Intellectual development in conception refers to the process by which a person's cognitive abilities, knowledge, and understanding of the world evolve and mature from the point of conception until adulthood. This process is an integral part of human development and is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and experiences.
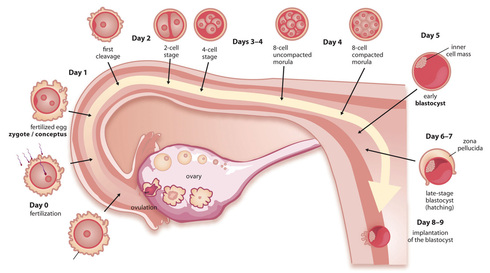
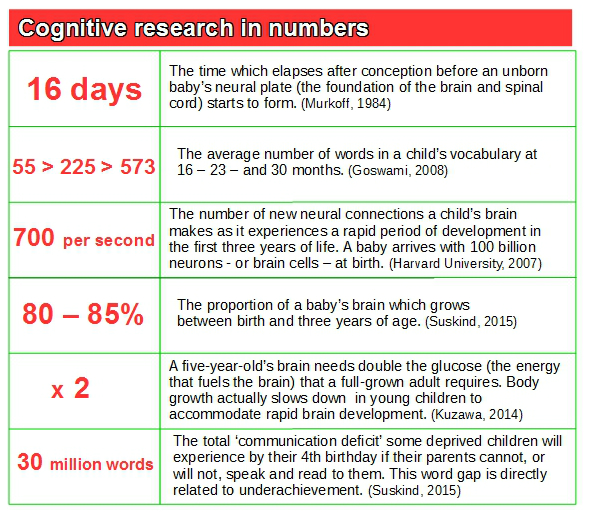
During the prenatal stage of development, the brain undergoes rapid growth and differentiation, forming the foundation for later cognitive development. The brain's structure and function are influenced by genetics, with certain genes playing a role in determining the size and complexity of the brain. However, the environment also plays a significant role in shaping the developing brain. For example, the prenatal environment can influence the development of the brain's structure and function through exposure to toxins, stress, and nutrition.
After birth, a child's intellectual development continues to be influenced by both genetics and the environment. A child's experiences and interactions with the world around them play a crucial role in their intellectual development. For example, engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as reading and solving puzzles, can stimulate cognitive growth and development. On the other hand, a lack of stimulating experiences and opportunities can hinder a child's intellectual development.
As a child grows and develops, their cognitive abilities continue to evolve and mature. During the early years of life, a child's brain is highly receptive to new information and experiences, and their cognitive abilities undergo rapid growth and development. As a child enters adolescence and adulthood, their cognitive abilities continue to mature and improve, although at a slower pace.
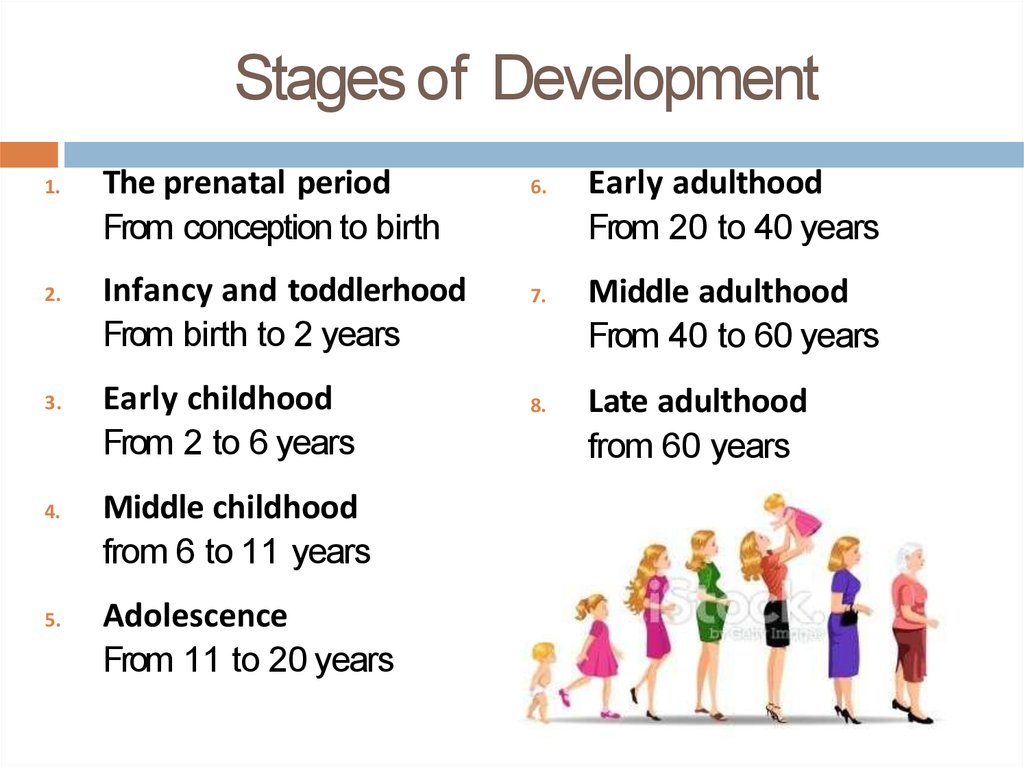
There are several key stages of intellectual development that occur during a person's lifetime. During the sensorimotor stage, which occurs from birth to approximately two years of age, a child's understanding of the world is based on their sensory experiences and physical actions. As a child moves into the preoperational stage, which occurs from about two to seven years of age, they begin to develop symbolic thought and the ability to represent objects and events with words and images. The concrete operational stage, which occurs from about seven to eleven years of age, is marked by the development of logical thought and the ability to perform mental operations. The formal operational stage, which occurs during adolescence and adulthood, is marked by the development of abstract thinking and the ability to think logically about hypothetical situations.
In conclusion, intellectual development in conception is a complex process that begins at the point of conception and continues throughout a person's lifetime. It is influenced by both genetics and the environment, with experiences and interactions with the world playing a crucial role in shaping a person's cognitive abilities, knowledge, and understanding of the world.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tips-for-supporting-your-babys-brain-development-4707581-final-3f0ce122a6ea4370875d518c76e3238b.png)