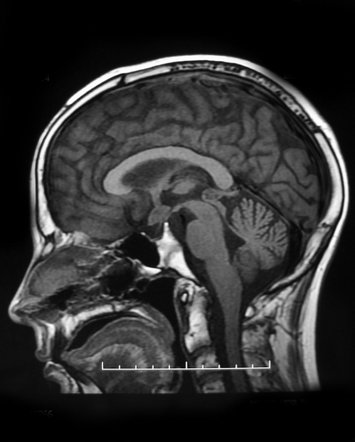
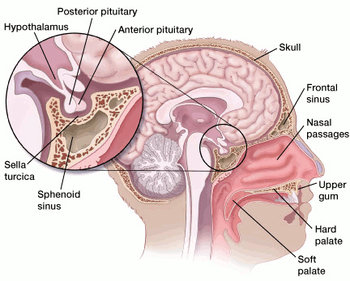
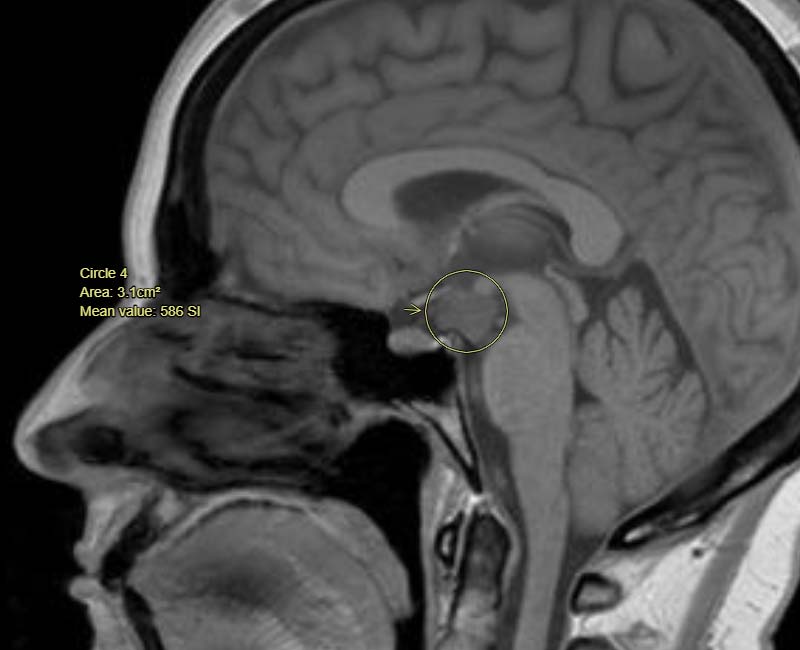
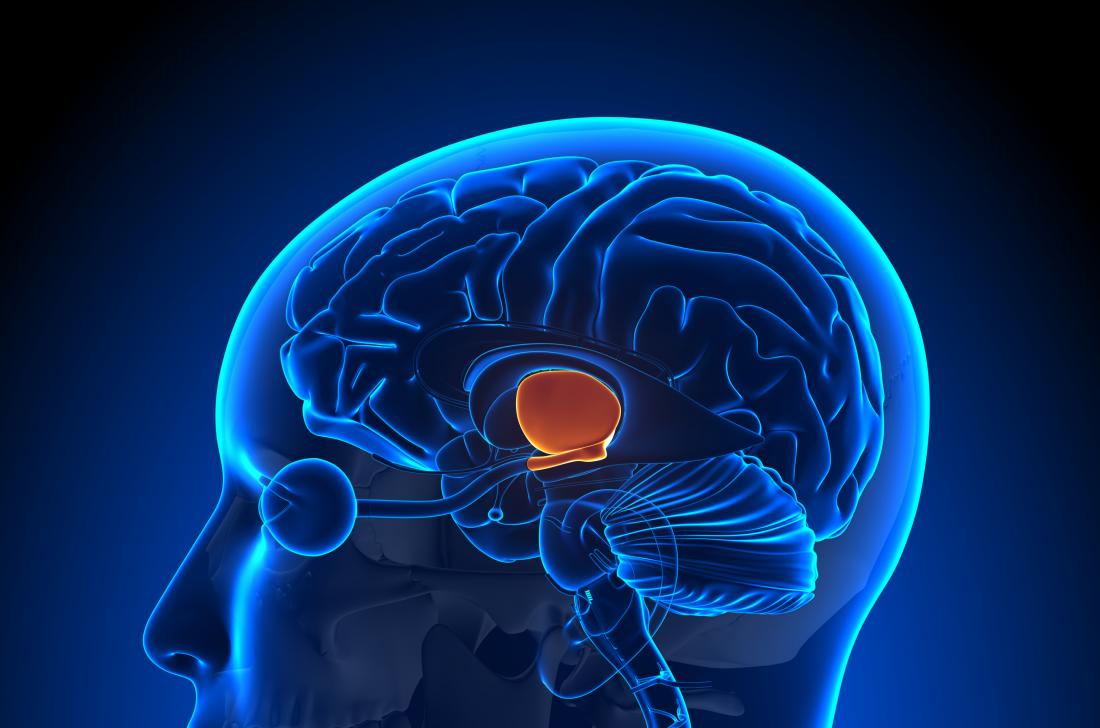
A hypothalamic tumor is a rare type of brain tumor that occurs in the hypothalamus, a small region of the brain located just above the brainstem. The hypothalamus plays a critical role in regulating many important bodily functions, including temperature, appetite, thirst, and hormone production. As a result, hypothalamic tumors can have a significant impact on a person's overall health and well-being.
There are several different types of hypothalamic tumors, including adenomas, craniopharyngiomas, and germinomas. Adenomas are the most common type of hypothalamic tumor, and they are typically non-cancerous (benign). Craniopharyngiomas are also benign tumors that typically occur in children, while germinomas are more likely to occur in adolescents and young adults.
Symptoms of a hypothalamic tumor can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor, as well as the specific functions of the hypothalamus that are affected. Common symptoms may include changes in appetite, weight, and hormone production; vision problems; and changes in behavior or mood. In some cases, a hypothalamic tumor may also cause seizures or problems with the pituitary gland, which can lead to additional symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, or weakness.
Diagnosing a hypothalamic tumor can be challenging, as the symptoms may be similar to those of other medical conditions. To confirm a diagnosis, a healthcare provider may order a variety of tests, including imaging studies such as an MRI or CT scan, as well as blood tests and other diagnostic tests.
Treatment for a hypothalamic tumor will depend on the specific type and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove the tumor. Other treatments may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or hormone replacement therapy.
Living with a hypothalamic tumor can be difficult, as the condition can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to manage their symptoms and maintain their overall health and well-being. Support from loved ones can also be crucial in helping individuals with hypothalamic tumors cope with the challenges of the condition.