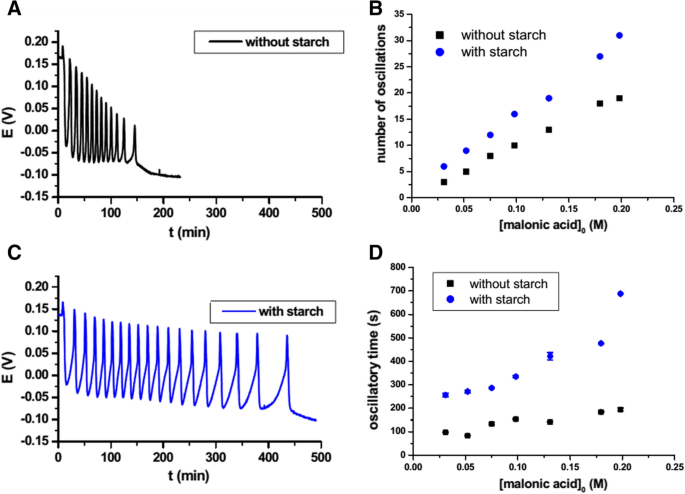
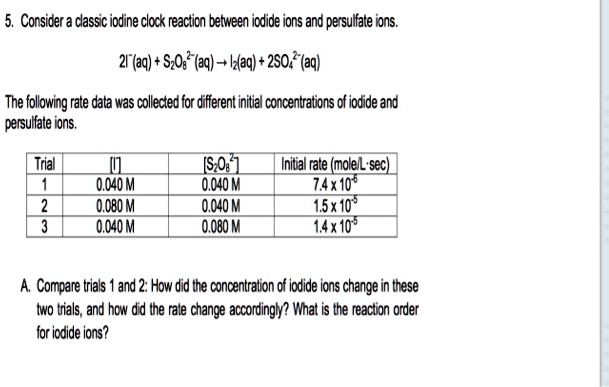
The persulfate-iodide clock reaction is a classic chemical kinetics experiment that demonstrates the concept of a rate-determining step and the effect of various factors on the rate of a chemical reaction. In this reaction, a solution of potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) and sodium iodide (NaI) is mixed together and the time it takes for the solution to change color is measured. The reaction can be written as follows:
2K2S2O8 + 2NaI -> 2K2SO4 + I2 + 2Na2SO4
The key feature of this reaction is that it proceeds through a series of intermediate steps, rather than occurring all at once. The first step is the slowest, or rate-determining step, and controls the overall rate of the reaction. This step involves the formation of intermediate species known as iodide ions (I-) and persulfate ions (S2O8^2-).
The rate of the persulfate-iodide clock reaction is affected by a number of factors, including the concentration of the reactants, the temperature, and the presence of catalysts. Increasing the concentration of the reactants will generally increase the rate of the reaction, since there are more reactant molecules present to collide and react. Similarly, increasing the temperature will also increase the rate of the reaction, as the increased kinetic energy of the reactant molecules will make it more likely that they will successfully collide and react.
Catalysts can also affect the rate of the persulfate-iodide clock reaction. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. In the persulfate-iodide clock reaction, a variety of substances can act as catalysts, including certain metals and organic compounds. These catalysts work by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to proceed through, which can be faster than the uncatalyzed reaction.
In summary, the persulfate-iodide clock reaction is a useful tool for demonstrating the concept of a rate-determining step and the effect of various factors on the rate of a chemical reaction. By carefully controlling the conditions of the reaction, it is possible to gain a better understanding of the underlying kinetics and mechanisms involved in the reaction.


+%2B+2+I-+(aq)++2+SO42-+(aq)+%2B+I2+(aq).jpg)