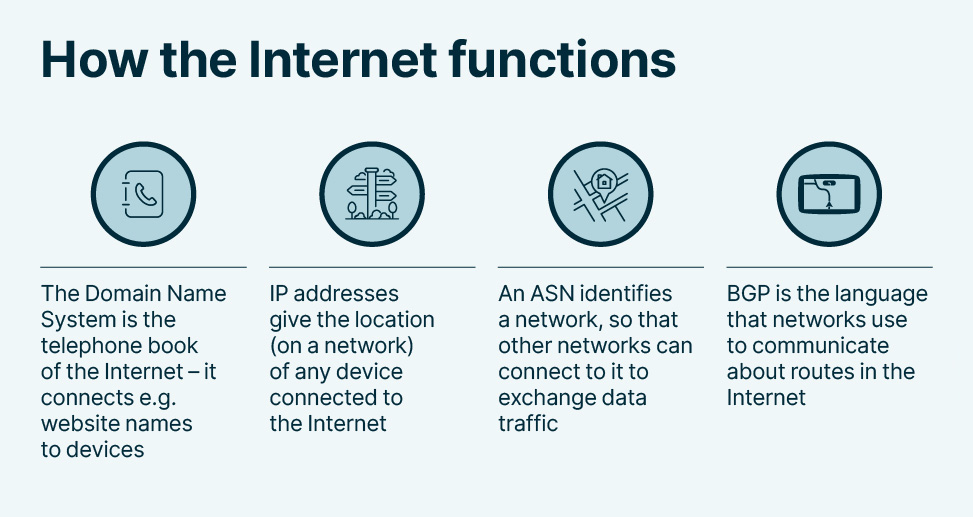
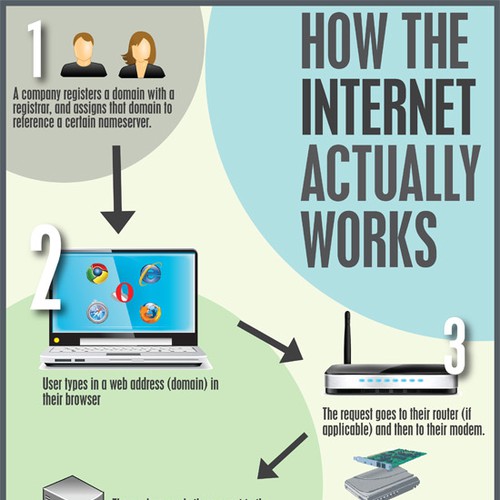
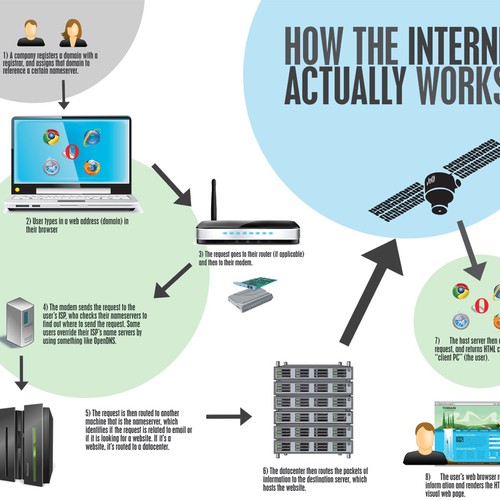
The internet is a vast network of interconnected computers and servers that allows people from all around the world to communicate and access information in real time. It has revolutionized the way we live, work, and interact with one another, and has become an integral part of modern society.
But how does the internet actually work? To understand that, we need to first understand the concept of networking.
Networking is the practice of connecting computers and devices together to share data and resources. A network can be as simple as two computers connected by a single cable, or it can be as complex as a global network of millions of computers and devices.
At the heart of every network is a device called a router. A router is a hardware device that directs traffic between different networks. It is responsible for sending data packets from one network to another, based on the destination address of the packet.
The internet is essentially a global network of networks, connected by a vast network of routers. When you connect to the internet, you are joining this global network and can communicate with other devices on the network.
To connect to the internet, you need a device that can communicate with a router, such as a computer, smartphone, or tablet. These devices are equipped with a special type of software called an operating system, which allows them to communicate with other devices on the network.
Once you are connected to the internet, you can access information from servers located all around the world. A server is a computer that is specifically designed to store and deliver data to other computers on the network. When you type in a website address, your computer sends a request to the server associated with that website, and the server responds by sending back the data that makes up the website.
The data that is transmitted over the internet is divided into small packets, each of which contains a destination address and a piece of data. These packets are transmitted from one device to another, passing through routers and other devices along the way, until they reach their destination.
The internet has come a long way since its humble beginnings in the 1960s, when it was a small network used primarily by government agencies and research institutions. Today, it is a global network that connects billions of people and devices, and it continues to evolve and grow at a rapid pace.
In conclusion, the internet is a global network of interconnected computers and servers that allows people to communicate and access information in real time. It is made possible by the concept of networking, and relies on devices such as routers and servers to transmit and store data. The internet has had a profound impact on the way we live and work, and it is likely to continue shaping the world for years to come.