At the corporate level, businesses are constantly facing challenges and opportunities that can impact the success and profitability of the company. These challenges and opportunities can range from external factors such as changes in market conditions, technological advances, and shifts in consumer behavior, to internal factors such as organizational structure, leadership, and employee engagement. To navigate these challenges and take advantage of opportunities, businesses must develop strategies and make decisions at the corporate level that will guide the direction and operations of the company.
One key aspect of corporate decision-making is the alignment of business goals with the values and mission of the company. By establishing clear goals and values, businesses can ensure that their actions and decisions are in line with their overall purpose and vision. This can also help to create a sense of purpose and meaning for employees, which can lead to higher levels of engagement and productivity.
Another important aspect of corporate decision-making is the consideration of stakeholders. Stakeholders include anyone who has a vested interest in the success of the company, such as shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, and the local community. By taking the needs and perspectives of these stakeholders into account, businesses can make decisions that are not only financially sound, but also socially and ethically responsible.
Effective leadership is also critical at the corporate level. Strong leaders are able to inspire and motivate employees, while also setting clear expectations and providing guidance and support. They must also be able to adapt to changing circumstances and make difficult decisions when necessary.
Ultimately, the success of a business at the corporate level depends on its ability to effectively manage and navigate the challenges and opportunities it faces. By establishing clear goals and values, considering the needs of stakeholders, and providing effective leadership, businesses can position themselves for long-term success.
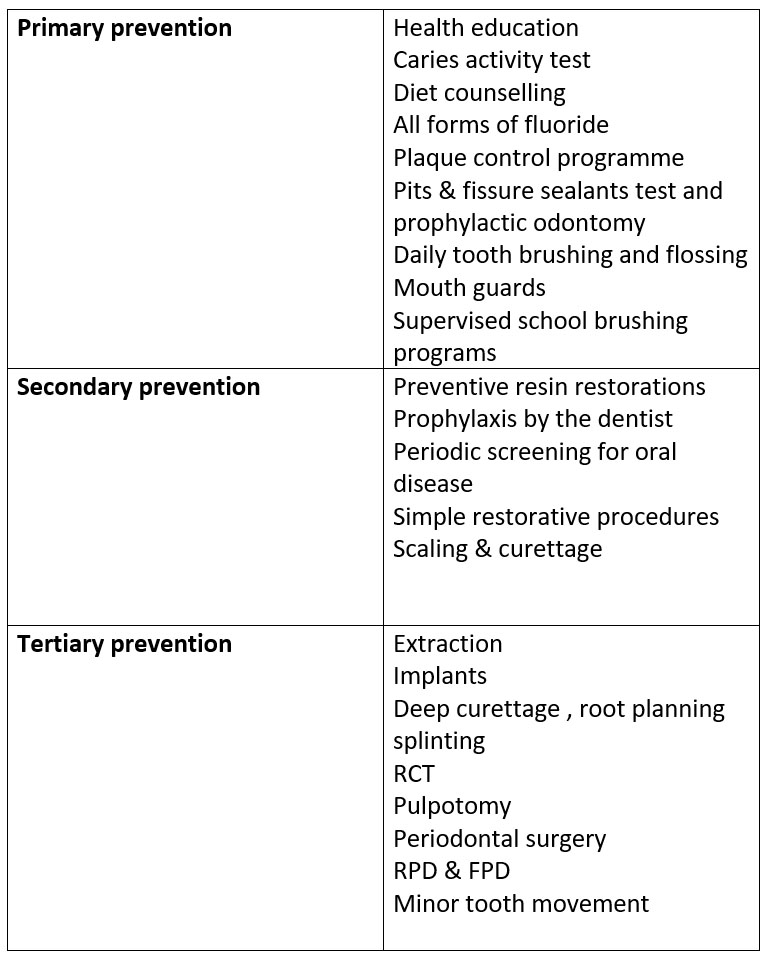
Types of Prevention: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary

Therefore, employers should consider starting with primary interventions, where possible, as they focus on the root causes of stress. What are examples of tertiary prevention for child maltreatment? Depending on the condition or medical situation, a patient may receive tertiary care more than once, too. Levels of Prevention in Nursing There are three levels of prevention in nursing and health care. Primary prevention aims at preventing the initiation of substance abuse or delaying the age of initiation. It will also discuss the implementation of three specific programs in Australia that provide an intervention for each level of response. Recommendations change frequently, and it can be challenging for them to stay current on best practices.
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Prevention

For example, oncologists are doctors with a trained specialty in treating cancers, and many have further specialties in a specific type of cancer, like breast cancer, lung cancer or skin cancer. Let's say an infant is diagnosed with a heart murmur that is going to require frequent monitoring and possible surgery. According to American Diabetes Association website, the 2011 diabetes statistics in America is 25. The program encouraged the individuals to continue with the exercising by offering free classes. What steps can be taken to avoid illness and complications in infants? Patients that are not compliant are at risk of progression of diabetes. Tertiary Prevention in Nursing Tertiary prevention in nursing for infants means providing interventions when a chronic condition has been diagnosed. As shown in the figure below, three levels of intervention primary, secondary, and tertiary levels are available to support students.
Table: Three Levels of Prevention

Some focus further on specific areas like substance abuse and addiction medicine or adolescent mental health. Related: 32 Career Paths in the Medical Field To Explore What is primary care? Examples include screening patients with diabetes for microalbuminuria, rigorous treatment of diabetes mellitus, and post-myocardial infarction prophylaxis with b-blockers and aspirin. They also assist with pain medication following surgery. They also help coordinate your care with specialists or higher levels of care when needed, typically through referrals. Primary Prevention As we have learned, primary prevention has the goal of avoiding disease altogether. After the surgery, Leon will have to adopt a new diet and attend regular checkups to receive continuous treatment for his heart condition. However, it is even more specialized and highly unusual.
What Are Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Levels of Care?

Primary care is the first and most frequent level of care for medical concerns, illnesses, conditions, symptoms or non-life-threatening emergencies. Offering primary prevention will optimize the patient's health. Quaternary care is an advanced level of specialized care. With a little work, you can prevent many of the most serious diabetes complications or even head off the disease altogether. After the surgery, Leon will have to adopt a new diet and attend regular checkups to receive continuous treatment for his heart condition. What are examples of primary prevention? This is done by helping people manage long-term, often-complex health problems and injuries e.