The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical measure used to rank countries based on their level of human development. It is calculated by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and is used as a benchmark for assessing the progress of countries towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The HDI is calculated using three main dimensions: health, education, and standard of living. Each dimension is measured using specific indicators, such as life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, and gross national income per capita. These indicators are then combined to create a composite index, which is used to rank countries on a scale from 0 to 1, with 1 being the highest level of human development.
The health dimension of the HDI is measured using indicators such as life expectancy at birth and mortality rates for children under five years old. A country with a high HDI score in this dimension would have a long life expectancy and low child mortality rates.
The education dimension is measured using indicators such as mean years of schooling and enrollment rates in primary, secondary, and tertiary education. A country with a high HDI score in this dimension would have a high level of educational attainment and high enrollment rates in all levels of education.
The standard of living dimension is measured using indicators such as gross national income per capita and access to electricity. A country with a high HDI score in this dimension would have a high standard of living and widespread access to electricity and other basic amenities.
The HDI is an important tool for policymakers and development practitioners as it provides a comprehensive overview of a country's human development status. It allows for comparison between countries and can highlight areas where progress needs to be made in order to achieve the SDGs.
However, the HDI has been criticized for its narrow focus on certain indicators and its failure to capture other important aspects of human development, such as inequality and social inclusion. In response to these criticisms, the UNDP has developed other indices, such as the Multidimensional Poverty Index and the Gender Development Index, which aim to measure other aspects of human development.
Overall, the HDI is a valuable tool for assessing the progress of countries towards the SDGs and improving the lives of their citizens. It provides a useful benchmark for policymakers and development practitioners and can help to guide efforts to achieve greater human development for all.
New method of calculation of Human Development Index (HDI)

Shortcomings and Critique of Human Development Index HDI : Some shortcomings of HDI as a true indicator of well-being for purposes of estimating development disparities among nations may be noted: ADVERTISEMENTS: First, for estimating literacy rate, expected years of schooling by children at the entrance age is used which overstates the literacy rate as in many countries including India many children who join primary school later drop out at some stage. Higher per capita real income usually represents a higher standard living. IHD is also called the Here is a summary of how the index of hydrogen deficiency IHD works. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. For Generica, the formula would look like this: 0. Do not forget that when double bonds and rings are involved, geometric isomers are possible. Calculating the HDI The HDI is found by taking the geometric mean of the life expectancy, education and income indexes.
Human Development Index: Construction of HDI (With Example)

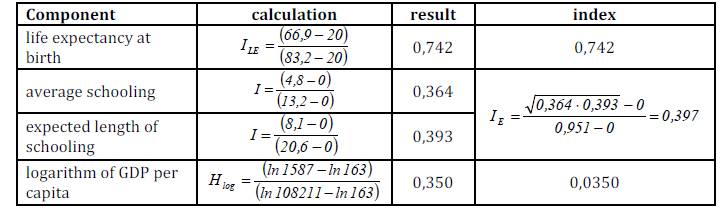
And, indeed, they are partly right. The recent change in HDI occurred in 2010 report. Life expectancy at birth means how many years a newly born infant can hope to live in this world. Precisely, this is because the GDP per capita is not static in any country as it grows with years. Thus, in our view, human development index hides more than it reveals. Gross National Income Per Capita The gross national income per capita, or GNI, measures the annual income of the average citizen based on purchasing power parity, or PPP. Assuming maximum value and minimum value of life expectancy to be 80 and 20 respectively for a particular year, the life expectancy index can be calculated as follows: As calculated above, the individual indices of educational attainments and adjusted real GDP per capita can be found out for a particular year.
HDI: a measure of human capabilities

Human development does not end there, however, other choices highly valued by many people range from political, economic and social freedoms to opportunities for being creative and productive and enjoying self-respect and guaranteed human rights. ADVERTISEMENTS: Human development index as an indicator of development was developed by the United Nations Development Programme UNDP. Therefore, it is better to judge and assess the development performance of different countries by a number of indicators that reflect different aspects of development rather to judge it by a single composite index of HDI. For example, there is a big difference between extra year of life for a healthy well-educated person and extra one year life for a person who is bed-ridden and has limited capability to do work. When we divide the GDP at constant price by the total population of the country, we get real GDP per capita. The new methodology of Human Development Index HDI calculation is to be discussed here. For example, HDI is based on three measures that are easy to collect and evaluate in terms of availability of data.