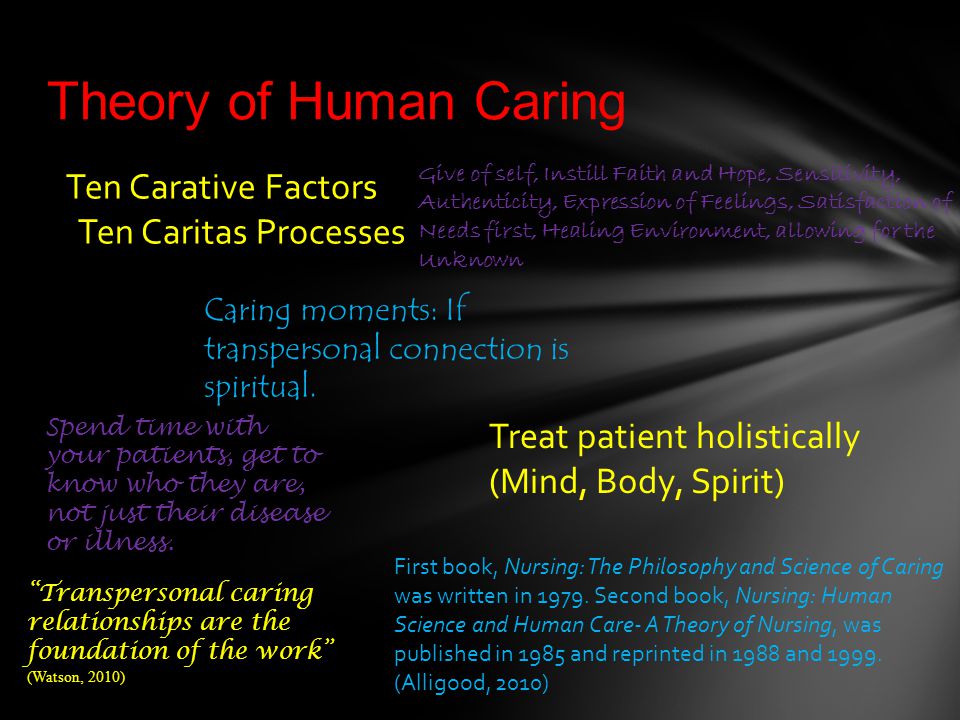
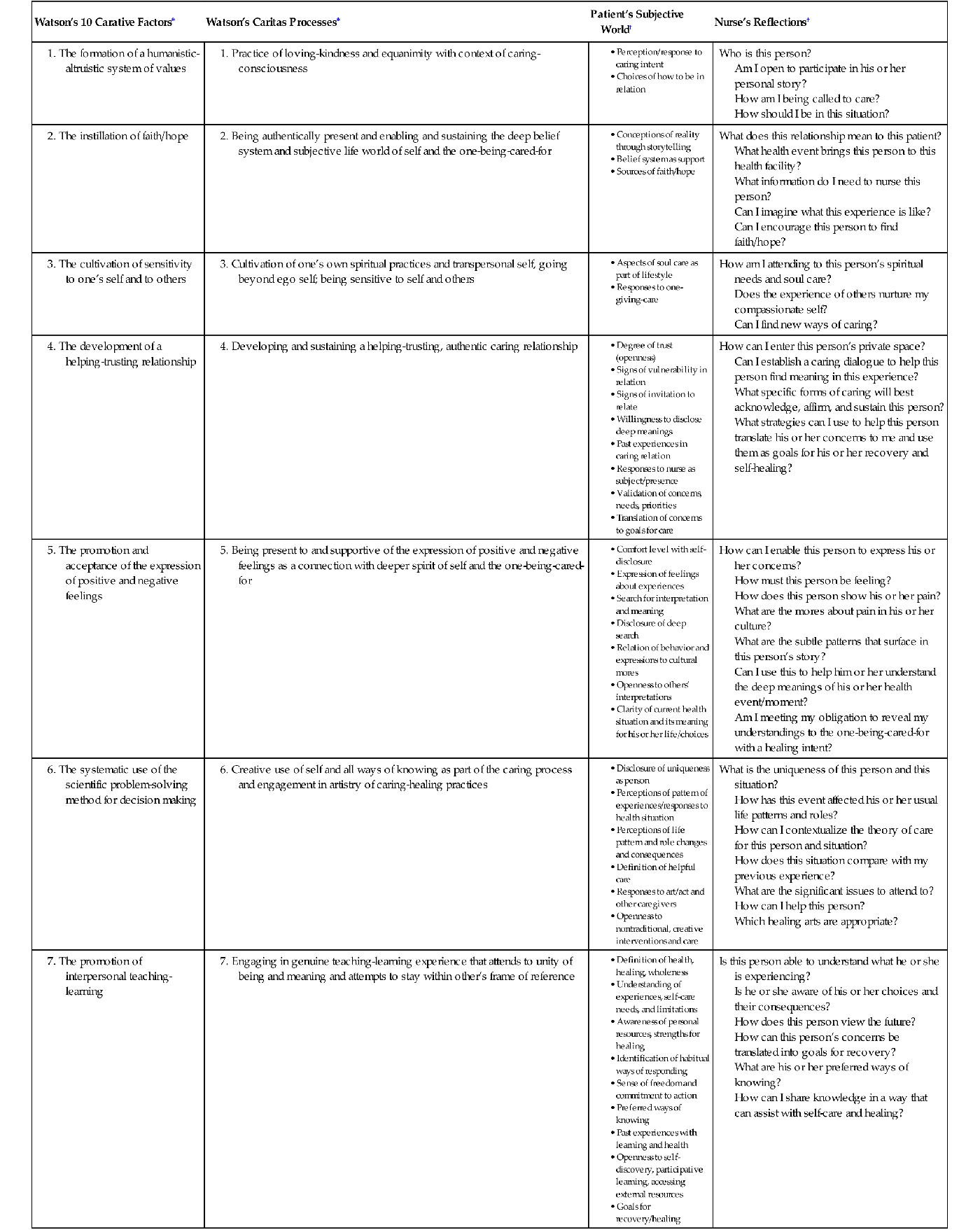
Jean Watson's carative factors are a set of 10 principles that guide the practice of nursing and prioritize the human caring relationship between the nurse and the patient. These factors were developed by Watson, a renowned nursing theorist, as a way to move beyond the traditional focus on disease and illness in nursing and instead emphasize the importance of caring for the whole person.
The 10 carative factors are:
- Human caring relationships
- Health promotion and prevention of illness
- Facilitation of healing relationships
- Supporting patient autonomy and independence
- Maintaining trust and confidentiality
- Expression of positive and negative feelings
- Cultivation of human caring consciousness and mindfulness
- Development of a helping-trusting, supportive relationship
- Promotion of patient education
- Provision of a supportive, protective, and corrective mental, physical, socio-cultural, and spiritual environment
Watson believed that these carative factors were essential for creating a caring and healing environment for patients. She argued that nurses who embody these principles are able to create a sense of trust and connection with their patients, which can have a positive impact on the patient's overall health and well-being.
One of the key carative factors is the human caring relationship between the nurse and the patient. Watson believed that this relationship is central to the nursing process and should be based on mutual respect, trust, and compassion. Nurses should strive to understand the patient's unique experiences, needs, and preferences, and should work to establish a strong, supportive relationship with the patient.
Another important carative factor is health promotion and prevention of illness. Watson argued that nurses should not just focus on treating illness, but should also work to prevent it. This can involve educating patients about healthy lifestyles, providing resources and support for patients to make healthy choices, and identifying and addressing potential health risks.
Facilitation of healing relationships is another key carative factor. Nurses should work to create a healing environment for patients, which can involve providing emotional support, creating a sense of safety and security, and helping patients to develop a sense of purpose and meaning in their lives.
Supporting patient autonomy and independence is another important carative factor. Nurses should respect and support the patient's right to make their own decisions about their healthcare, and should work to empower patients to take control of their own health and well-being.
Maintaining trust and confidentiality is crucial in the nursing profession. Nurses should be mindful of the sensitive nature of the information they handle and should strive to protect the privacy and confidentiality of their patients.
Expression of positive and negative feelings is another important carative factor. Nurses should be able to recognize and acknowledge the emotions of their patients, and should be able to provide support and guidance to help patients cope with difficult feelings.
Cultivation of human caring consciousness and mindfulness is another key carative factor. Nurses should strive to be present and attentive to their patients, and should work to cultivate a sense of caring and compassion for others.
The development of a helping-trusting, supportive relationship is another important carative factor. Nurses should work to establish a strong, supportive relationship with their patients, which can involve providing emotional support, listening to patients' concerns, and helping patients to navigate the healthcare system.
Promotion of patient education is an essential carative factor. Nurses should work to educate patients about their health conditions, treatment options, and ways to manage their health.
Finally, provision of a supportive, protective, and corrective mental, physical, socio-cultural, and spiritual environment is another key carative factor. Nurses should work to create a healing environment for patients that meets their physical, emotional