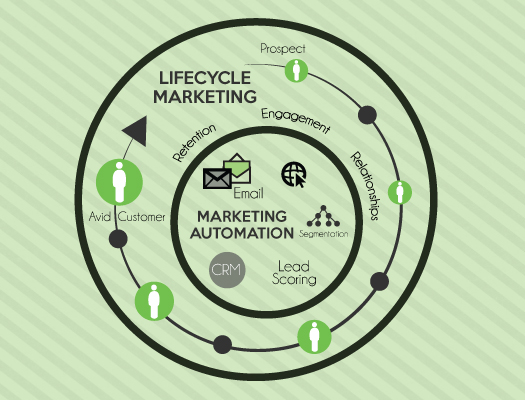
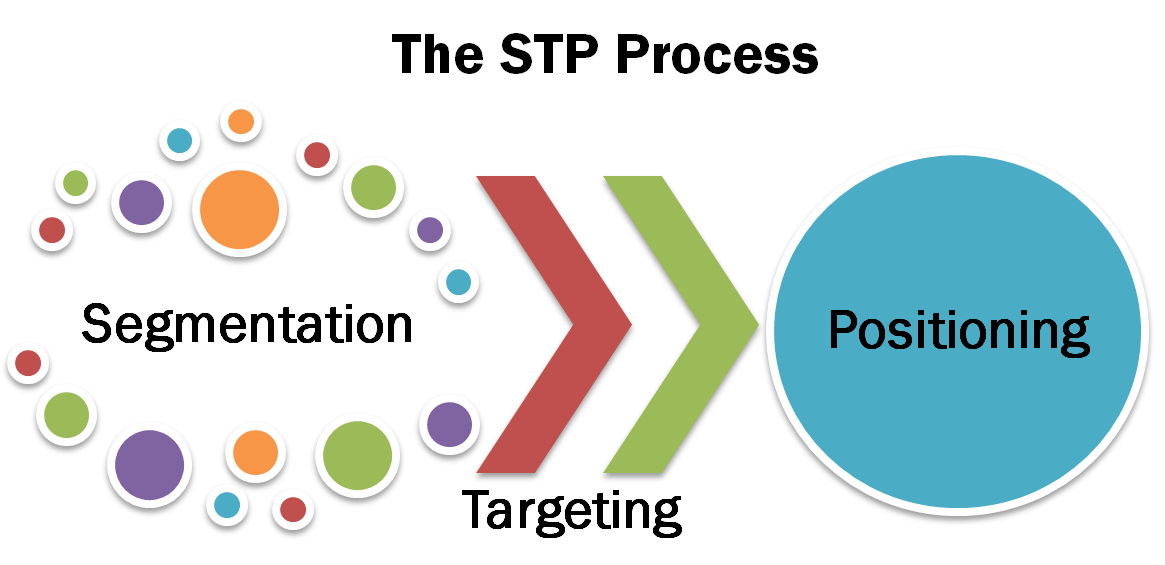
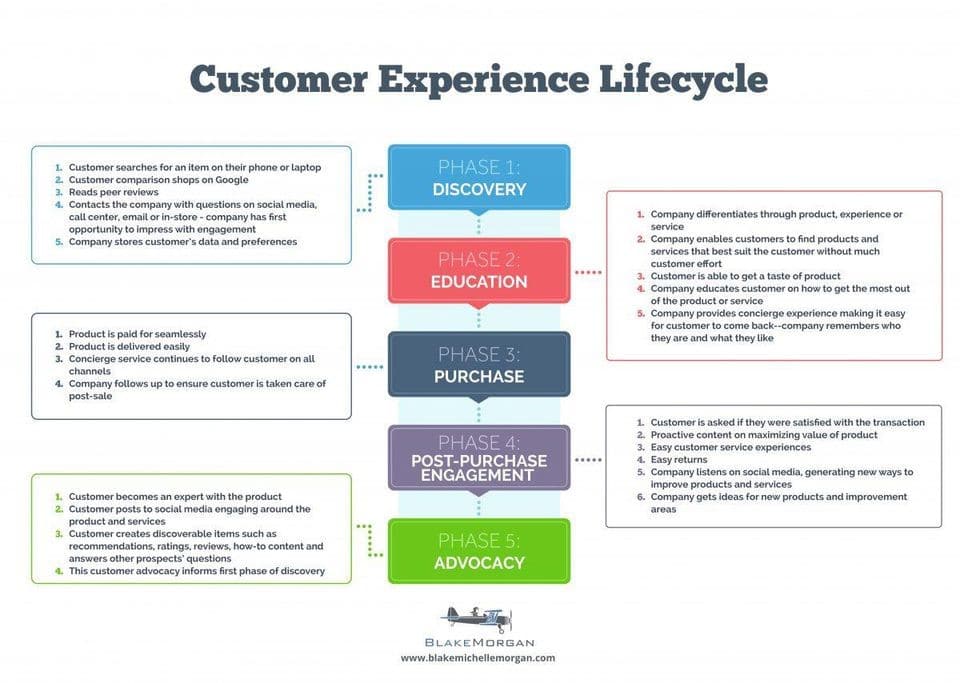
Life cycle segmentation is a marketing strategy that divides consumers into groups based on the stage they are in within the product or brand's life cycle. This strategy is often used by businesses to better understand and target their customer base, as well as to develop marketing and sales strategies that are tailored to each stage of the life cycle.
There are typically four main stages in a product's life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage has its own unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities for businesses.
During the introduction stage, a new product is launched into the market. This is often a risky and expensive phase for businesses, as they are investing heavily in research and development, marketing, and production to get the product off the ground. The goal at this stage is to create awareness and interest in the product, and to establish a customer base.
As the product enters the growth stage, sales start to increase and the product begins to gain traction in the market. This is a crucial time for businesses, as they need to continue to invest in marketing and sales efforts in order to sustain and accelerate the product's growth.
During the maturity stage, the product has reached its peak in terms of sales and market share. Competition may also be more intense at this stage, as other companies may have introduced similar products. Businesses may need to focus on maintaining market share and maximizing profits through cost-cutting measures, as well as exploring new market segments or innovation in order to keep the product relevant and competitive.
The decline stage marks the end of the product's life cycle, when sales start to decrease and the product becomes obsolete or is replaced by newer, more advanced products. At this stage, businesses may decide to phase out the product and discontinue production, or they may continue to sell it to a smaller, more loyal customer base.
Life cycle segmentation allows businesses to tailor their marketing and sales strategies to the unique needs and characteristics of each stage of the life cycle. For example, during the introduction stage, a business may focus on generating awareness and building a customer base through heavy marketing and promotional efforts. In the maturity stage, the focus may shift to maximizing profits through cost-cutting measures and targeting new market segments.
By understanding the stage of the life cycle that a product or brand is in, businesses can make informed decisions about how to allocate their resources and develop strategies that are most likely to drive success. In turn, this can help businesses to more effectively target and engage with their customer base, leading to increased sales and profitability.