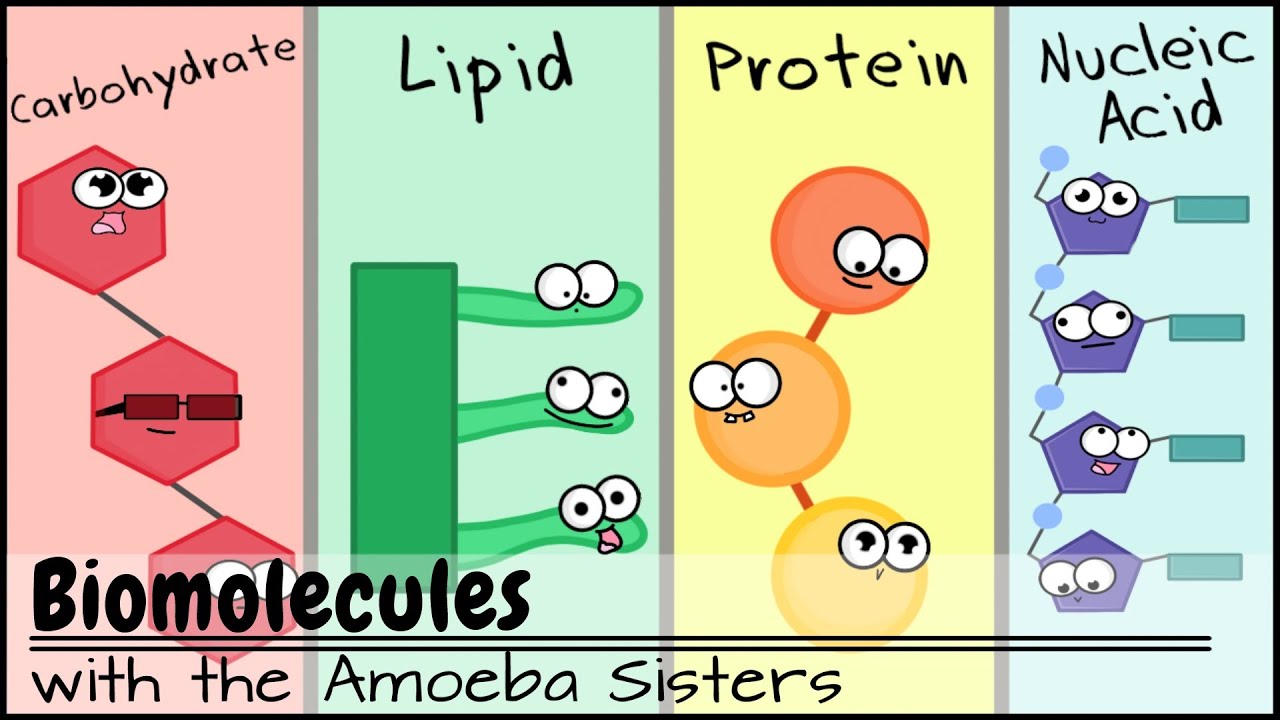
Biomolecules are molecules that are essential for the proper functioning of living organisms. They play a vital role in the various processes that take place within our bodies and are necessary for our survival. Some of the most important biomolecules include carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. These molecules perform a wide range of functions, including providing energy, aiding in communication and signaling, and participating in the synthesis of other biomolecules.
Carbohydrates are a group of biomolecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are important sources of energy for the body and are found in a variety of foods, including grains, fruits, and vegetables. Carbohydrates can be divided into two main categories: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are quickly absorbed by the body and provide a quick burst of energy. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are broken down more slowly and provide a sustained source of energy.
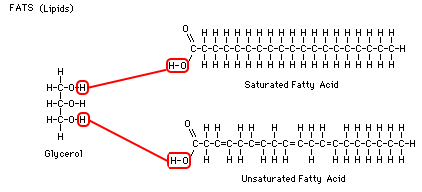
Lipids are another important group of biomolecules that are essential for the proper functioning of the body. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and are characterized by their ability to dissolve in nonpolar solvents such as oil. Lipids play a variety of roles in the body, including serving as an energy source, a structural component of cell membranes, and a means of storing fat-soluble vitamins.
Nucleic acids are biomolecules that are composed of nucleotide monomers, which are made up of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA is responsible for storing the genetic information that is passed down from generation to generation, while RNA plays a key role in the synthesis of proteins.
Proteins are large, complex biomolecules that are composed of amino acid monomers. They are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs. Proteins can be divided into four main categories: structural, contractile, regulatory, and transport. Structural proteins provide support and structure to the body's tissues, contractile proteins are responsible for muscle contraction, regulatory proteins play a role in the regulation of various processes within the body, and transport proteins are responsible for the movement of substances within and between cells.
In conclusion, biomolecules are essential for the proper functioning of the body. They play a variety of roles, including providing energy, aiding in communication and signaling, and participating in the synthesis of other biomolecules. Without these molecules, life as we know it would not be possible.