In D.H. Lawrence's novel Sons and Lovers, relationships play a central role in the development of the main character, Paul Morel. Throughout the novel, Paul struggles to find his place in the world and to define his own identity, and his relationships with those around him are a significant factor in this process.
One of the most significant relationships in the novel is that between Paul and his mother, Gertrude. Gertrude is a strong and fiercely independent woman who has a deep love for her son and wants the best for him. However, she is also possessive and controlling, and her need for Paul's attention and affection often conflicts with his desire for independence and his own identity. This tension between Paul and Gertrude is a central theme of the novel and is ultimately a major factor in Paul's struggle to find his own way in the world.
Another important relationship in the novel is that between Paul and his lover, Miriam. Miriam is a quiet, introspective young woman who is deeply in love with Paul and wants to be with him. However, Paul is torn between his feelings for Miriam and his duty to his mother, and his inability to fully commit to Miriam causes her great pain. This conflict ultimately leads to the end of their relationship, and Paul is left to deal with the consequences of his actions.
In addition to these relationships, Paul also has a number of other significant relationships in the novel, including those with his friends and his sister. These relationships help to shape his understanding of the world and his place in it, and they also serve as a source of support and guidance as he navigates the complexities of life.
Overall, the relationships in Sons and Lovers play a crucial role in the development of the main character and in the exploration of the themes of identity, love, and family. Through these relationships, Paul is able to understand his own feelings and desires and to find his place in the world, even as he struggles with the challenges and conflicts that inevitably arise in any relationship.
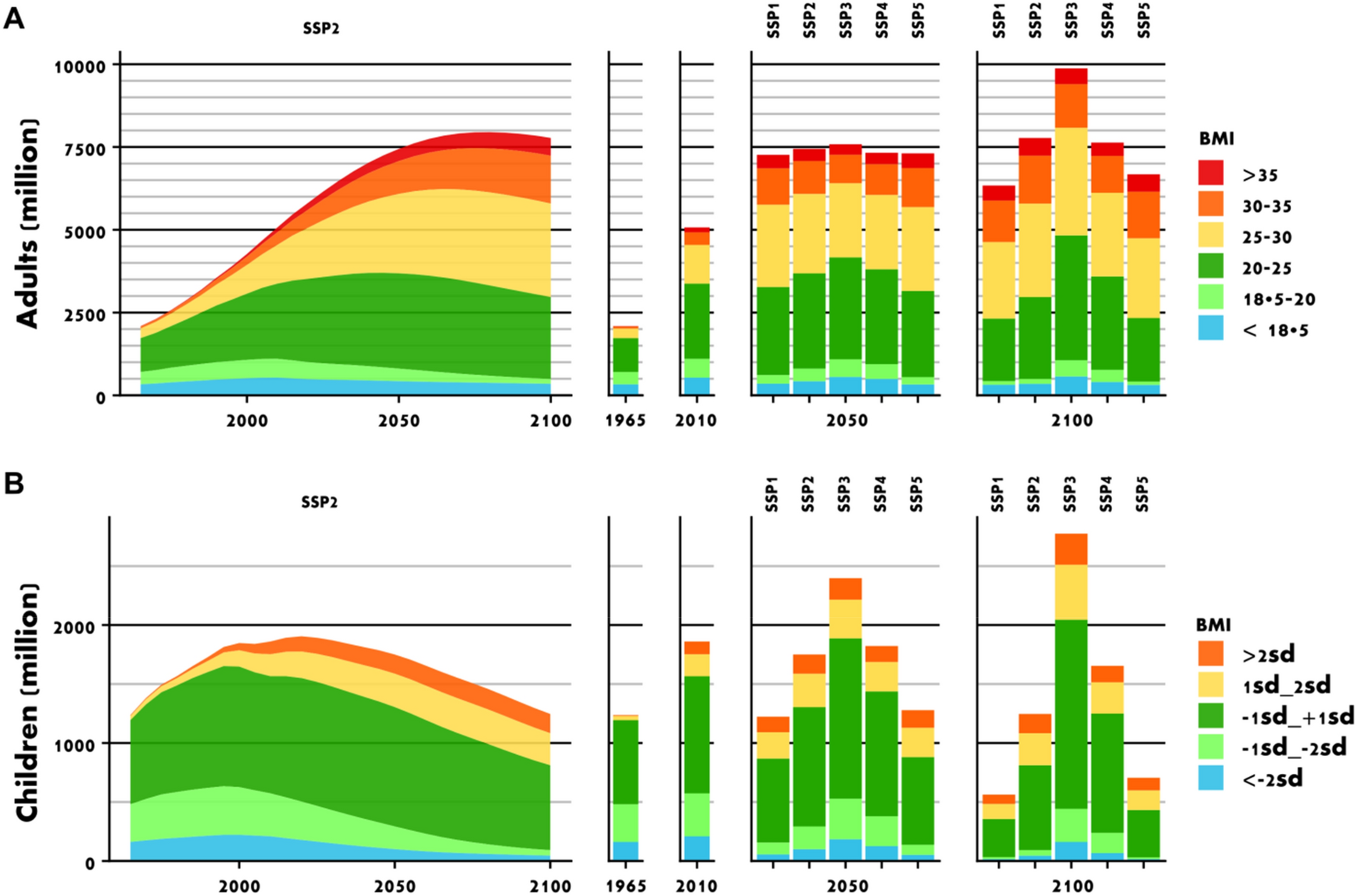
Transitions, or changes in a child's environment, can have a significant impact on their development. These transitions can be positive, such as moving to a new home or starting a new school, or negative, such as experiencing a divorce or the loss of a loved one. Regardless of the type of transition, it is important for caregivers to understand the potential effects on a child's development and to provide support to help them adjust.
During early childhood, transitions can be particularly challenging for children as they are still learning how to regulate their emotions and cope with change. For example, starting preschool or transitioning to a new caregiver can be stressful for young children, and they may exhibit behaviors such as crying, clinging, or regressing to earlier behaviors. It is important for caregivers to be patient and understanding during these times and to provide a sense of routine and consistency to help the child feel secure.
As children enter middle childhood, they become more adept at managing their emotions and handling transitions. However, significant changes, such as moving to a new neighborhood or changing schools, can still be challenging. It is important for caregivers to provide support and help children understand and cope with these changes. For example, caregivers can talk to children about the upcoming transition, provide them with information about the new environment, and help them make connections with others in the new setting.
Adolescence is a time of significant change and transition, as young people begin to separate from their parents and develop their own identities. These changes can be both exciting and stressful, and it is important for caregivers to provide support and guidance as adolescents navigate these transitions. For example, caregivers can help adolescents develop coping skills, such as problem-solving and communication skills, to help them manage the challenges of adolescence.
Overall, transitions can have a significant impact on a child's development, and it is important for caregivers to provide support and guidance to help children navigate these changes. By understanding the potential effects of transitions and providing a sense of security and stability, caregivers can help children cope with change and continue to grow and develop.