Cause and effect writing is a type of writing that examines the relationship between two events or situations, specifically focusing on the reasons why one event or situation occurs and the consequences or effects that result from it. This type of writing is often used in academic and professional contexts to analyze and understand complex phenomena and to identify the underlying causes of problems or issues.
Cause and effect writing begins by identifying and explaining the cause of an event or situation, which is often referred to as the "cause" in this type of writing. This can be a specific event, a set of circumstances, or a combination of both. The writer then goes on to describe the effects or consequences that result from the cause, which are often referred to as the "effects" in this type of writing.
One of the key characteristics of cause and effect writing is that it is analytical in nature, meaning that it involves examining and analyzing data and evidence in order to understand the underlying causes and effects of a particular event or situation. This may involve using a variety of research methods, including interviews, surveys, experiments, and other methods, to gather data and evidence that can help to support the writer's arguments and conclusions.
In addition to being analytical, cause and effect writing is also often argumentative in nature, as the writer may be trying to persuade the reader to accept a particular point of view or to take a specific course of action. As such, cause and effect writing may involve the use of logical reasoning and evidence to support the writer's arguments and to convince the reader of their validity.
Overall, cause and effect writing is an important tool for understanding and explaining the relationships between events and situations, and for identifying and addressing problems and issues in a variety of contexts. By examining and analyzing the underlying causes of events and situations, and by exploring the consequences or effects that result from them, writers can help to shed light on complex phenomena and to inform decision-making and problem-solving efforts.
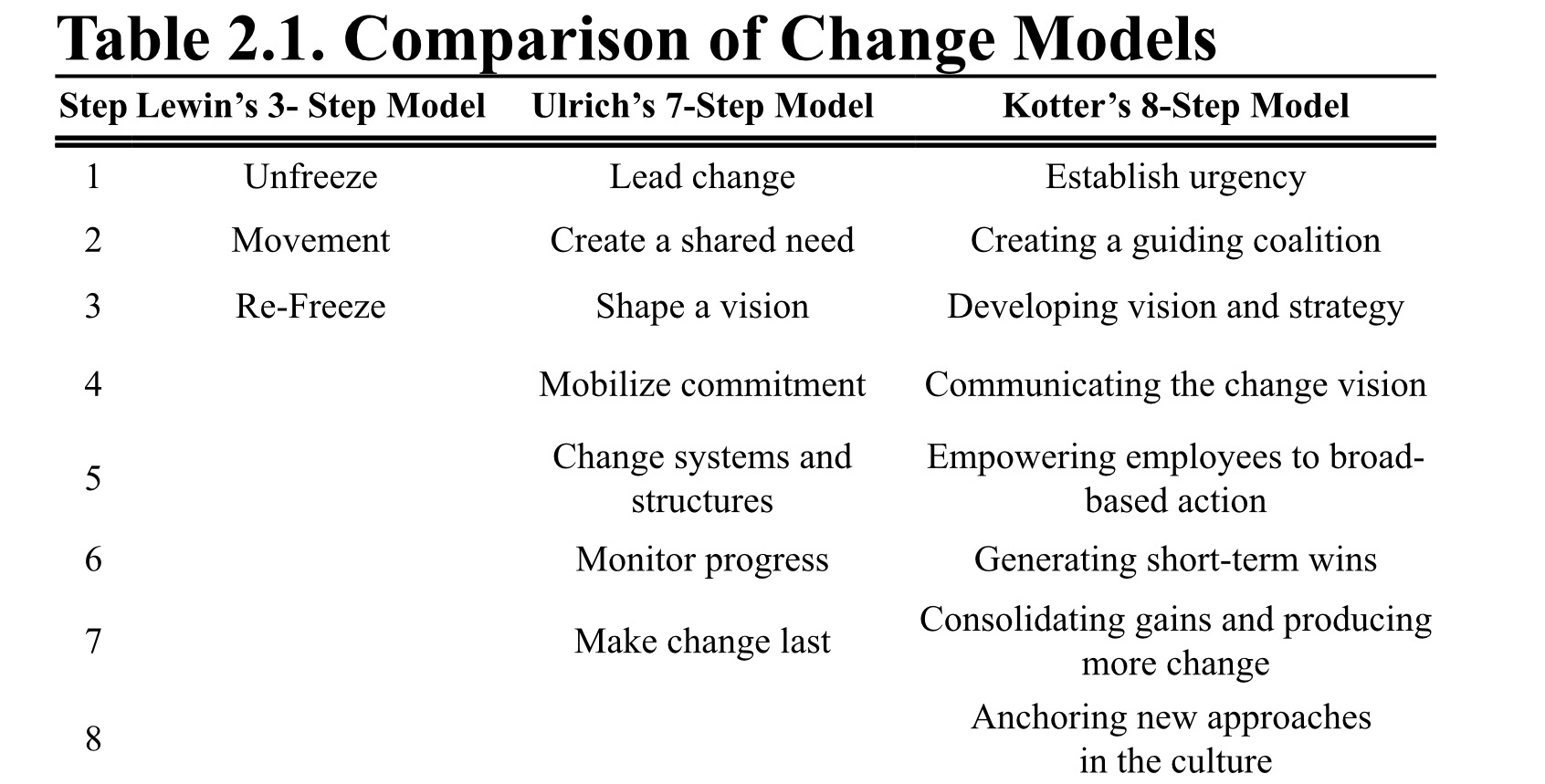
Kurt Lewin and John Kotter are two well-known figures in the field of organizational change management. Their respective models, known as the Lewin Change Model and the Kotter Change Model, offer valuable insight into the process of implementing and managing change within an organization.
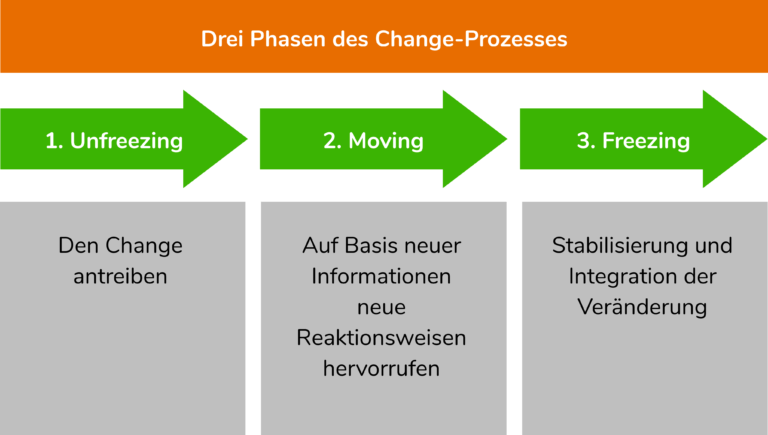
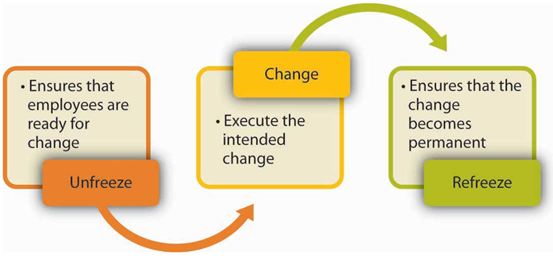
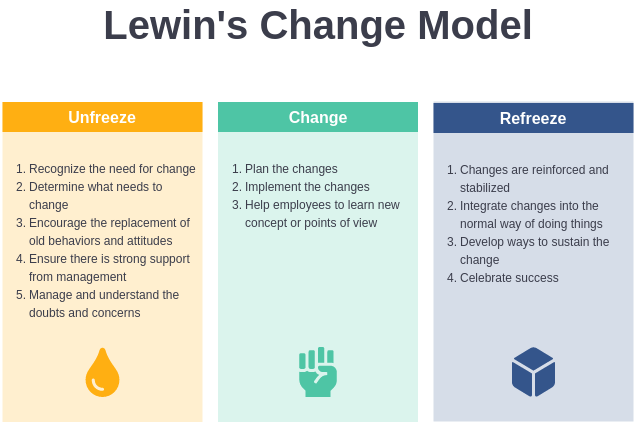
The Lewin Change Model, also known as the "Unfreeze-Change-Freeze" model, was developed by Kurt Lewin in the 1950s. It consists of three stages: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing.
The first stage, unfreezing, involves breaking down the existing mindset and behaviors of individuals within the organization. This can be achieved through various means, such as communication, training, and education. The goal of this stage is to create a sense of dissatisfaction with the status quo and to motivate individuals to embrace change.
The second stage, changing, involves implementing the actual changes to be made. This can involve revising policies and procedures, introducing new technologies, or reorganizing the structure of the organization. It is during this stage that the majority of the effort and resources are put into making the desired changes.
The final stage, refreezing, involves solidifying the changes made in the previous stage and integrating them into the organization's culture and daily operations. This stage is critical for ensuring that the changes made are sustainable and become the new norm for the organization.
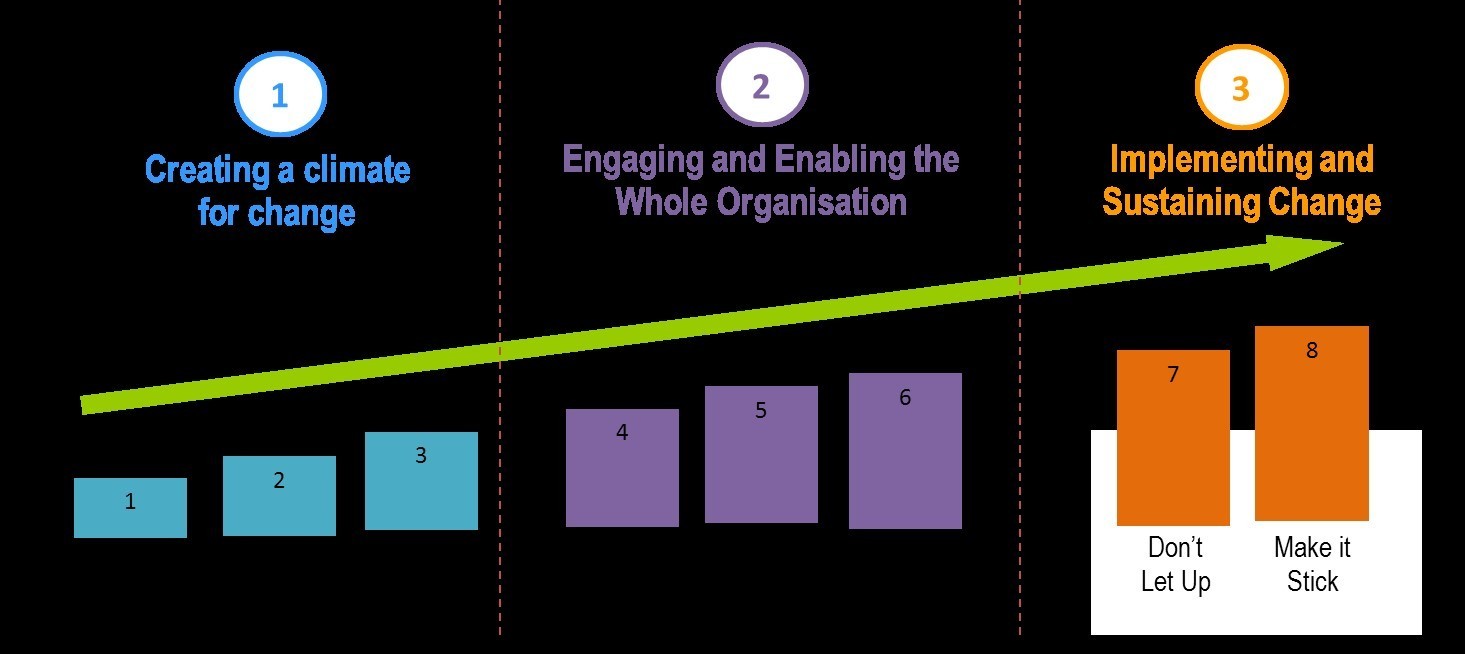
The Kotter Change Model, also known as the "8-Step Process," was developed by John Kotter in the 1990s. It consists of eight steps: establishing a sense of urgency, forming a guiding coalition, creating a vision and strategy, communicating the change vision, empowering others to act on the vision, creating short-term wins, consolidating gains and producing more change, and anchoring new approaches in the organization's culture.
The first step in the Kotter Change Model is establishing a sense of urgency. This involves identifying the need for change and communicating it to the organization. This step is critical for building support for the change effort and mobilizing the necessary resources.
The second step is forming a guiding coalition. This involves bringing together key stakeholders, such as executives, managers, and employees, to lead the change effort. The guiding coalition should be diverse and representative of all levels of the organization.
The third step is creating a vision and strategy for the change. This involves identifying the desired outcomes of the change and developing a plan for achieving them. The vision should be clear and compelling, and the strategy should be realistic and achievable.
The fourth step is communicating the change vision to the organization. This involves ensuring that the vision and strategy are understood and supported by all members of the organization. This step is critical for gaining buy-in and commitment to the change effort.
The fifth step is empowering others to act on the vision. This involves providing the necessary resources and support to those who will be responsible for implementing the changes. It also involves removing any barriers or roadblocks that may hinder the change effort.
The sixth step is creating short-term wins. This involves identifying and achieving small, tangible victories that demonstrate progress and build momentum for the change effort.
The seventh step is consolidating gains and producing more change. This involves building on the successes achieved in the previous step and continuing to drive the change effort forward.
The final step is anchoring new approaches in the organization's culture. This involves embedding the changes made into the organization's daily operations and making them the new norm.
Both the Lewin Change Model and the Kotter Change Model offer valuable insights into the process of managing change within an organization. They provide a structured approach for identifying the need for change, implementing and communicating the changes,