The heat of neutralization is the heat released or absorbed when an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. This process is known as neutralization because the resulting solution is neutral, meaning it has a pH of 7. Neutralization reactions are important in many chemical and biological processes, and the heat of neutralization can provide valuable information about the reactivity of different acids and bases. In this essay, we will discuss how to find the heat of neutralization using calorimetry, a technique that measures the heat exchanged during a chemical reaction.
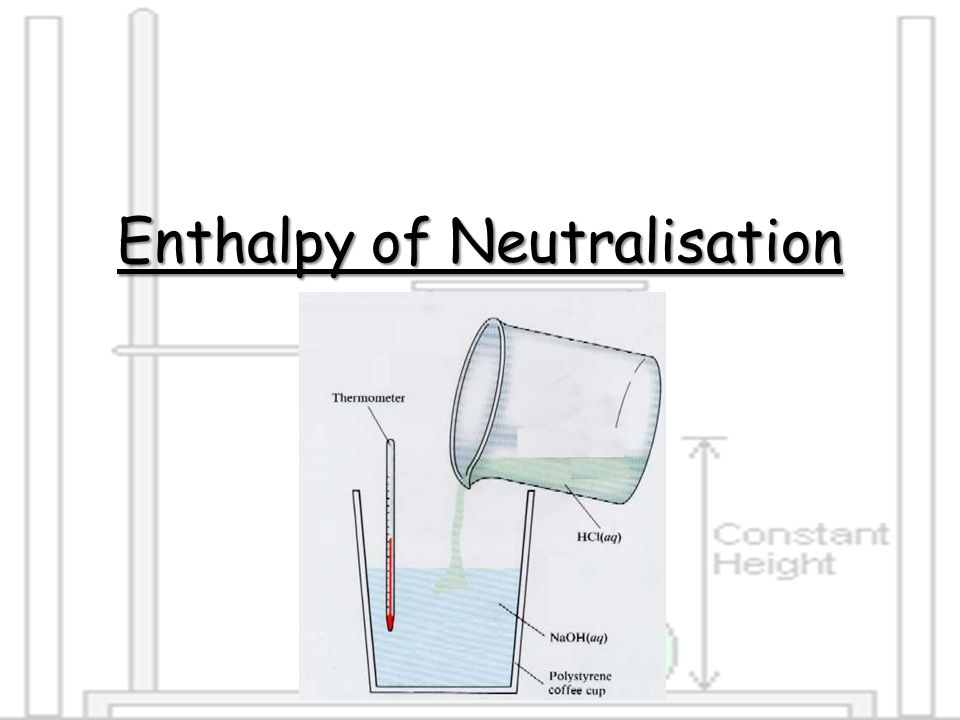
To find the heat of neutralization, you will need a calorimeter, a device that measures the heat exchanged by a chemical reaction. There are several types of calorimeters, including bomb calorimeters, which are used to measure the heat of combustion reactions, and constant-pressure calorimeters, which are used to measure the heat of reactions that occur at constant pressure. For the purpose of measuring the heat of neutralization, we will focus on a simple type of calorimeter called a coffee cup calorimeter, which is a simple, low-cost device that is commonly used in chemistry labs.
To use a coffee cup calorimeter to find the heat of neutralization, you will need to follow these steps:
Set up the calorimeter by placing a known mass of water in a styrofoam cup and attaching a thermometer to the cup. Make sure to record the initial temperature of the water.
Measure out a known volume and concentration of an acid and a base. The acid and base should be chosen such that they will completely react to form a salt and water.
Carefully add the acid to the base in the calorimeter, making sure to stir the mixture as you go. The acid and base will react to form a salt and water, and the heat of the reaction will be absorbed by the water in the calorimeter.
Continuously stir the mixture and measure the temperature of the water at regular intervals. The temperature will increase as the heat of the reaction is absorbed by the water.
When the reaction is complete, record the final temperature of the water.
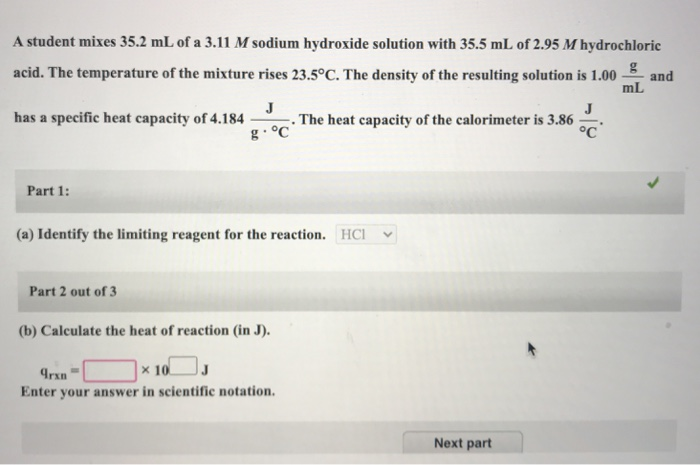
Calculate the heat of neutralization by using the following equation:
Heat of neutralization = (mass of water x specific heat of water x change in temperature) / (moles of acid + moles of base)
The mass of water and the specific heat of water can be found from the initial setup of the calorimeter. The change in temperature is the difference between the initial and final temperatures of the water. The moles of acid and base can be calculated from the concentration and volume of the acid and base used in the reaction.
By following these steps, you can use a coffee cup calorimeter to find the heat of neutralization for a given acid-base reaction. This information can be useful in understanding the reactivity of different acids and bases, and can also be used to predict the energy released or absorbed in other chemical reactions.