Heat of neutralization is a measure of the amount of heat that is released or absorbed during a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. This process is known as neutralization, as the acid and base cancel out each other's properties and produce a neutral solution. The heat of neutralization is an important concept in chemistry, as it can be used to determine the strength of acids and bases and to understand the energetics of chemical reactions.
The heat of neutralization is usually measured in units of energy per mole of reactants, such as joules per mole (J/mol) or calories per mole (cal/mol). It is important to note that the heat of neutralization is a specific heat, meaning that it is dependent on the reactants and products involved in the reaction, as well as the temperature and pressure at which the reaction occurs.
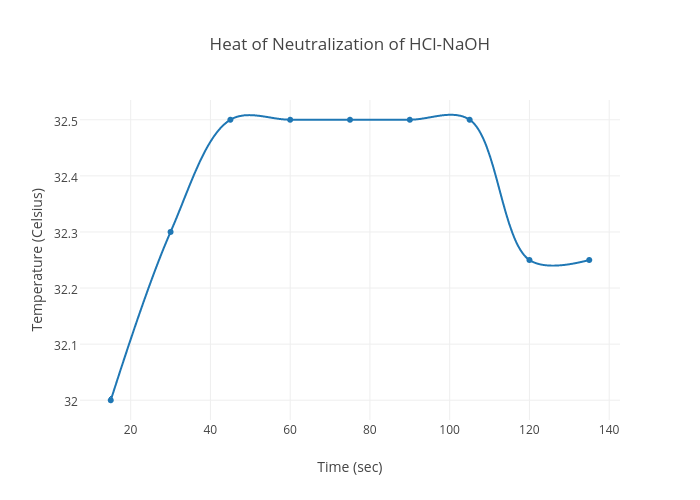
The heat of neutralization can be determined experimentally by measuring the temperature change that occurs during the neutralization reaction. This can be done using a calorimeter, which is a device that is specifically designed to measure the heat transfer between a chemical reaction and its surroundings. To measure the heat of neutralization, a known volume of acid and a known volume of base are mixed together in the calorimeter, and the temperature change is measured as the reaction proceeds. From this information, the heat of neutralization can be calculated.
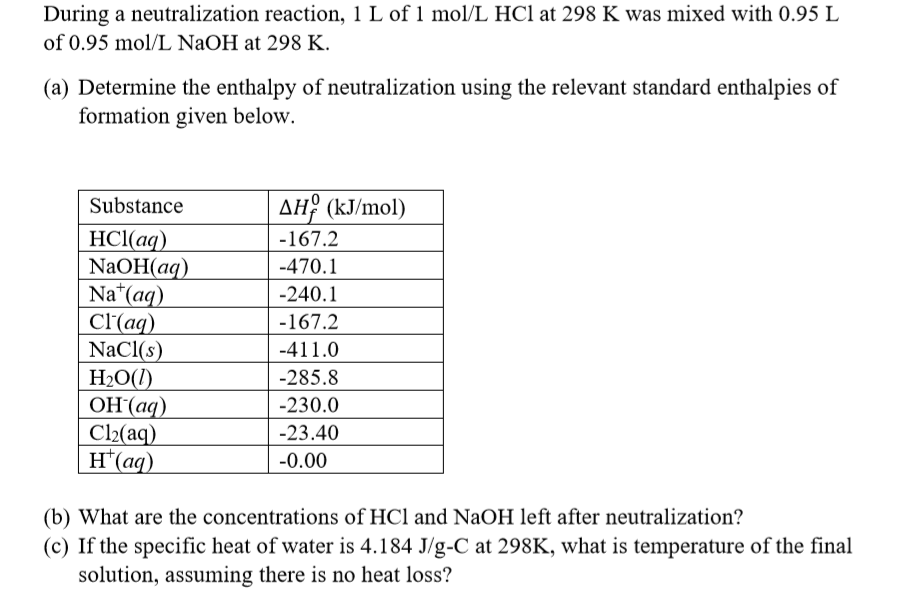
The heat of neutralization can also be calculated theoretically using thermodynamic data and the stoichiometry of the reaction. The heat of neutralization is equal to the enthalpy change for the reaction, which can be calculated using the standard enthalpies of formation for the reactants and products.
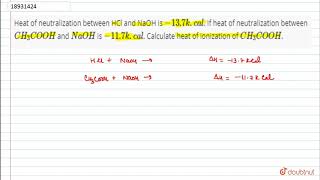
The heat of neutralization can be used to determine the strength of acids and bases. Strong acids and bases have a large heat of neutralization, indicating that they are highly reactive and release a large amount of heat when they react. On the other hand, weak acids and bases have a small heat of neutralization, indicating that they are less reactive and release less heat when they react.
In summary, the heat of neutralization is a measure of the amount of heat that is released or absorbed during the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base. It is an important concept in chemistry that can be used to understand the energetics of chemical reactions and to determine the strength of acids and bases.