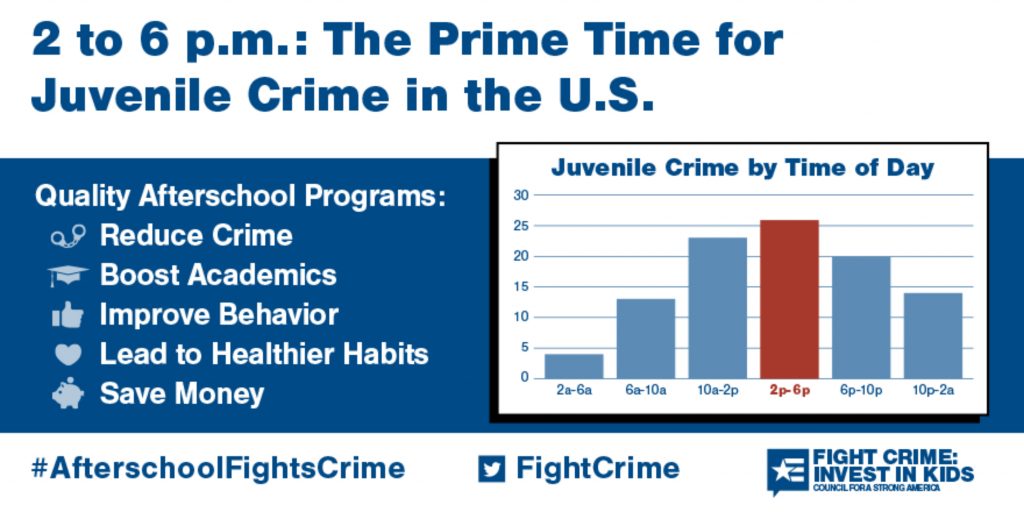
Juvenile crime has long been a concern for society, as it not only has immediate consequences for those involved, but also has the potential to lead to future criminal behavior. In order to effectively address and prevent juvenile crime, it is important to understand the factors that contribute to it and the most effective approaches for addressing it.
There are a range of factors that can contribute to juvenile crime, including individual, family, and societal factors. At the individual level, factors such as personality traits, cognitive abilities, and mental health can play a role in whether a young person engages in criminal behavior. Family factors, such as parental involvement and supervision, family structure and dynamics, and parental substance abuse or criminal behavior, can also influence a young person's likelihood of engaging in crime. Societal factors, such as poverty, lack of access to education and employment opportunities, and community violence, can also contribute to juvenile crime.
Research has also shown that certain risk factors, such as prior involvement in the criminal justice system, substance abuse, and association with delinquent peers, can increase a young person's likelihood of engaging in criminal behavior. On the other hand, protective factors, such as positive relationships with adults, involvement in prosocial activities, and academic achievement, can reduce the likelihood of juvenile crime.
There are a variety of approaches that can be effective in addressing and preventing juvenile crime. One approach is through the use of rehabilitation and treatment programs, which can address the underlying issues that contribute to criminal behavior and help young people develop the skills and coping mechanisms they need to make positive choices. Another approach is through the use of alternative sanctions, such as community service and restitution, which can hold young people accountable for their actions while also providing them with opportunities to make amends and give back to their communities.
Preventative strategies, such as early intervention and prevention programs and building positive relationships with young people, can also be effective in reducing the likelihood of juvenile crime. These strategies can help young people develop the skills and resilience they need to make positive choices and avoid risky behaviors.
In conclusion, juvenile crime is a complex issue with a range of contributing factors. To effectively address and prevent it, it is important to understand these factors and utilize a range of approaches, including rehabilitation, alternative sanctions, and preventative strategies. By taking a comprehensive approach, we can work towards creating a safer and more just society for all.