Mitosis is the process by which cells divide and replicate their genetic material in order to produce two identical daughter cells. This process is essential for the growth and repair of tissues and organs in the body, and it occurs in all multicellular organisms. There are several stages of mitosis, each of which plays a critical role in the overall process of cell division.
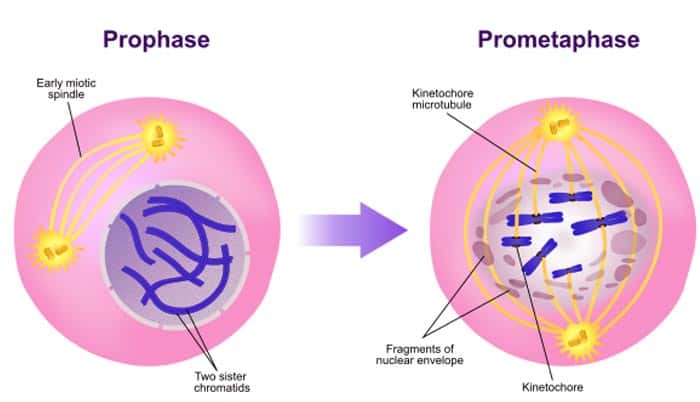
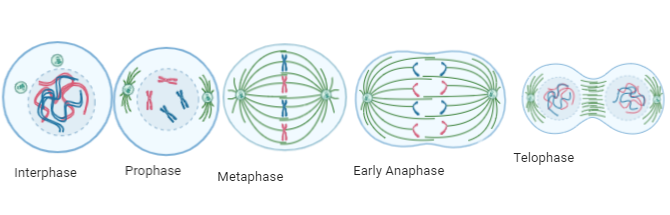
The first stage of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, the nuclear envelope breaks down and the nucleolus disappears. The chromosomes, which are made up of DNA and protein, become visible and start to condense. The centrosomes, which are responsible for organizing the mitotic spindle, also begin to move to opposite poles of the cell.
The second stage of mitosis is metaphase. During metaphase, the chromosomes line up at the equatorial plane of the cell, which is the midpoint between the two poles. This alignment is achieved through the action of the mitotic spindle, which consists of microtubules that attach to the chromosomes at their centromere.
The third stage of mitosis is anaphase. During anaphase, the centromere of each chromosome splits and the two sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the mitotic spindle. This separation ensures that each daughter cell will receive a complete set of chromosomes.
The fourth stage of mitosis is telophase. During telophase, a new nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes, and a new nucleolus appears. The cell also starts to pinch in the middle, forming two daughter cells.
The final stage of mitosis is cytokinesis. During cytokinesis, the cell cytoplasm is divided into two, forming two distinct daughter cells. In animal cells, this is achieved through the formation of a cleavage furrow, which starts at the equatorial plane and deepens until the cell is completely divided. In plant cells, the cell plate, a structure formed during telophase, grows and develops into a cell wall, separating the two daughter cells.
Overall, the stages of mitosis are essential for the proper division and replication of cells in the body. Without mitosis, organisms would not be able to grow or repair damaged tissues, and ultimately would not be able to survive.