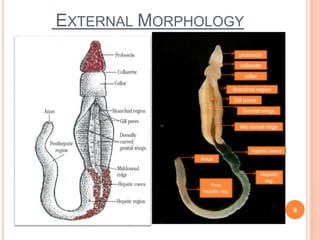
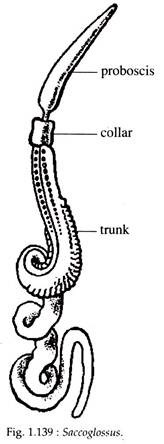
Hemichordata is a phylum of marine invertebrates that includes the acorn worms and the pterobranchs. The acorn worms, also known as enteropneusts, are worm-like animals with a simple, tubular body and a simple digestive system. They are named after the acorn-shaped proboscis, or feeding organ, that protrudes from the front of their body. The pterobranchs, on the other hand, are small, colonial animals that live in tubes and have a more complex anatomy.
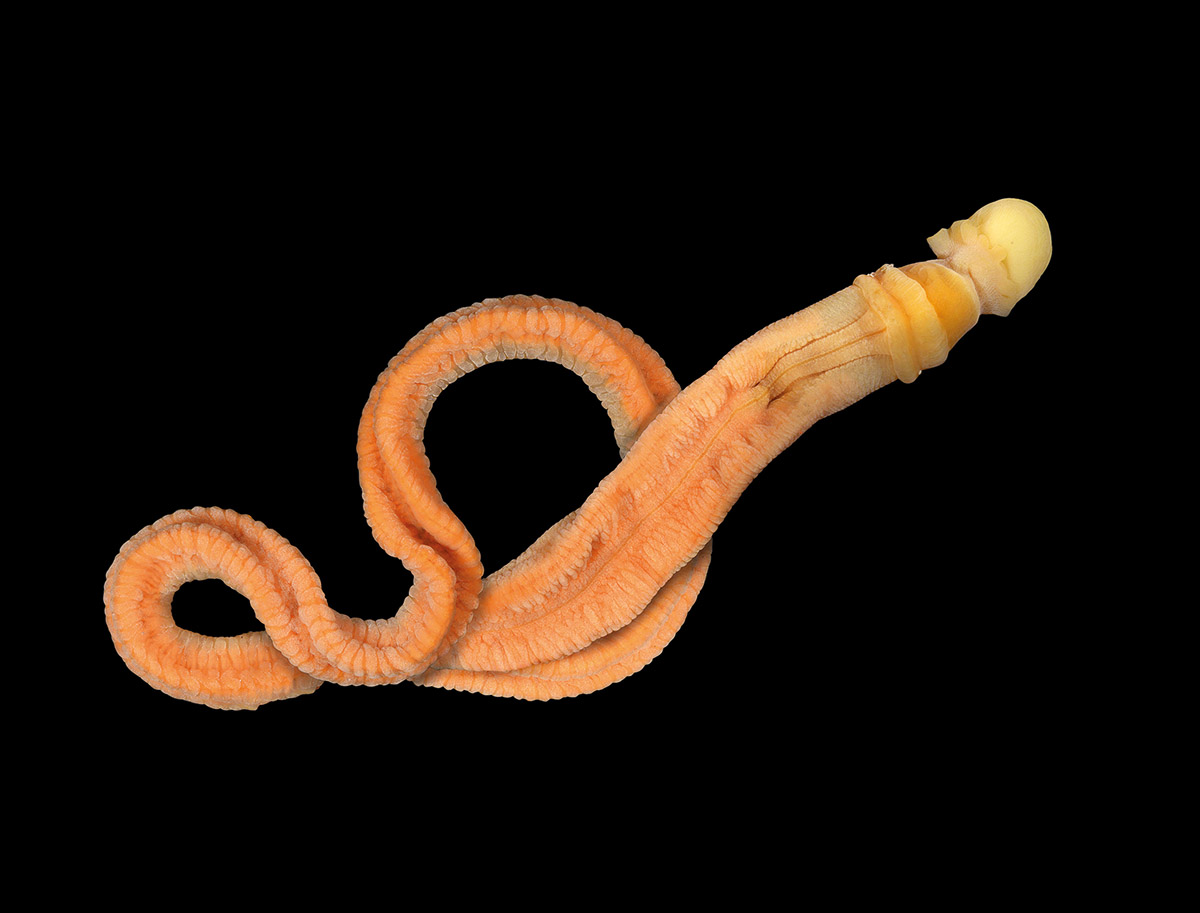
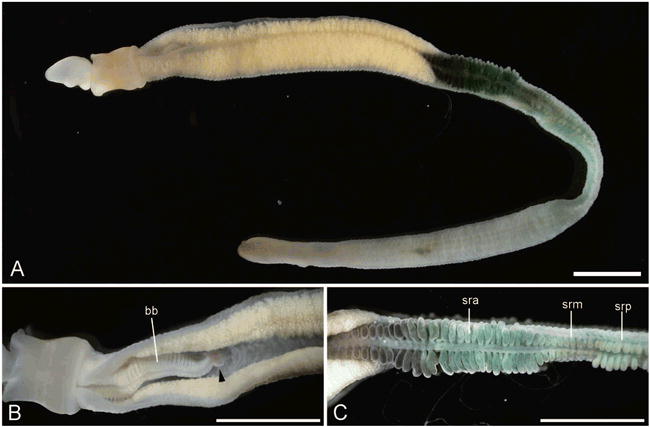
One well-known member of the hemichordata phylum is the acorn worm Balanoglossus. Balanoglossus is a burrowing animal that lives in soft sediments at the bottom of the ocean. It has a long, slender body with a series of gill slits along the sides and a simple digestive system. The front part of its body is modified into a proboscis, which it uses to filter small particles from the water for food.
Balanoglossus is an important organism in the study of evolutionary biology because it is thought to be a transitional form between invertebrates and vertebrates. It has many features that are found in both groups, such as a notochord (a flexible rod that provides support and movement), a hollow nerve cord, and pharyngeal gill slits (which are used for respiration and feeding). These features suggest that Balanoglossus may have evolved from a common ancestor with the vertebrates.
Despite its importance in evolutionary studies, little is known about the biology and ecology of Balanoglossus. It is found in shallow, tropical waters, but very little is known about its behavior or reproductive habits. Further research on this fascinating animal could help us understand the early evolution of vertebrates and the relationships between different groups of animals.