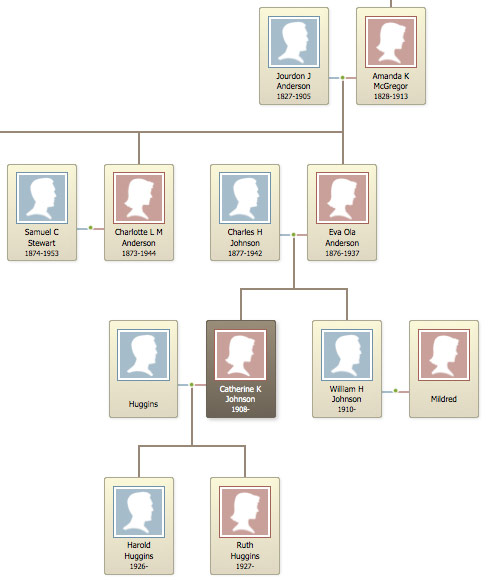
Jourdan Anderson was a former slave who gained fame for his letter to his former owner, Thomas Anderson, in which he requested to purchase his freedom. Anderson was born into slavery in 1825 in Tennessee and spent much of his life working on the Anderson plantation. Despite facing numerous challenges and difficulties as a slave, Anderson was a skilled craftsman and became known for his ability to build and repair various structures on the plantation.
In 1862, Anderson wrote a letter to his former owner, Thomas Anderson, in which he requested to purchase his freedom. In the letter, Anderson stated that he had saved enough money to buy his freedom and asked if Thomas Anderson would consider selling it to him. Anderson argued that he had worked hard and been a good servant, and that he deserved the opportunity to be a free man.
Thomas Anderson ultimately agreed to sell Anderson his freedom for $1000, which Anderson was able to pay in full. Anderson was then able to leave the plantation and start a new life as a free man.
After gaining his freedom, Anderson moved to Ohio, where he found work as a contractor and builder. He became known for his skills in the construction industry and was able to provide for his family and live a comfortable life. Anderson also became involved in the abolitionist movement and worked to help other former slaves gain their freedom.
In conclusion, Jourdan Anderson's letter to his former owner, Thomas Anderson, is a powerful reminder of the resilience and determination of slaves who fought for their freedom. Despite facing numerous challenges and hardships, Anderson was able to achieve his goal of becoming a free man and build a successful life for himself. His story serves as an inspiration for all those who have faced obstacles in their lives and fought for what they believe in.
The National Health Service and Community Care Act 1990 is a significant piece of legislation that was passed in the United Kingdom. It was intended to reform and modernize the National Health Service (NHS) and to provide better community care for people in need.
One of the main objectives of the Act was to provide more choice and control for patients in the NHS. It introduced the concept of fundholding, which allowed GPs to purchase services on behalf of their patients from different providers, including hospitals and other healthcare organizations. This was intended to increase competition and improve the quality of care.
Another important aspect of the Act was the introduction of the internal market within the NHS. This allowed hospitals and other healthcare providers to compete with each other for contracts to provide services to patients. This was seen as a way to increase efficiency and drive down costs, but it also led to some criticism as it was perceived as introducing a more commercialized approach to healthcare.
The Act also established the Department of Health as the central body responsible for the administration and management of the NHS. It also created the position of the Chief Executive of the NHS, who was responsible for overseeing the operation of the service and implementing government policy.
In addition to these changes within the NHS, the Act also introduced significant reforms to community care. It aimed to provide better care for people who needed support to live independently in their own homes, rather than being institutionalized in hospitals or nursing homes. It introduced the concept of community care assessments, which were used to determine the needs of individuals and the type of support that they required.
Overall, the National Health Service and Community Care Act 1990 was a major reform of the NHS and community care in the United Kingdom. While it brought about some significant changes, it also sparked controversy and debate about the direction of healthcare in the country.