Linear perspective is a method of representing three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface, such as a painting or drawing, in a way that creates the illusion of depth and distance. This technique has a long history, dating back to ancient times, and has had a significant impact on the development of art and architecture.
The earliest known example of linear perspective is found in the art of ancient Egypt, where artists used a system of parallel lines to create the illusion of depth on the flat surface of a tomb wall. However, it was not until the Renaissance that linear perspective was fully developed and widely used.
During the Renaissance, a number of artists and mathematicians, including Leonardo da Vinci and Albrecht Dürer, began to study the principles of perspective and how it could be used to create more realistic and convincing paintings and drawings. They discovered that by using a single vanishing point, objects in a painting could be arranged in such a way that they appeared to recede into the distance, creating the illusion of depth.
The use of linear perspective became widespread in the Renaissance, and it had a major influence on the development of art and architecture. Many artists and architects began to use perspective in their work to create more realistic and lifelike representations of their subjects. This led to a new level of realism in art and architecture, and it also had a profound impact on the way people perceived and interacted with the world around them.
In the centuries since the Renaissance, linear perspective has continued to evolve and has been used in a variety of different media, including painting, drawing, photography, and film. Today, it remains an important tool for artists and architects, and it continues to shape the way we perceive and understand the world around us.
Overall, the history of linear perspective is a fascinating story of how artists and mathematicians have worked together to create the illusion of depth and distance on a two-dimensional surface. It is a technique that has had a profound impact on the development of art and architecture, and it continues to be an important part of our visual culture today.
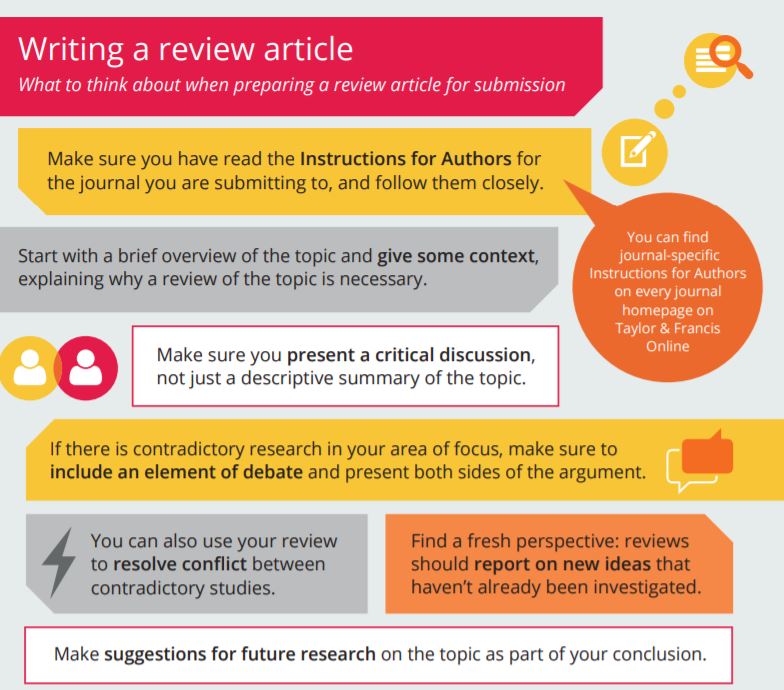
Writing a journal article review involves critically reading and evaluating a published research article and expressing your thoughts and opinions about its strengths and limitations. Here are some steps to help you write a journal article review:
Choose an article to review: Start by selecting a research article that interests you and is relevant to your field of study.
Read and understand the article: Begin by reading the article carefully, taking notes and highlighting key points as you go. It may be helpful to read the article more than once to fully grasp the main ideas and arguments presented.
Summarize the article: In your review, it is important to provide a summary of the main points and findings of the article. This should include a brief overview of the research question, study design, sample size, and key results.
Evaluate the strengths and limitations of the article: As you are writing your review, consider the strengths and limitations of the article. Some questions to consider may include: Is the research question clearly defined and relevant to the field? Is the study design appropriate for answering the research question? Are the results clearly presented and supported by the data? Are the conclusions drawn by the authors supported by the data?
Provide your own perspective: In addition to summarizing and evaluating the article, it is important to express your own thoughts and opinions about the article. What do you think about the research question and the findings? Do you agree or disagree with the conclusions drawn by the authors? Do you have any suggestions for future research in this area?
Use appropriate citation style: Be sure to properly cite the article in your review using the appropriate citation style. This will allow others to easily locate the original article and acknowledge the work of the authors.
Edit and proofread your review: Before submitting your review, be sure to carefully edit and proofread for grammar and spelling errors. A well-written and thoughtful review will add value to the research community and help others to better understand and evaluate the research being published.