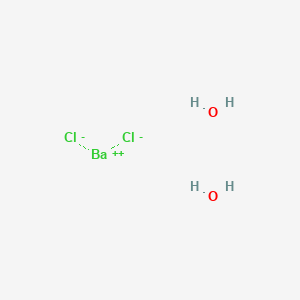
Hydrated barium chloride, also known as barium chloride dihydrate, is a chemical compound with the formula BaCl2·2H2O. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and has a number of important industrial and scientific applications.
The chemical formula for hydrated barium chloride can be written as BaCl2·2H2O, which indicates that it consists of one barium atom, two chlorine atoms, and two molecules of water. The water molecules are chemically bound to the barium and chlorine atoms and are not freely available. The compound is classified as a hydrate, which means that it contains a certain number of water molecules per formula unit. In this case, the number of water molecules is two, hence the name "dihydrate."
Hydrated barium chloride is commonly used as a laboratory reagent and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. It can also be used as a drying agent, as it has a strong affinity for water and can remove moisture from the air. In industry, it is used in the production of pigments, dyes, and other chemicals. It is also used in the purification of water, as it can remove impurities such as sulfates and carbonates.
Despite its widespread use, hydrated barium chloride can be toxic if ingested or inhaled. It should be handled with caution and protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn when working with it. In addition, it should be stored in a well-ventilated area, away from heat and flames.
In conclusion, hydrated barium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula BaCl2·2H2O. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and has a number of important industrial and scientific applications. However, it should be handled with caution due to its toxicity.