Linguistic imperialism is a term that refers to the spread and promotion of a particular language as a means of exerting power and control over other linguistic communities. This phenomenon has a long history and has played a significant role in shaping the linguistic landscape of many countries around the world.
One of the earliest examples of linguistic imperialism can be traced back to the spread of Latin throughout the Roman Empire. Latin was the language of the Roman elite and was imposed on the conquered peoples as a means of cultural assimilation. This led to the suppression of indigenous languages and the promotion of Latin as the language of education, administration, and social prestige.
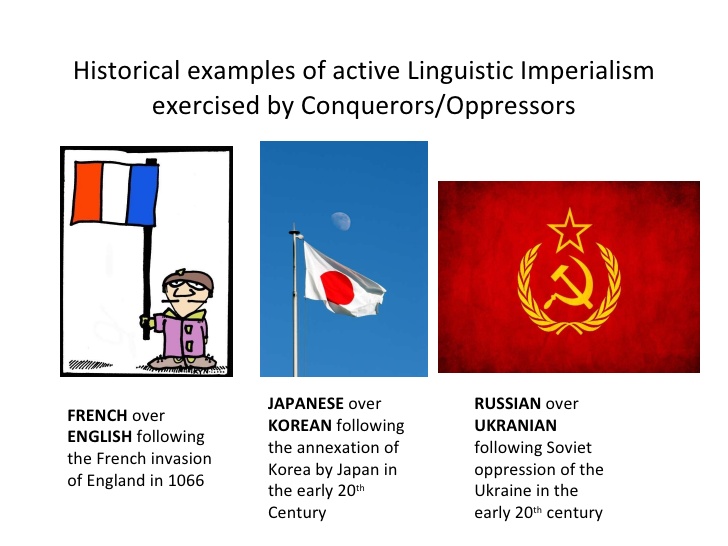
Another notable example of linguistic imperialism occurred during the colonial period, when European powers such as Britain, France, and Spain sought to exert control over their overseas territories through the promotion of their own languages. In many cases, indigenous languages were suppressed and replaced with the colonizers' languages, which were seen as a sign of cultural superiority. This led to a proliferation of European languages in many parts of the world, including Latin America, Africa, and Asia.
In the modern era, linguistic imperialism has taken on new forms, as the spread of English has become increasingly influential. English has become the dominant language of international communication, commerce, and science, and it has been promoted as the language of choice for education and business in many countries. This has led to a situation in which speakers of other languages may feel pressure to learn English in order to succeed in certain fields or to participate in global discourse.
Linguistic imperialism has had a number of negative consequences for linguistic diversity and cultural identity. It has often resulted in the suppression of indigenous languages, which can lead to their eventual extinction. It has also contributed to linguistic homogenization and the erosion of cultural diversity, as more and more people are encouraged to adopt a single dominant language.
Despite these negative impacts, linguistic imperialism has also had some positive consequences. The spread of languages such as English and French has facilitated communication and understanding between people from different linguistic and cultural backgrounds. It has also made it possible for people to access a wealth of knowledge and resources that are available in these languages.
Overall, the history of linguistic imperialism highlights the complex and often fraught relationship between language and power. While the promotion of certain languages can bring about positive changes, it can also have negative consequences for linguistic diversity and cultural identity. As such, it is important to recognize the potential impacts of linguistic imperialism and to work towards more equitable and inclusive linguistic policies.