High bypass ratio engine advantages. Turbofan Engines 2022-12-28
High bypass ratio engine advantages
Rating:
6,2/10
446
reviews
A high bypass ratio engine is a type of jet engine that has a higher proportion of air flowing around the engine core, rather than through it. This design has several advantages over traditional jet engines with lower bypass ratios.
One major advantage of high bypass ratio engines is increased fuel efficiency. Because more of the air flows around the engine core, there is less heat generated within the core. This reduces the amount of fuel required to reach and maintain high temperatures within the core, resulting in lower fuel consumption.
High bypass ratio engines also have lower emissions than traditional jet engines. The lower heat generation within the core reduces the amount of nitrogen oxides (NOx) produced, which are a major contributor to air pollution. In addition, the increased airflow around the core cools the exhaust gases, further reducing NOx emissions.
Another benefit of high bypass ratio engines is that they are quieter than traditional jet engines. The increased airflow around the core creates a barrier that absorbs and deflects sound waves, resulting in a quieter operation. This is especially important in areas with noise restrictions, such as near airports or residential areas.
High bypass ratio engines also have a longer lifespan compared to traditional jet engines. The lower heat generation within the core reduces wear and tear on the engine components, resulting in a longer service life. This can save money on maintenance and repair costs over the lifetime of the engine.
Overall, high bypass ratio engines offer significant advantages in terms of fuel efficiency, emissions, noise reduction, and lifespan. These benefits make them a popular choice for use in modern commercial and military aircraft.
Turbofan Engines

Worldwide growth in air traffic has been on a continuous upward curve for decades. For instance, by using the single stage variable pitch propulsive fan 30, the ultra high BPR turbofan engine 10 can avoid the noise that is typically experienced by counter rotating turbofans with variable pitch, which generate noise by the interactions between the two stages of fans. The discussion begins with a review of the fundamental aerodynamic studies of such diffusers without upstream turbine stages. Research on the level of noise alleviation possible with open rotor engines has shown sensitivity to maximum takeoff weight. Much of that work was done at NASA Glenn in Cleveland Ohio. The nacelle 14 of the present embodiment is configured to minimize weight and drag based on one or more of the following design parameters: minimizing the number of components within the outer nacelle 14, minimizing the number of functions in the outer cowl 70, maximizing the cold nozzle 82 outer radius 86 and the inlet throat diameter, minimizing the nacelle 14 maximum radius and the inlet contraction ratio, and minimizing the inlet diffuser section 96 length. The intermediate ducts and especially the intermediate turbine diffuser will become a key component of future aero engine architectures.
Next
US20140363276A1
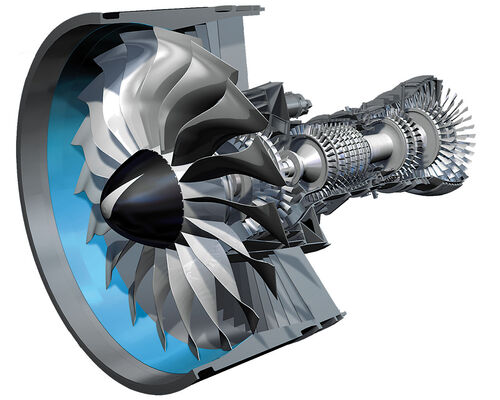
The aero-engine companies increasingly employ electronics to balance and optimise the characteristics of components and to fulfil the essential monitoring wherever possible, in what is an increasingly complex product. So that also goes for increasing thrust from 0 to something. The tail surfaces on a FBW airliner can be made smaller, thus reducing drag, or fuel can be held in tanks in the fin or horizontal tail surfaces to move the aircraft centre of gravity aft. Provide details and share your research! It combines the advantages of both of turboprop engines high propulsive efficiency and thrust and turbojet engines high flight speed and altitude. By then, work will probably be underway on the following generation of UHBR engines.
Next
jet engine

This is necessary to capture all effects occurring in a real aero engine. The core contains the remaining compressor, the combustion chamber, and the turbine wheels. The forward engine mount 78 can be mounted to the outer cowl 70 to protrude from the outer cowl nacelle loft line and be enclosed within a pylon connected to the aircraft's structure. For some cycle parameters, the outer nacelle 14 thickness can be set to avoid spillage drag at the inlet 12, which is described in greater detail below. In one embodiment not illustrated , the forward engine mount 78 can be mounted on the outer cowl 70 above the OGVs 64. Read more Navigate Down Introduction J.
Next
Why are high bypass engines more efficient than low bypass? : aerospace
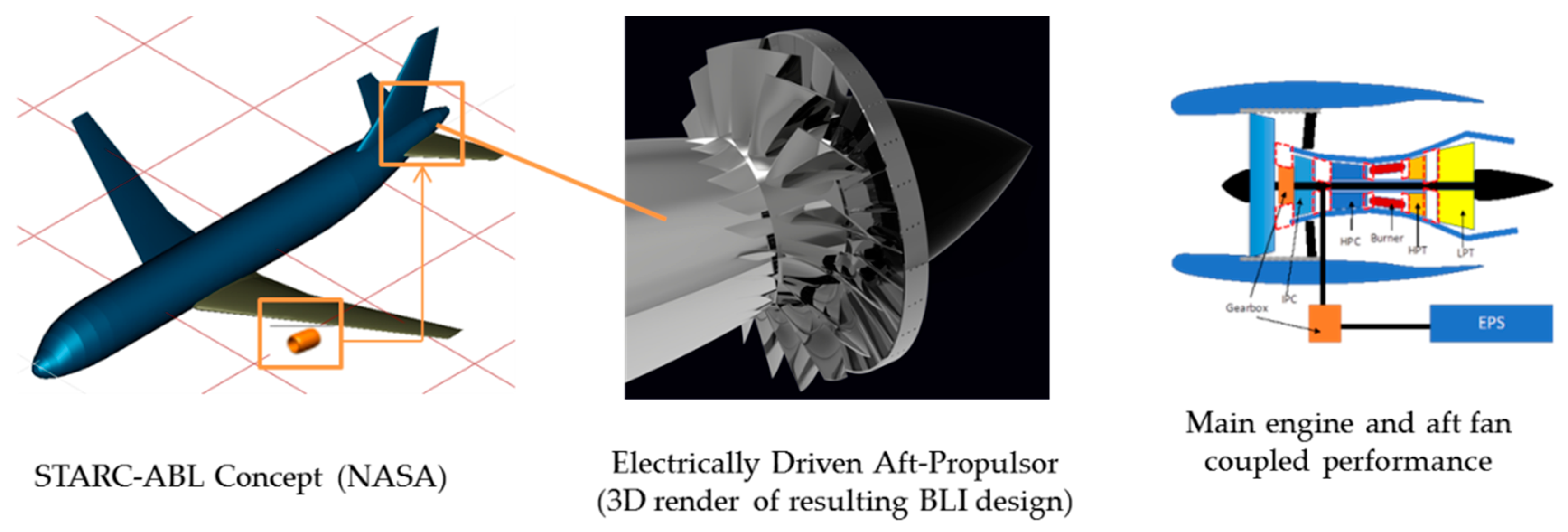
What is a high bypass jet engine? Claims 20 a single stage variable pitch fan and a low pressure turbine coupled together by a reduction gearbox, wherein the reduction gearbox reduces the speed of the single stage variable pitch fan relative to the low pressure turbine and the ratio of the reduction gearbox is greater than or equal to about 4. As shown in FIG. A similar conclusion and use can be drawn from FIG. Comparing the two types of engine the turbojet has a sfc in the range 0. . This would require either better materials which are not available or lower times between overhauls which are costly. Research programmes are still government sponsored, but overall the streamlining of the vehicle creation process is almost complete.
Next
Bypass ratio
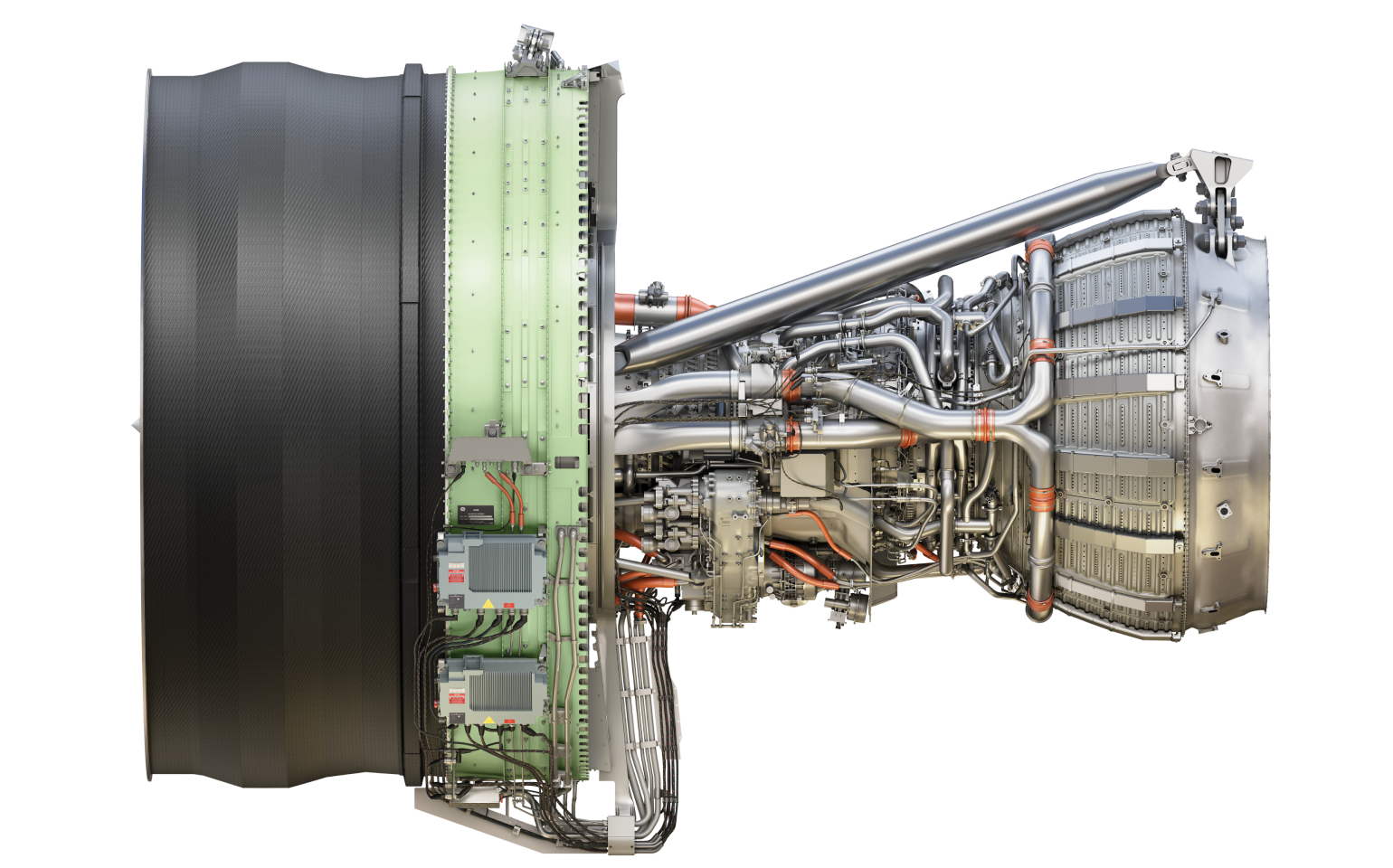
But I thought this explanation might be conceptually easier to grasp. Although the ultra high BPR turbofan engine 10 is described herein as employing a two-spool design gas turbine engine 16, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that a single-spool or three-spool, or other turbofan machinery configuration, can alternatively be employed. For a turbojet engine the specific fuel consumption sfc is defined as the rate of consuming fuel mass divided by the thrust. Under subsonic flow conditions, the most efficient operation of propellers and fan blades is achieved. This is called bypass flow. This trend has led to the development of small turbofans, such as the DGEN 380 in Figure 7-31 and Williams International FJ44 in Figure 7-32. In this case the wake remains in the same plane as it started and evolves in an approximately self-similar manner as discussed in Chapter 9.
Next
Ultra High Bypass Ratio Engine Technology Review

Further, mounting the forward engine mount 78 to the core rather than for example to the outer cowl 70, can eliminate or substantially reduce core engine reaction loads from being transferred through the OGVs 64 to the forward engine mount 78 on the outer cowl 70. As the velocity deficit in the wake decays in the downstream direction the material volume of the particles in the wake must be stretched as illustrated in Fig. Those data were given for the JT3D-3B. The JT3D is a two-shaft engine with a six-stage low-pressure compressor and integral two-stage fan, a seven-stage high-pressure compressor, a single-stage high-pressure turbine, and a three-stage low-pressure turbine. However, the power supplied to the fan is transmitted to the air and therefore acts much like a propeller.
Next
What Is A High Bypass Turbofan Engine?

AEROREPORT is an aviation magazine published by MTU Aero Engines, Germany's leading engine manufacturer. Combustor design relies heavily on numerical simulations, experimental measurements, and testing. Van Zante 2015 presents a concise description of current US research into open rotor engines and relates it to the historical background as indicated by Table 10. For commercial passenger aircraft, as well as for civilian and military jet transports, high bypass designs are the most common configuration. The amount of inlet spillage drag can become excessive at the onset of inlet spillage drag. The underlying principle behind bypass is trading exhaust velocity for extra mass flow which still gives the required thrust but uses less fuel. Pressures and fan and jet exit velocities are taken from Flight March 1959, pp.
Next
(PDF) Performance Analysisof Cold Sections of High BYPASS Ratio Turbofan Aeroengine
Note that the engines of the When a Another problem remains, however. If it is all transferred to a separate big mass of air with low kinetic energy, the aircraft is best suited to zero speed hovering. The aerodynamic situation of ducts equipped with load-carrying struts is also shown and the additional difficulties for the designer are highlighted. While these distortions are potentially detrimental to the life and stability of the fan, it is also known that the presence of the fan itself changes the conditions at which separation occurs. However, the energy required to increase DV depends quadratically on DV, simply through the definition of kinetic energy. Note, that this does not say high-bypass engine would be more efficient at slow speed than at high speed. The reacting governing equations will be detailed in Chapter 2.
Next
High

Can turbofans go supersonic? Read more Navigate Down The combustor Paul PaliesPrincipal Scientist, in Stabilization and Dynamic of Premixed Swirling Flames, 2020 1. C Fan blade rotation at angular speed Ω in a swirling flow in solid body rotation with angular speed Ω o, 3D view and D downstream cross-sectional view. This is the name given to aircraft such as the Airbus A400M, whose wings are mounted flush with the upper edge of the fuselage. Additionally, or alternatively, the length of the diffuser section 96 can be reduced by maximizing the diffuser angle β prior to separation. Aero-engine industry design teams, like those in the airframe business, refine the aerodynamic and structural design of their products through equivalent technical research. A No rotation, 3D view and B downstream cross-sectional view. The open rotor engine is a rational response to the desire to incorporate the efficiency of the propeller, the high-speed capability of the turbofan, and the reliability of the turbine engine.
Next
What prevents jet engine designs with larger bypass ratios?

Use MathJax to format equations. Accordingly, the variable blade pitch propulsive fan 30 can be configured to perform the thrust reversing duties of the ultra high BPR turbofan engine 10, for example by selectively reversing the fan blade pitch of the blades of the propulsive fan 30, and thus take the place of a thrust reverser that is typically disposed for example in the nacelle outer portion of separate flow type turbofans. The continuity of the mass flux requires that U w x L w x is constant. While most are business jets, recently a new class of turbofan-powered jets has emerged, the Personal Jet. Courtesy of Rolls-Royce Plc Turboprop engines are usually designed to run at a constant rotational speed, the power absorbed by the propeller being varied by varying the pitch of the blades. Figure 7-33 shows the change in total pressure and Mach number of the airflow through a theoretical turbofan. The variable pitch mechanism 60 serves to prevent or substantially reduce the likelihood of fan operability issues that could otherwise be caused by the ultra high bypass ratio of the ultra high BPR turbofan engine 10.
Next







