Horticultural societies are those in which the primary means of subsistence is the cultivation of crops and the raising of domestic animals. These societies are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions where the climate is suitable for year-round farming. They are characterized by small, relatively self-sufficient communities that rely on simple tools and techniques for cultivating crops and raising animals.
One of the key features of horticultural societies is their reliance on human labor for the cultivation and harvesting of crops. This is in contrast to agricultural societies, which rely on machines and draft animals for these tasks. As a result, horticultural societies tend to have a lower population density than agricultural societies, as there is a limit to the amount of land that can be effectively cultivated by hand.
Another characteristic of horticultural societies is the diversity of crops that they cultivate. These societies often grow a wide variety of crops in order to ensure a reliable food supply throughout the year. This diversity is also reflected in the diet of horticultural societies, which tends to be more varied than that of agricultural societies.
Horticultural societies also tend to have a relatively egalitarian social structure, with little differentiation between social classes. Decisions regarding the cultivation of crops and the use of natural resources are typically made by the community as a whole, rather than by a centralized authority. This level of community involvement helps to ensure that resources are used sustainably and that the needs of all members of the community are taken into account.
Despite their simplicity, horticultural societies have played a vital role in human history. They have provided the foundation for the development of more complex societies and have contributed to the spread of knowledge and technology. Today, horticultural societies continue to exist in many parts of the world, although they are increasingly being influenced by modern technology and globalization.
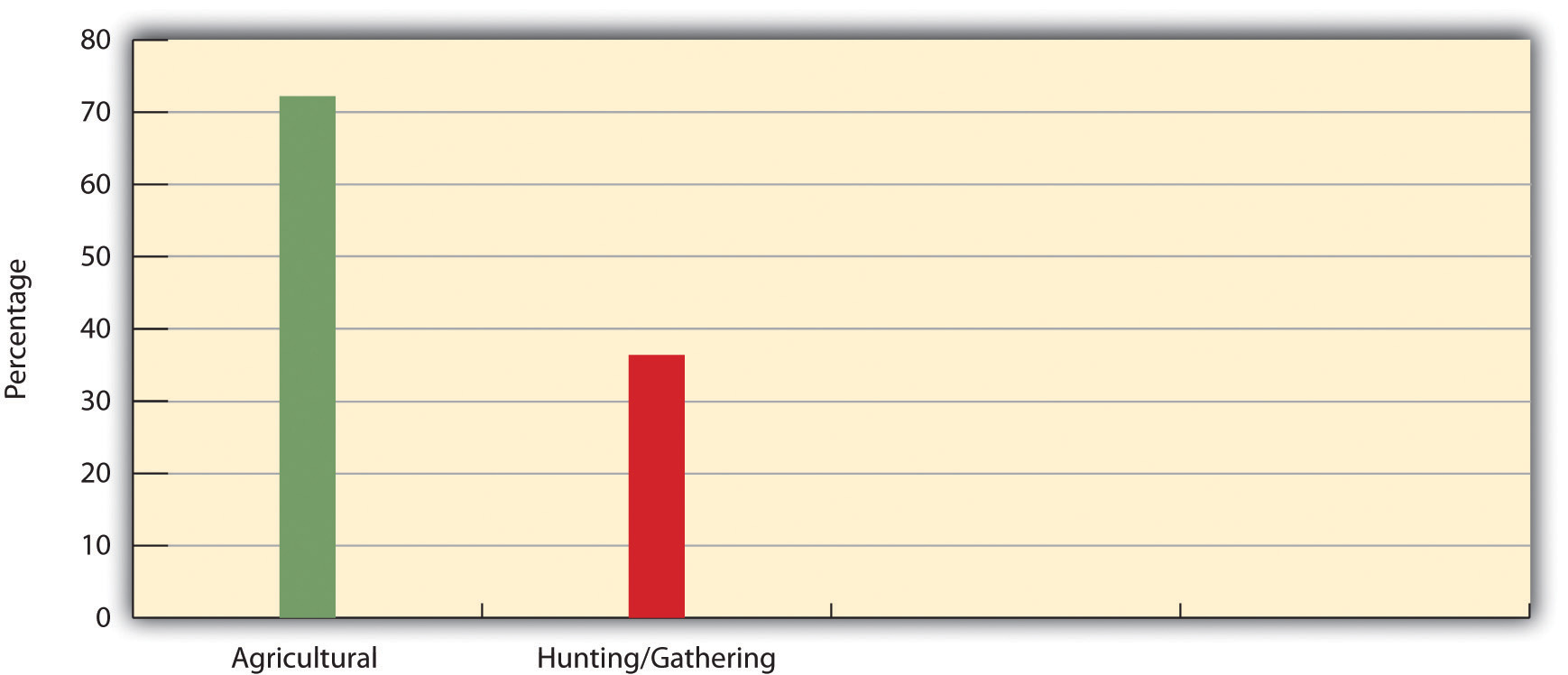
Soci midterm 1 part 2
Another type of horticulture is the dependence on long-growing trees, when societies plant trees that live for many years but require very little work. Men handle large animals, but in some cultures women do the milking. When horticulturalists shift their plantings from plot to plot Multiple select question. For example, most horticultural societies use nothing more than sticks and hoes. Family is one important source of inequality.
Horitcultural Societies in History & Today (Ethics forum at permies)

Living with kin in lowland horticultural societies. My place is mostly forest. The society occasionally educated its members concerning the basic herding methods. Traditional Kumeyaay food sources such as acorns and pine seeds, for example, were placed in these holes, then smashed and ground into meal using a mano stone tool. When the plants of a particular field fail to yield, they will then abandon the area and plant somewhere else. A farmer raises wheat and pays a portion of it as a tax that is collected by government agents and sent to a central storage facility. See topsoil depletion, expulsion of freshwater, snow melt, rainwater to the oceans causing the drying up of the continents, dominator cultures, etc.
Horticultural and Pastoral Societies » StudyExcell

Money buys labor power. Nonindustrial economies are typically arranged along a cultivation continuum because Multiple choice question. Again, according to the work of the Embers, the horticulturalists of Samoa plant things like banana and coconut trees, both of which will produce fruit for years. They also understood the suitability of each soil for their crops as well as the effects of erosion and over-farming. Most horticultural societies mainly use simple farming tools in raising their crops; hence domestication of crops is their primary source of livelihood Walker et al.
Sociology Module 10

Women often play a major role in food production. In the second photo, I was pleased to see. In some cases, people combine horticulture with hunting or fishing, or with the keeping of a few domesticated farm animals. Before Australia became part of the British empire, the aborigines there Multiple choice question. They all depend to some extent on government assistance. .
Horticultural society

Men handle large animals, but in some cultures women do the milking. . These horticulturalists recognized 10 principle and 30 derivative soil categories. However, they can be distinguished by their higher contents of ceramic and lithic artifacts and by their characteristic black color in sharp contrast with the yellowish to reddish adjacent soils. As reported by famous anthropologists Carol and Melvin Ember, the Yanomami usually farm a piece of land for a few years, filling it with things like plantains and sweet potatoes. How would Durkheim describe the importance of a social structure such as family? To begin, horticulture is often defined as a means of food production in which vegetation is cultivated using very rudimentary tools and without permanently cultivated fields.







