The Mali Empire was a West African civilization that flourished in the 13th and 14th centuries. Located in the western Sudan, the empire was founded by the Malinke people and was characterized by its strong centralized government, military prowess, and economic success.
The empire's growth can be traced back to the 13th century, when the Malinke king Sundiata Keita united a number of smaller kingdoms under his rule. Sundiata was a skilled warrior and strategist, and he used his military might to expand the empire's territory and bring other ethnic groups under its control.
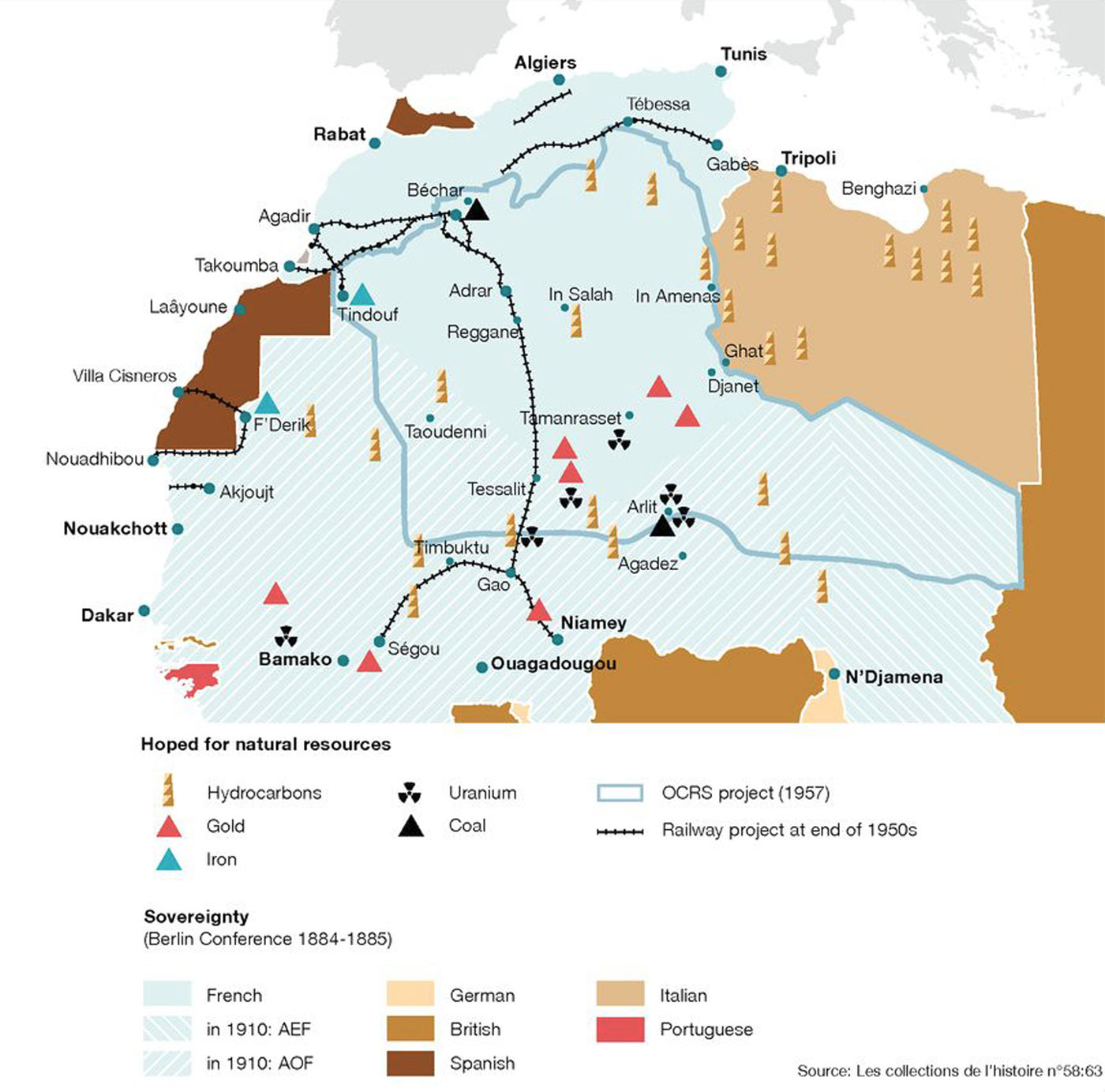
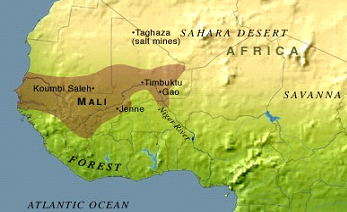
One key factor in the Mali Empire's prosperity was its location at the crossroads of trade routes in West Africa. The empire controlled the trans-Saharan trade routes that linked West Africa to the Mediterranean and the Middle East, and it also had access to the lucrative trade routes that ran along the Niger River. The empire's wealth was further enhanced by the abundance of natural resources within its borders, including gold, salt, and other minerals.
The Mali Empire was also renowned for its cultural achievements. Its capital city, Timbuktu, became a center of learning and scholarship, and the empire was home to a number of famous scholars and intellectuals. The empire's rulers were known for their patronage of the arts, and the Mali Empire is remembered for its contributions to literature, music, and architecture.
The Mali Empire's success was not without its challenges, however. The empire faced frequent invasions from neighboring states and was also beset by internal conflicts. Nevertheless, it was able to withstand these challenges and maintain its dominance for several centuries.
In conclusion, the Mali Empire grew and prospered due to a combination of military strength, economic success, and cultural achievements. Its strategic location at the crossroads of trade routes, abundance of natural resources, and strong centralized government all contributed to its rise as one of the most powerful empires in West African history.
1) how did the mali empire grow and prosper? a) monopolized the cattle trade and built up a good fishing

All goods passing in, out of, and through the empire were heavily taxed. Europeans and Arabs both sought commerce as their primary reason for being in Africa. Why was the Niger River important to the growth of the Mali Empire? The Mali Empire grew and prospered by monopolizing the gold trade and developing the agricultural resources along the Niger River. Tenochtitlan was unique because it was located in a lake, thus being built in a place totally surrounded by water. How did the Mali Empire grow and prosper? When did the Mali Empire reach its peak? The city was named Tenochtitlan, and the city's location, initially being a huge challenge, turned out to be a big advantage, as being totally surrounded by water was an excellent natural defense.
How did the Mali Empire grow?

Why did Mali became a strong and well known empire during the 14th century? Where was the Golden Age of Mali located? Mali is among the ten poorest nations of the world, is one of the 37 Heavily Indebted Poor Countries, and is a major recipient of foreign aid from many sources, including multilateral organizations most significantly the World Bank, African Development Bank, and Arab Funds , and bilateral programs funded by the … How did the Empire of Mali get formed? He then led them to overthrow the rule of the Soso. Mali is a landlocked country that borders Niger, Nigeria, and Burkina Faso. How did the Mali Empire thrive? Timbuktu was the capital of the Mali Empire and it was the most important city in the world. What made Mali a prosperous kingdom? How did the Songhai empire prosper and gain power and influence? What resources did Mali need? The Tutsi refugee who had fled the country were coming back to reclaim their property and help to rescue other refugees. Like Ghana, Mali prospered from the taxes it collected on trade in the empire. Around 1610, the last ruler of the Mali Empire, Mansa Mahmud IV, died and the realm was divided by his sons into three parts. Like Ghana, Mali prospered from the taxes it collected on trade in the empire.