Labeling theory is a sociological perspective that explains how people's identities and behaviors are influenced by the labels and categories assigned to them by society. This theory suggests that people's self-concept and the way they are treated by others are largely shaped by the labels that are applied to them, whether those labels are positive or negative. In this essay, we will explore some examples of how labeling theory operates in sociology and how it can have both positive and negative consequences for individuals and groups.
One example of labeling theory can be seen in the way that people with mental illnesses are often labeled and stigmatized by society. People with mental illnesses may be labeled as "crazy," "dangerous," or "unpredictable," which can lead to discrimination and social exclusion. This labeling can have a significant impact on people's self-esteem and self-worth, and it can make it difficult for them to access the support and treatment they need. In contrast, if people with mental illnesses are labeled in more positive and supportive ways, such as "courageous" or "resilient," it can help to reduce stigma and improve their quality of life.
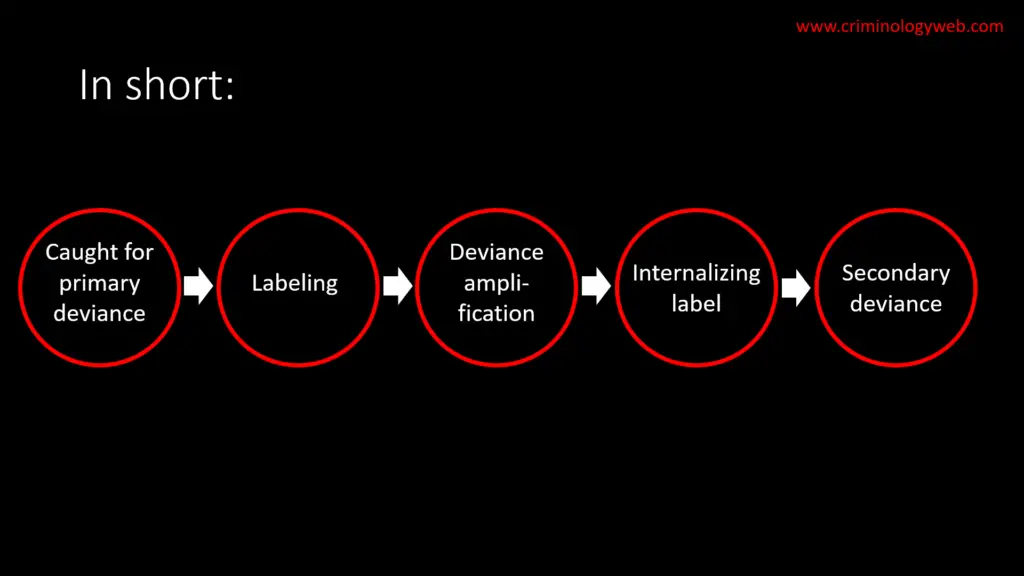
Another example of labeling theory can be seen in the way that people who are convicted of crimes are labeled and treated by society. When people are labeled as "criminals," they may face discrimination and social exclusion, which can make it difficult for them to find housing, employment, and other resources they need to rebuild their lives after serving their sentences. This labeling can also reinforce negative stereotypes and prejudices, leading to further marginalization and discrimination. In contrast, if people who have been convicted of crimes are given the opportunity to "pay their debt to society" and are then supported in reintegrating into their communities, it can help to reduce recidivism and improve public safety.
A third example of labeling theory can be seen in the way that people who belong to certain social groups or categories are labeled and treated by society. For example, people who are racial or ethnic minorities may be labeled as "other," "different," or "inferior," which can lead to discrimination and social exclusion. This labeling can have significant consequences for people's opportunities and outcomes in life, and it can perpetuate social inequalities and injustices. In contrast, if people are treated with respect, dignity, and fairness, regardless of their social group or category, it can help to create a more inclusive and equitable society.
In conclusion, labeling theory is a useful sociological perspective that helps us understand how people's identities and behaviors are influenced by the labels and categories assigned to them by society. By examining the ways in which labeling can have both positive and negative consequences for individuals and groups, we can work to create a more inclusive and just society.