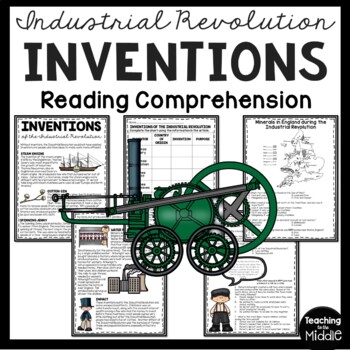
The Industrial Revolution was a period of rapid industrialization that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It marked a major turning point in history and had a profound impact on the economies, societies, and cultures of the countries that experienced it.
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain and spread to the rest of Europe, North America, and eventually the world. It was fueled by a number of factors, including the availability of cheap coal and iron, the development of new technologies and machines, and the growth of international trade.
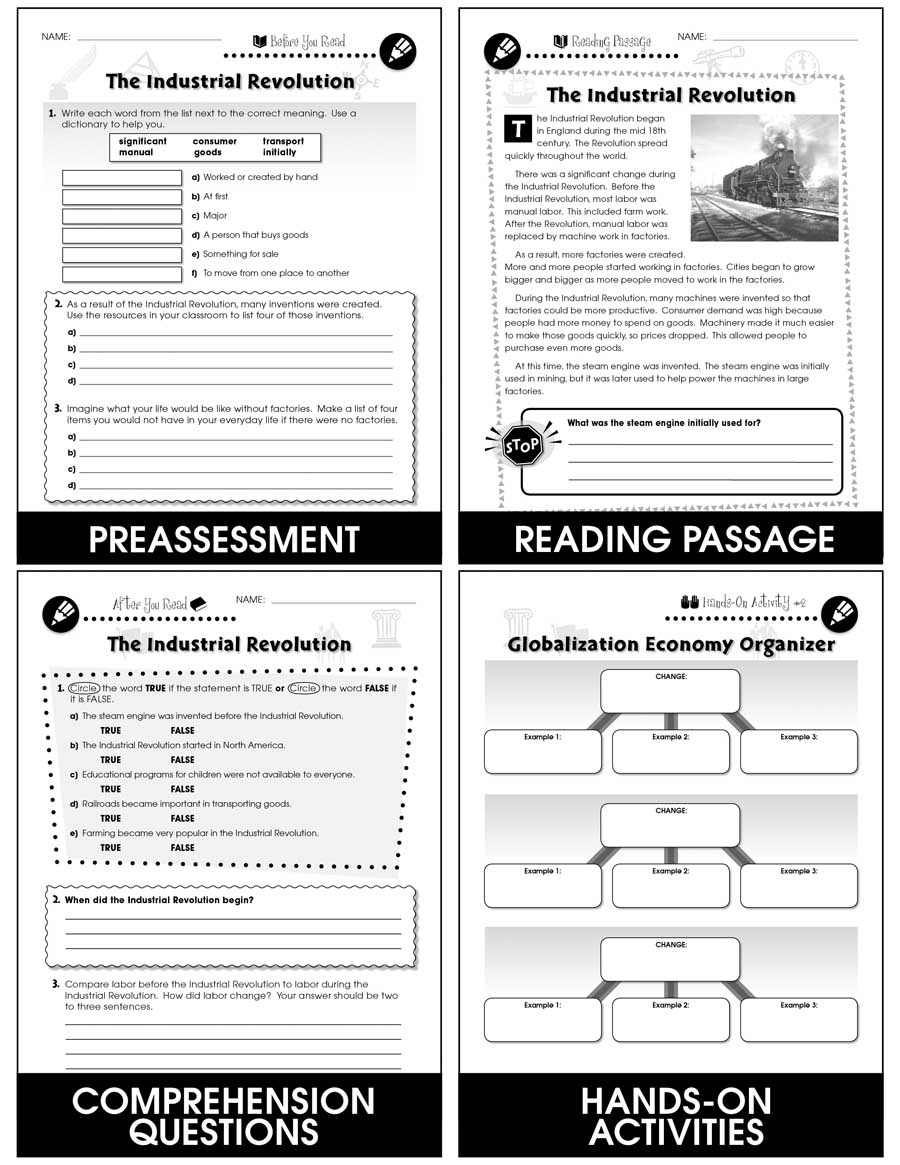
One of the most significant changes brought about by the Industrial Revolution was the shift from an agrarian society to an industrial one. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, most people lived and worked on farms, producing their own food and other goods. With the rise of factories and mass production, however, many people began to leave the countryside and move to the cities in search of work. This led to the growth of urbanization and the development of a new class of factory workers.
Another significant change brought about by the Industrial Revolution was the growth of international trade. As new technologies and transportation methods developed, it became easier and cheaper to transport goods around the world. This led to a surge in international trade and the expansion of global markets.
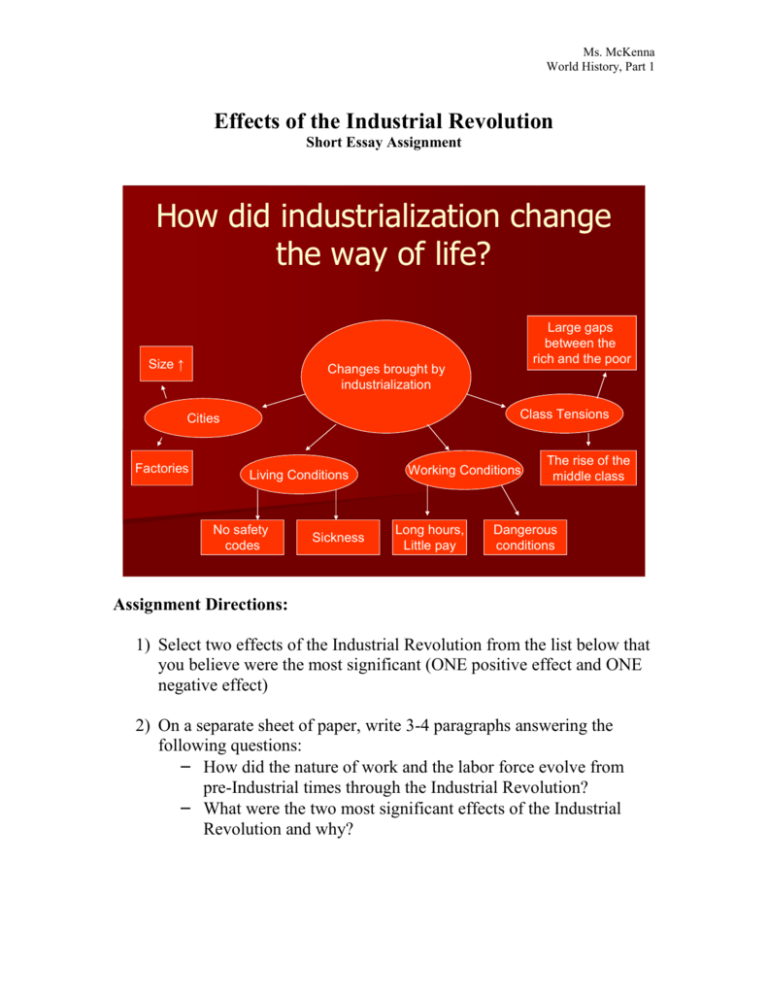
The Industrial Revolution also had a major impact on the nature of work. With the advent of machines, many jobs became automated, leading to the development of new jobs in the fields of engineering and management. At the same time, however, the rise of factories led to the exploitation of workers, who often worked long hours in dangerous and unhealthy conditions for low wages.
Overall, the Industrial Revolution was a complex and transformative period in history that had a lasting impact on the world. It brought about significant changes in the way people lived and worked, and laid the foundation for the modern industrialized societies we see today.