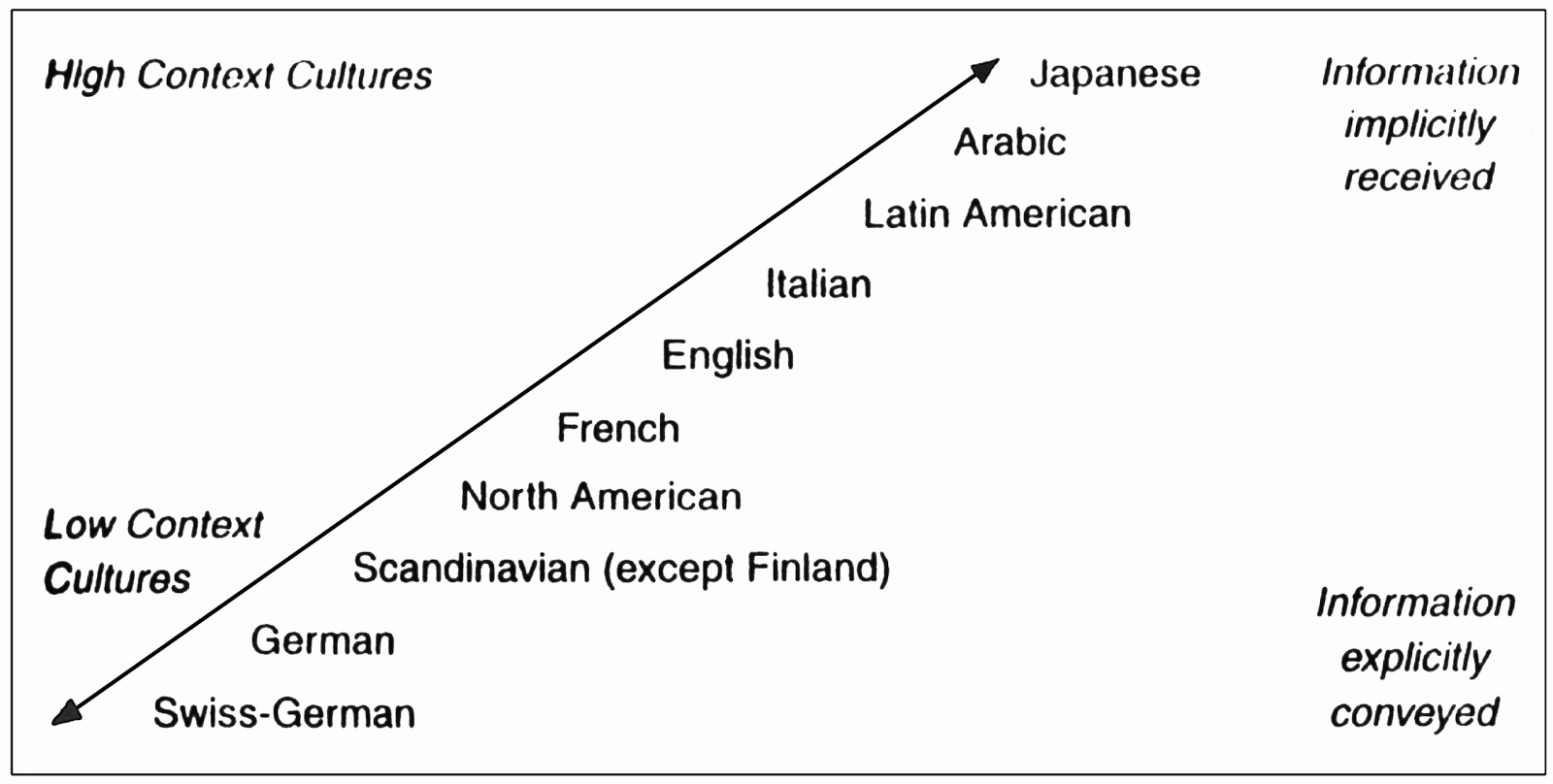
High context and low context cultures refer to the ways in which people communicate and convey meaning in different cultural settings. In a high context culture, people rely more on nonverbal cues and shared meanings to communicate, while in a low context culture, people rely more on explicit verbal communication to convey meaning.
High context cultures tend to be more collectivistic, where people place a strong emphasis on relationships and social connections. These cultures often have a strong sense of community and a shared history, which helps to create a shared set of values and norms. In a high context culture, people rely more on nonverbal cues and contextual information to understand what is being said, as opposed to relying on explicit verbal communication.
Examples of high context cultures include many Asian, African, and Latin American countries, as well as some European cultures such as Spain and Italy. In these cultures, people may rely on body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions to convey meaning, and may not always say exactly what they mean directly. For example, in a high context culture, it may be more common for people to use indirect language or to rely on subtle cues to convey their meaning, rather than stating things directly.
Low context cultures, on the other hand, tend to be more individualistic, with a focus on individual autonomy and independence. In these cultures, people rely more on explicit verbal communication to convey meaning and may not rely as much on nonverbal cues and contextual information. Low context cultures tend to be more direct and explicit in their communication, and may not always rely on shared meanings or cultural norms to understand what is being said.
Examples of low context cultures include many Western cultures such as the United States, Canada, and Australia, as well as some European cultures such as Germany and the Netherlands. In these cultures, people may be more likely to state things directly and to rely on explicit verbal communication to convey their meaning.
It is important to note that no culture is purely high context or low context, and that all cultures use a combination of both high and low context communication. However, some cultures may tend more towards one end of the spectrum, and understanding the differences between high and low context cultures can be helpful in effective communication and cross-cultural interactions.
Low Context Culture: Examples, Definition & Countries (2022)

People in lower-context cultures tend to write things down to make sure that ideas and processes remain transparent. It relies on the straightforward use of language, without depending much on nonverbal cues. This is because, as the names suggest, some cultures use more words than others to convey the same message. To put it simply, people from high context cultures tend to leave some things unsaid, while people from low context cultures are quite direct and mean what they say as they said it. Hypotheses The characteristics of HC and LC cultures outlined above raise questions regarding the contrasts between the characteristics of HC cultures and the Internet, which was developed in LC cultures. What is important to the collective is more important than individual thoughts and preferences. HC cultures are thus characterized by indirect and cyclical approaches in their conversation and writing styles, often communicating without mentioning the subjects directly, whereas LC cultures will get straight to the point.
High Context Culture vs Low Context Culture: Communication Design For Avoiding Uncertainty

Low-context cultures are individualistic. In most instances, menus like the examples above are supported by other, more LC versions. This allows individuals of different generations to communicate through a shared set of values, which, in turn, provides stability to the culture. Similar studies of noncommercial Web sites are needed in order to test the extent to which the identified tendencies obtain in other genres of Web sites. Out of the 15 items, 11 are significant at the. Visual communication on Web sites is expressed through layout and the use of images, photographs, and animation.
High
This makes high-context cultures difficult to navigate for those who do not understand the culture's unwritten rules. Logical, linear thinking patterns would imply linear navigation throughout the site, with a consistent layout throughout the pages of the site, thus promoting a structured and timesaving quality. Supplementary research should focus on further exploration of communication strategies present on Web sites. For instance, while China is generally regarded as a high-context culture many communications are indirect and non-verbal , certain aspects of society require low-context transactions to take place between members of the society. Crest toothpaste advertisements Taken from Two different advertisements, catered to differing context cultures, were analyzed by He Bai with the English Teaching Institute in Beijing. Examples of low-context cultures include the United States, Australia, and many European countries. .
Intercultural communication high and low context cultures

We just have some cultural differences to iron out! Marketing and Online Communication A 2005 study by Elizabeth Wurtz demonstrates how cultural differences shape marketing and advertising. It can imply understanding or agreement, but it can also mean their converse—a lack of certainty. This means that the members' identity is heavily rooted in groups, i. How does high-context vs low context contrasting pairs differ from the other? As the final tendency presented in the results section showed, the consistency in layout and opening of links in the same browser windows in LC Web sites is in contrast to the HC Asian Web sites where new pages would open in new browser windows, giving the visitor a multitude of starting points for further Web site navigation. This is in contrast to high-context cultures, which communicate in ways that are implicit and rely heavily on nonverbal language. The fact that different communities express their culture relationship to time, communication patterns, verbal and nonverbal communication, definitions of trust, emphasis on task or relationship, emphasis on individuality or collectivism, social structure and more differently came as no surprise to me, but some of the communication nuances did.









