Institutionalism is a broad and multifaceted approach to understanding political and social phenomena that emphasizes the role of institutions in shaping human behavior and outcomes. It is a major theoretical perspective within political science that has gained widespread popularity in recent decades due to its ability to explain complex and diverse political and social processes in a systematic and coherent way.
Institutionalism suggests that institutions, or the formal and informal rules, norms, and practices that shape social and political interactions, play a central role in shaping behavior and outcomes. This perspective holds that institutions provide a framework for action and interaction, and that they are shaped by the preferences, beliefs, and interests of those who create and maintain them.
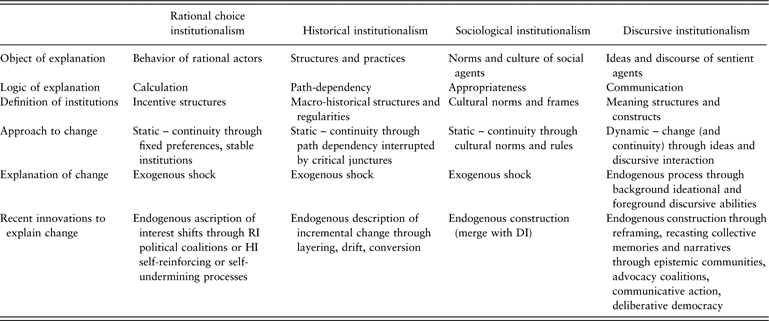
There are several different strands of institutionalism within political science, each with its own unique focus and set of assumptions. One of the most influential strands is rational choice institutionalism, which is based on the assumption that individuals act in their own self-interest and are guided by rational calculation. This perspective suggests that individuals will choose the course of action that is most likely to maximize their own benefits and minimize their costs, and that institutions are shaped by these rational calculations.
Another influential strand of institutionalism is sociological institutionalism, which emphasizes the cultural and social context in which institutions are embedded. This perspective suggests that institutions are shaped by the values, beliefs, and norms of the societies in which they exist, and that they reflect and reproduce these cultural and social norms.
Institutionalism has been applied to a wide range of political and social phenomena, including elections, policy-making, social movements, and international relations. It has also been used to understand the role of institutions in shaping economic outcomes, including economic growth, development, and inequality.
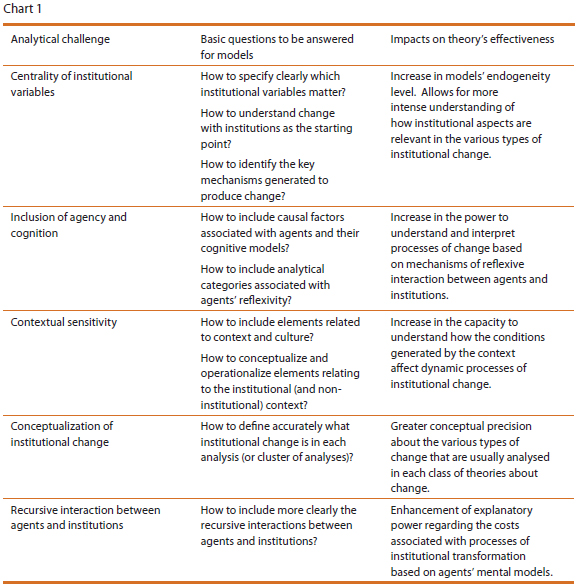
One of the key contributions of institutionalism is its ability to explain how institutions shape and are shaped by the actions and interactions of individuals within them. This perspective suggests that institutions provide a framework for action and interaction, and that they are shaped by the preferences, beliefs, and interests of those who create and maintain them. It also highlights the importance of understanding the cultural and social context in which institutions exist, and the ways in which they reflect and reproduce cultural and social norms.
Overall, institutionalism is a valuable approach to understanding political and social phenomena that emphasizes the role of institutions in shaping human behavior and outcomes. It offers a systematic and coherent way to understand complex and diverse processes and has been applied to a wide range of political and social phenomena.