India is a vast and diverse country located in South Asia. It is the seventh largest country in the world by land area, and it is also the second most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion people.
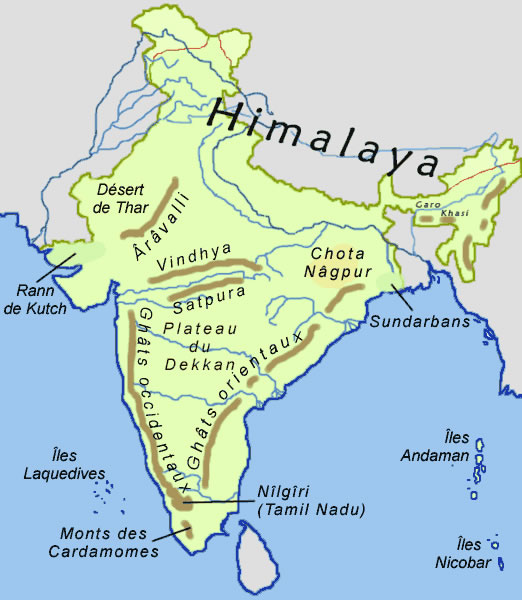
India is known for its diverse physical features, which include a range of mountains, rivers, forests, and deserts. One of the most notable physical features of India is the Himalayan mountain range, which stretches across the northern part of the country and into Nepal. The Himalayas are the highest mountain range in the world, and they are home to some of the highest peaks, including Mount Everest. The Himalayas also serve as a natural border between India and its neighbors, China and Nepal.
The Ganges River is another important physical feature of India. The Ganges is one of the longest rivers in the world, and it is considered sacred by many Hindus. The Ganges is the source of water for millions of people in India, and it is also an important transportation route.
India is home to several different types of forests, including tropical rainforests, deciduous forests, and coniferous forests. The forests of India are home to a wide range of plant and animal species, including tigers, elephants, and many different types of birds.
In addition to its mountains, rivers, and forests, India also has several deserts, including the Thar Desert in the northwest and the Great Rann of Kutch in the west. These deserts are home to a unique ecosystem and are a popular tourist destination.
Overall, India is a diverse and beautiful country with a wide range of physical features. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the sacred Ganges River and the diverse forests and deserts, India offers a wealth of natural beauty and resources.
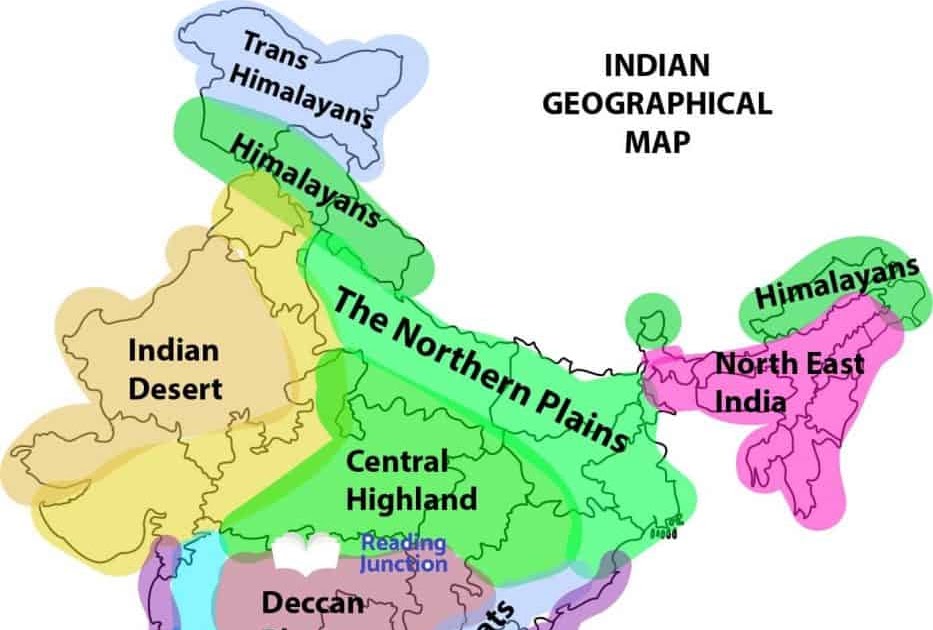
What is the Physical Geography of India?

The major rivers of Indus basin are the Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej. Due to its location on the western margin of the Penninsular Plateau, the Sahyadri Range is also called Western Ghats. Retrieved 19 November 2008. North of Zaskar range is the Ladakh range. The westernmost point of lndia lies in Gujarat and the eastern most in Arunachal Pradesh. All of the main Himalayan peaks are included in the Himadri, which has an average height of 6,000 metres. You will be fascinated to learn that this country has almost every feature for a complete study of different geographical landforms.
Physical Feature of India: Class 9th Notes

Thar Desert The only The Coastal Plains Coastal plains are situated along the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. See more interesting Northern Plains The three major river systems of India- Indus, Ganga and the Brahmaputra along with their tributaries have fed the foothills of the Himalayas. Vembanad Lake is the largest lake in this country, and it is located near the southeast coast of India in the state of Kerala. Broadly by how many hours does the local time of the eastern most point of India differ from that of the westernmost point? The mountains run from Afghanistan through Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Tibet before ending in Myanmar Burma. The same for the Lesser Himalayas is 4000 m. The average elevation of the plateau is 2,000 feet 610m above sea level.
Physical Features of India

These bodies of water include the Bay of Bengal on the East , Indian Ocean on the south , and Arabian Sea on the west. It is surrounded by hills from three sides. The defence of such an international boundary passing through various MODULE - 6 4 GEOGRAPHY kinds of terrains is certainly a difficult job. Sanctuaries Sanctuaries, on the other hand, provide shelter to animals like tigers and leopards, which are endangered species. The part of this plain lying in Uttar Pradesh is made up of MODULE - 6 10 GEOGRAPHY the deposits laid down, by the rivers like, Ganga, Yamuna, Ramganga, Gomati, Ghagra and Gandak. Little was known before today about what drove the Indian landmass to migrate so quickly.