The law of random segregation, also known as Mendel's law of segregation, is a fundamental principle in genetics that was first proposed by Gregor Mendel in the 19th century. It states that during the formation of gametes (sperm or eggs), the alleles (different versions of a gene) for a particular trait are randomly separated from each other. This means that each gamete has an equal chance of receiving either the dominant or recessive allele for a given trait.
This law is important because it helps to explain how traits are inherited from one generation to the next. It also helps to predict the probability of certain traits appearing in the offspring of two individuals.
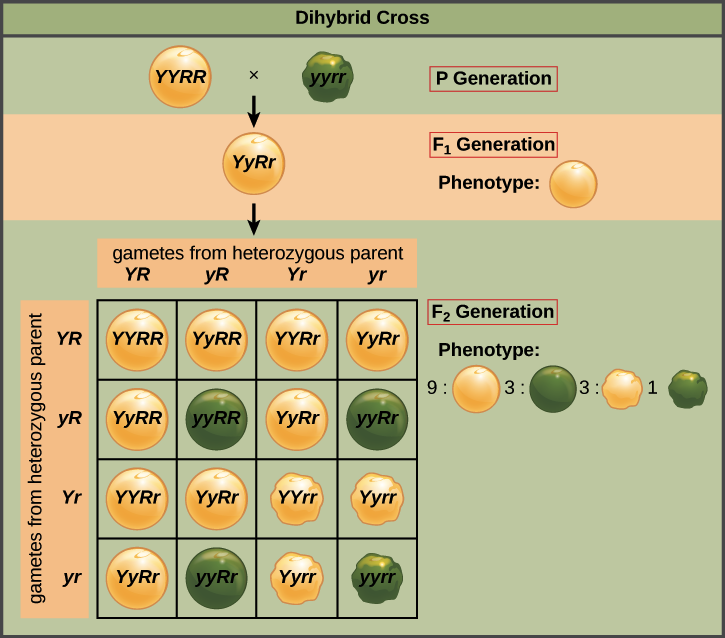
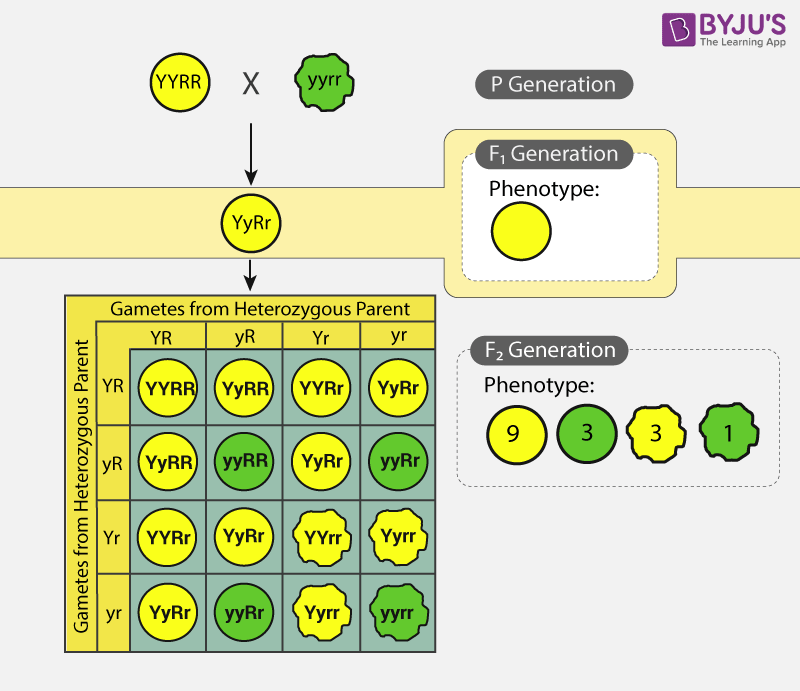
For example, if an individual has a dominant allele for a particular trait and a recessive allele for the same trait, they are known as a heterozygote. According to the law of random segregation, each gamete produced by this individual has a 50% chance of receiving the dominant allele and a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele. If this individual mates with another individual who is also a heterozygote for the same trait, there is a 25% chance that their offspring will inherit two copies of the recessive allele (homozygous recessive) and therefore exhibit the recessive trait. There is also a 50% chance that their offspring will inherit one copy of the dominant allele and one copy of the recessive allele (heterozygous) and exhibit the dominant trait.
The law of random segregation is also closely related to the concept of probability, as it helps to predict the likelihood of certain outcomes based on the inheritance of alleles. This can be useful in a variety of fields, including agriculture, medicine, and genetics research.
Overall, the law of random segregation is a crucial principle in genetics that helps to explain how traits are inherited and how the probability of certain traits appearing in offspring can be predicted. It continues to be a vital part of our understanding of genetics and how traits are passed down from one generation to the next.
Genes, Traits and Mendel's Law of Segregation
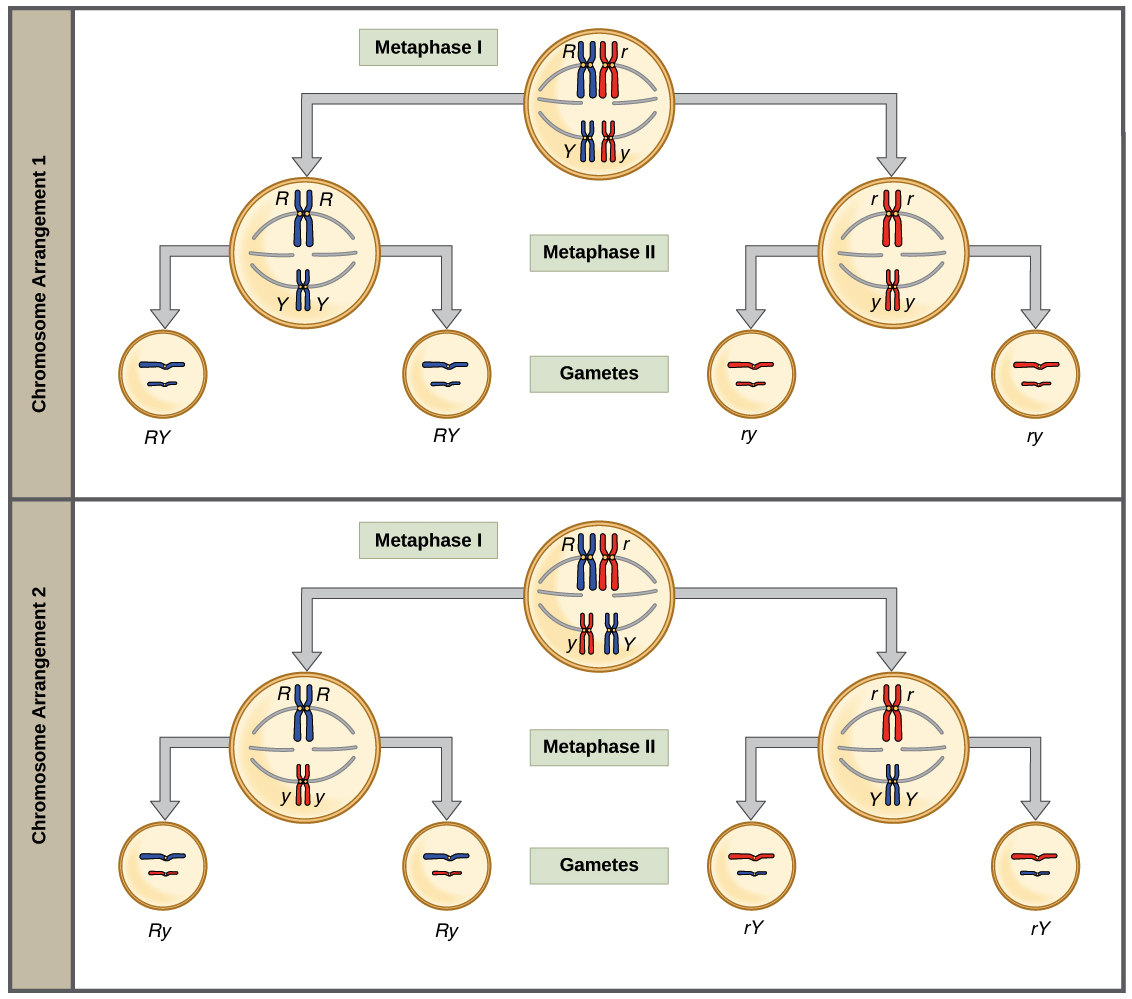
He started by crossing two pure breeding or true breeding pea plants for a certain trait. So what's going to happen, if you recall from meiosis, is the meiotic spindle is going to pull these chromosomes apart and as these chromosomes are pulled apart, what's going to ultimately happen is they're going to end up in separate gametes. One is taken from the mother, and one is taken from the father. Genes are passed down from the parents to the offspring. He conducted his experiments involving hybridization experiments in garden peas Pisum Sativum.
Mendel's Law of Segregation: Explanation
We also have to remember that the flying hamster, like most animals, is a diploid organism. A represents the dominant factor, and a represents the recessive factor. As a result, the diverse characteristics have an equal chance of happening together. Where does the law of segregation occur in meiosis? Because the alleles are selected randomly there is a mathematically predictable way of knowing the chance of each genotype and phenotype of the offspring. These are traits or Let's take a family where two parents are carriers of the hemochromatosis gene.
Mendel's Law of Segregation
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Independent-Assortment-58adf1b25f9b58a3c9ea3237.jpg)
Now, when we say dominant, what we mean is that when the coat color gene is heterozygous for these alleles, the hamster will be brown. For instance, in the case of the heterozygous hamster, one of the chromosome threes has the 'B' allele and the other chromosome three has the 'b' allele. The law of segregation states that, 'the alleles of a given locus segregate into separate gametes. These are two rules of genetics that explain the segregation of maternal and paternal genes during gametogenesis. These combine during the formation of a zygote. His results were so well-documented that it is still taught in schools and undergraduate courses on genetics. During meiosis, segregation occurs when allele pairs different characteristics of the same gene are separated so that they may be transferred to distinct gametes.
What Is Mendel's Law of Segregation?

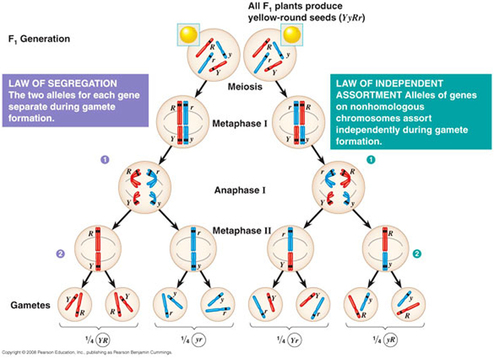
Law of Independent Assortment Mendel : Definition, Explanation, Example. Only one randomly selected allele for every trait out of each pair of alleles is passed into the offspring from parents. The alleles for a given gene segregate independently of the alleles for other genes. The Law of Segregation, the Law of Independent Assortment, the Law of Dominance, and the Law of Unit Characters are the four laws in question. The law says that alleles are selected at random and act independently when combined to create offspring.

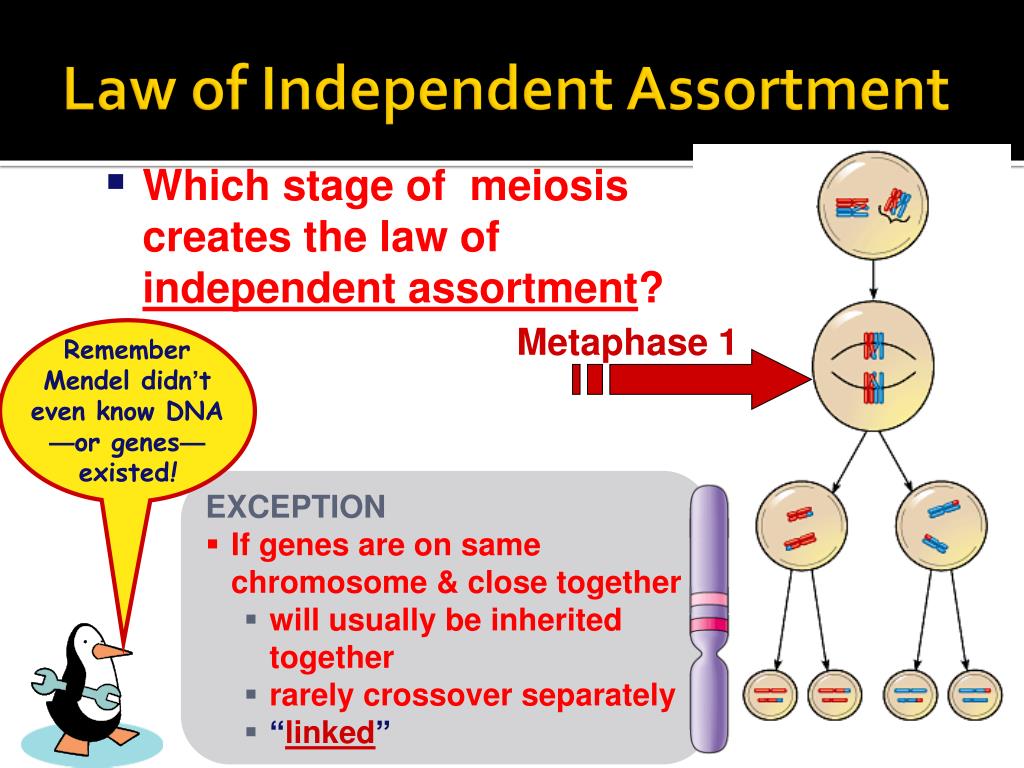


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Independent-Assortment-58adf1b25f9b58a3c9ea3237.jpg)