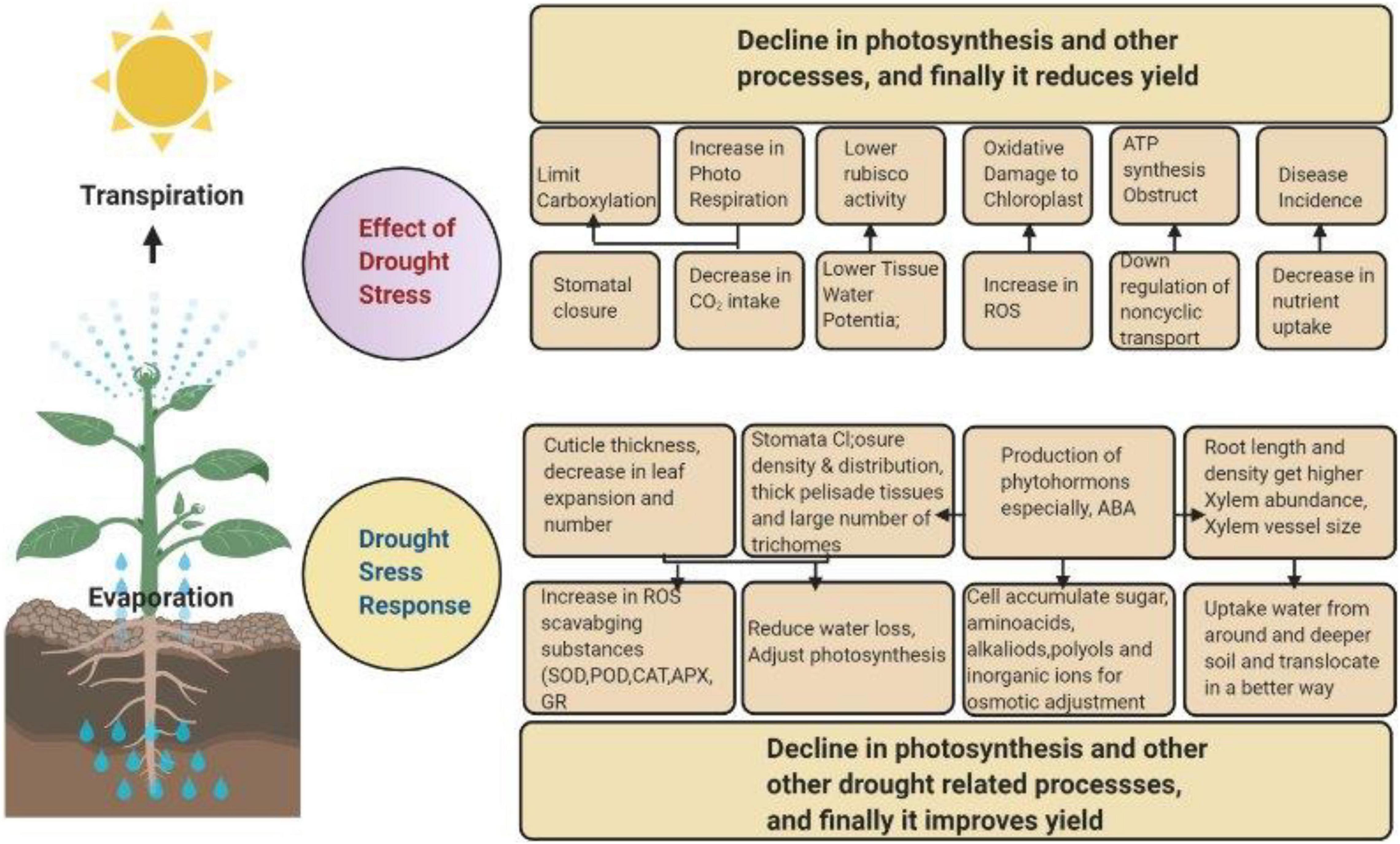
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata, which are found on the surface of leaves, stems, and other plant organs. While transpiration is a necessary process for plants to maintain their hydration and regulate their temperature, it can also have harmful effects on the plant if it occurs in excess.
One harmful effect of excessive transpiration is that it can cause the plant to lose a significant amount of water, leading to dehydration. This can be particularly detrimental to plants in hot, dry environments where the rate of transpiration is naturally higher. Dehydration can weaken the plant and make it more vulnerable to diseases and pests, as well as reducing its ability to photosynthesize and grow.
Another harmful effect of transpiration is that it can lead to nutrient imbalances in the plant. When a plant loses water through transpiration, it also loses dissolved nutrients that are essential for its growth and development. This can result in a deficiency of certain nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium, which can negatively impact the plant's health.
Excessive transpiration can also affect the plant's ability to regulate its temperature. As water vapor is released through the stomata, it cools the plant's surface, which can help the plant maintain a more stable internal temperature. However, if the rate of transpiration is too high, the plant may not be able to effectively regulate its temperature, leading to heat stress.
There are several factors that can contribute to excessive transpiration in plants, including high temperatures, low humidity, strong winds, and dry soil. To minimize the harmful effects of transpiration, it is important to maintain optimal growing conditions for plants, such as providing adequate water and nutrients, and protecting them from extreme weather conditions.
In conclusion, while transpiration is a necessary process for plants, it can also have harmful effects if it occurs in excess. Dehydration, nutrient imbalances, and temperature regulation issues can all result from excessive transpiration, and it is important to take steps to minimize these negative effects. By maintaining optimal growing conditions and protecting plants from extreme weather conditions, it is possible to minimize the harmful effects of transpiration and promote healthy plant growth.