List the levels of organization in the body. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body 2022-12-17
List the levels of organization in the body
Rating:
9,5/10
714
reviews
The human body is a complex and organized system that is made up of various levels of organization. These levels range from the smallest and most basic units of life, to the largest and most complex systems in the body. Understanding the different levels of organization in the body can help us better understand how the body functions and how it is able to maintain homeostasis, or a state of balance.
The smallest and most basic level of organization in the body is the cellular level. The human body is made up of trillions of cells, which are the basic units of life. Cells come in many different types, each with its own specific function. For example, red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body, while muscle cells allow us to move and tissues such as skin and bone provide structure and protection.
The next level of organization in the body is the tissue level. Tissues are made up of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. There are four main types of tissue in the body: epithelial tissue, which covers the surface of the body and lines internal organs; connective tissue, which supports and protects the body; muscle tissue, which allows movement; and nervous tissue, which carries electrical signals throughout the body.
The third level of organization in the body is the organ level. Organs are made up of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. For example, the heart is an organ made up of muscle tissue, connective tissue, and blood vessels that pumps blood throughout the body. Other organs in the body include the brain, liver, and kidneys.
The final level of organization in the body is the system level. Systems are made up of organs that work together to perform a specific function. There are eleven major systems in the human body, including the circulatory system, which transports blood throughout the body; the respiratory system, which brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide; and the nervous system, which coordinates and controls the body's responses to internal and external stimuli.
In conclusion, the human body is a complex and organized system that is made up of various levels of organization. Understanding these levels, from the cellular level to the system level, can help us better understand how the body functions and how it is able to maintain homeostasis.
A&P: Levels of structural organization : Anatomy & Physiology
For instance, digestive system organs cooperate to process food. From largest to smallest: biosphere, biome, ecosystem, community, population, and organism. Organ System Level of Organization An organ system is a collection of organs in the body that works together to perform a function. Tissue level— Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function. The levels of biological organization are the hierarchy of living organisms from simplest to most complex: atoms to molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, The human body maintains its life processes at different levels of structural organization. Muscle tissue is necessary for the body to maintain its posture and to move, as well as to move food through the digestive tract and pump blood.
Next
1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body

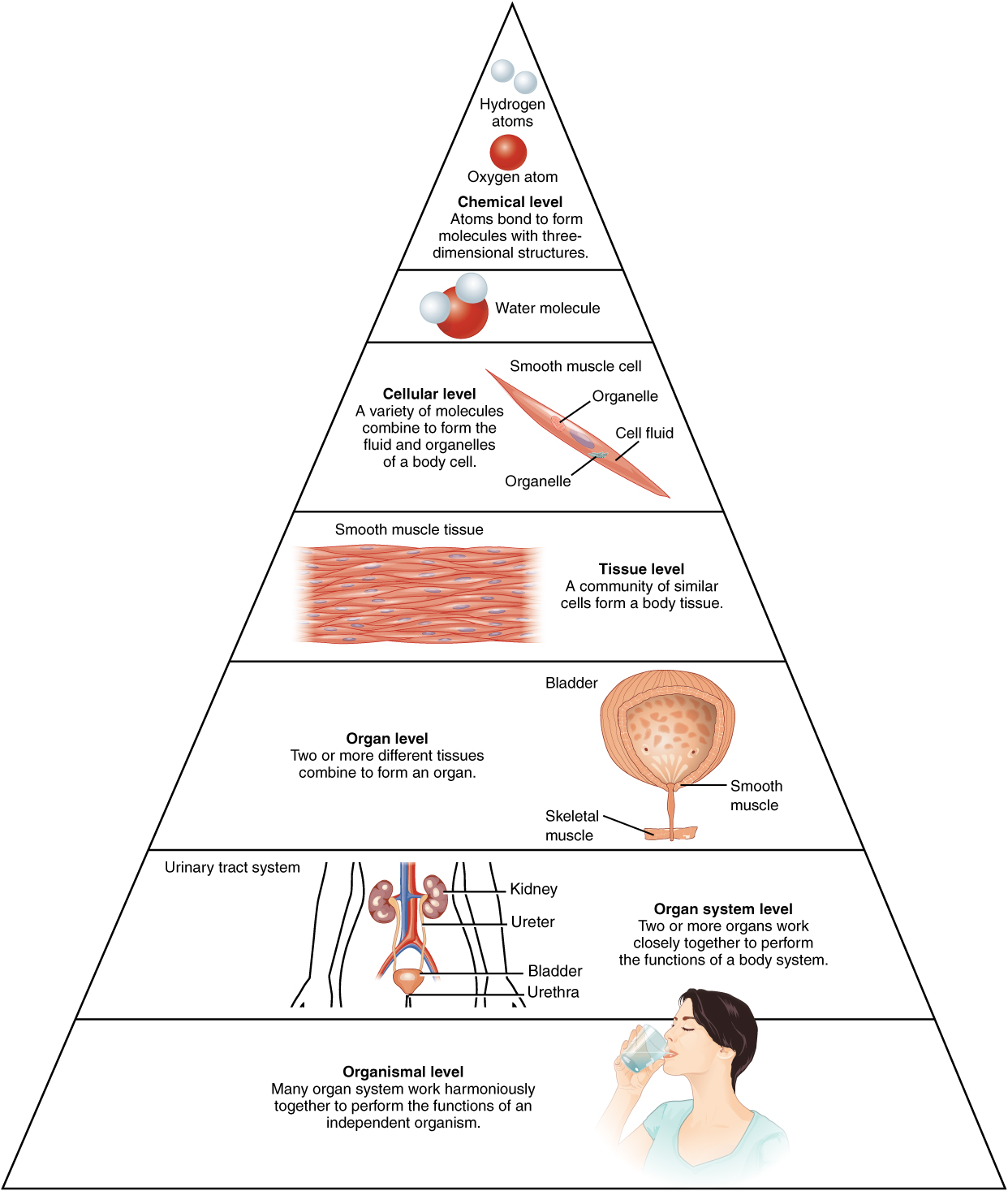
Connective tissue binds, connects, and cushions the body. The highest level of organization in the body is the organism level. The endocrine system is responsible for regulating processes like metabolism and homeostasis and is made up of organs like the pineal gland, the thymus, the pituitary gland, and the thyroid gland. The human body has 6 main levels of structural organization. Examples of organs include the heart, which is mainly muscular tissue and functions to pump blood throughout the body; the skin, which is made of epithelial tissue and provides external protection and temperature regulation; and the brain, which is composed of nervous tissues and processes sensory information. The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into energy, and it consists of the mouth, intestines, and stomach. It breaks down and absorbs nutrients and excretes the waste.
Next
Levels of Organization in the Human Body
Pellentesque dapibus efficitur la sum dolor sit amet, rem ipsum dolor sit ultrices ac magna. For instance, the heart and blood vessels work together and circulate blood throughout the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to cells. What are the levels of organization in the human organism list them from the smallest to the largest? Thus, without the cardiovascular system, there won't be enough oxygen, and thus not enough energy for the cells and they will die. Groupings of ecosystems form biomes, which include the geographic and climate state of several ecosystems. The kidneys remove waste products from the blood, and the liver has a variety of functions including breaking down harmful chemicals, filtering the blood, and secreting bile. The All of these systems together make up the entire organism, the human body. All living things reproduce.
Next
[Solved] List in sequence the levels of organization in the body from...
Cells require oxygen to make energy. They also secrete hormones, as does the endocrine system, therefore, ovaries and testes function within both the endocrine and reproductive systems. Examples include the brain, stomach, and liver. Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, and organs make up organ systems. Pellentesque dapibus effic ultrices ac magna. The human body is organized at different levels, starting with the cell.
Next
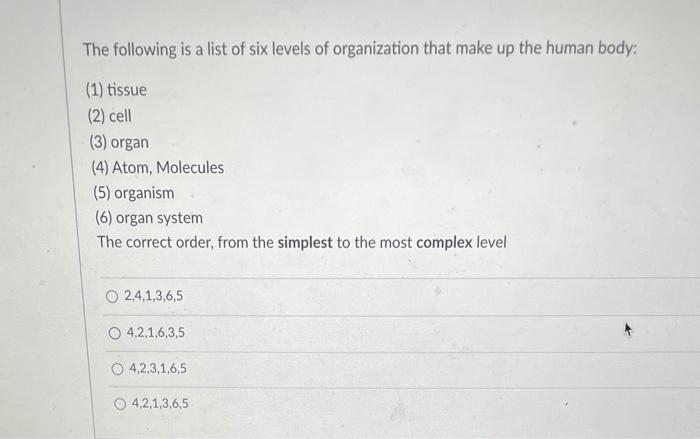
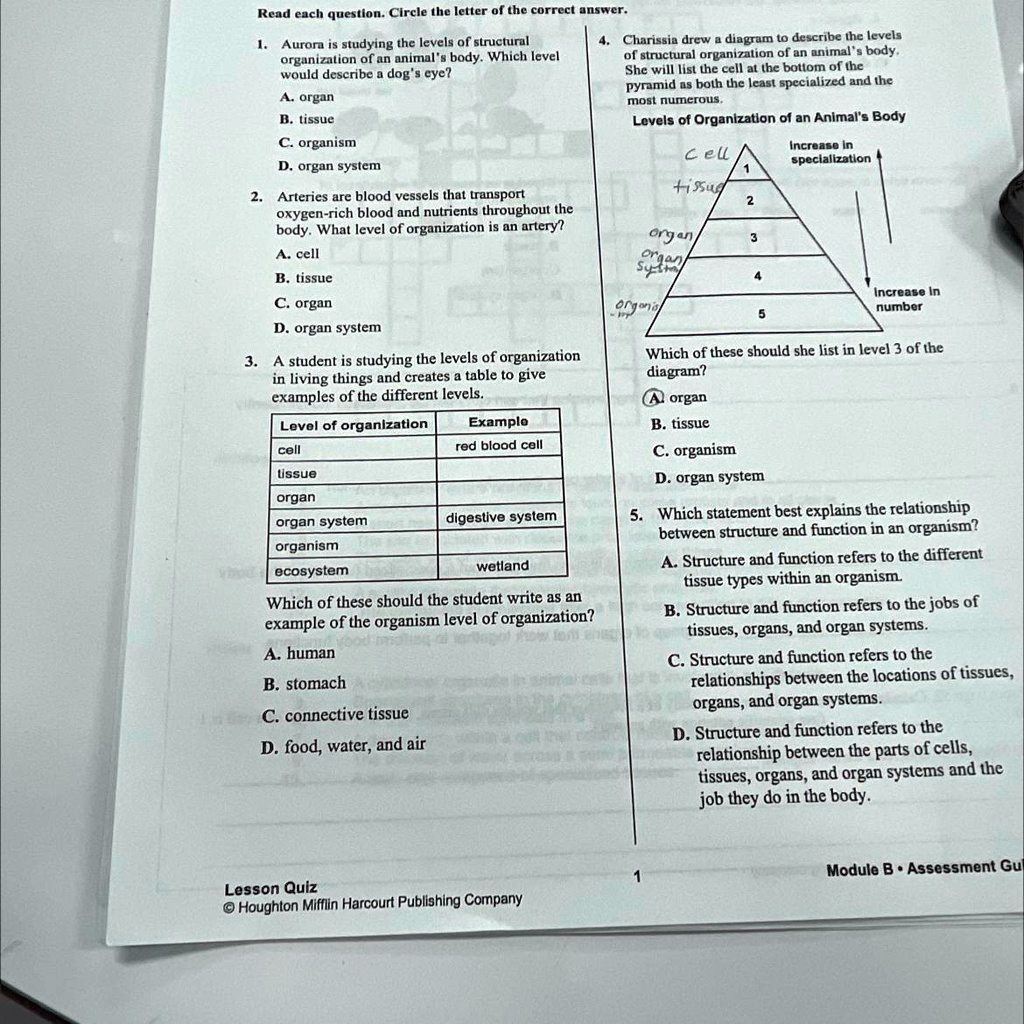
What are the six levels of organization of the human body?

What are the different levels of organization in the body? A tissue is a group of many similar cells though sometimes composed of a few related types that work together to perform a specific function. What is an element? In multi-cellular organisms, including humans, all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems of the body work together to maintain the life and health of the organism. For instance, the heart and blood vessels work together and circulate blood throughout the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to cells. The organism level is the highest level of organization. What makes up the structural organization of the body? Nam lacinia pulvinar tortor nec facilisis. The nervous system is responsible for electrochemical communication in the body. What are the levels of organization of the human body? Molecules are the building blocks to all structures in the human body.
Next
Levels of Organization Flashcards

The body is made of many different cell types, each with a particular function, for example muscle cells contract to move something, and red blood cells carry oxygen. Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous Organs Units made of multiple tissues that perform an independent function Heart Organ system Groups of organs that work together to perform a function Cardiovascular system Organism A single living thing made of multiple organ systems, organs, tissues and cells Human Cells are the basic units of life and make up all living things. Which of the terms represents the most basic level of body organization? The female ovaries and the male testes are a part of which body system? As in other multicellular organisms, cells in the human body are organized into tissues. These include the chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism level. The following sequence correctly lists levels of organization from simple to more complex: d cell, tissue, organ, organ system.
Next
What are the six levels of organization of life?
A tissue must contain two different types of cells. An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body. The anatomy of the human body can be classified based on six general levels of organization. We will begin this lesson with the simplest level within the structural hierarchy. Nam lacinia pulvinar tortor nec facilisis.
Next
1.1: Levels of Organization of the Human Organism

The particles and enzymes used to drive reactions and processes in an organism are made up of chemicals, as are the structural components of the living cell. Organismal level— The organismal level is the highest level of organization. Those molecules form the basic units of life, cells. Each bacterium is a single cell. The anatomy of the human body can be classified based on six general levels of organization. Read the description, and examples for each level in the pyramid: Chemical level, Cellular level, Tissue level, Organ level, Organ system level, and Organismal level. An organism is made up of four levels of organization: cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.
Next
What are the six levels of organization in the body from simplest to most complex?

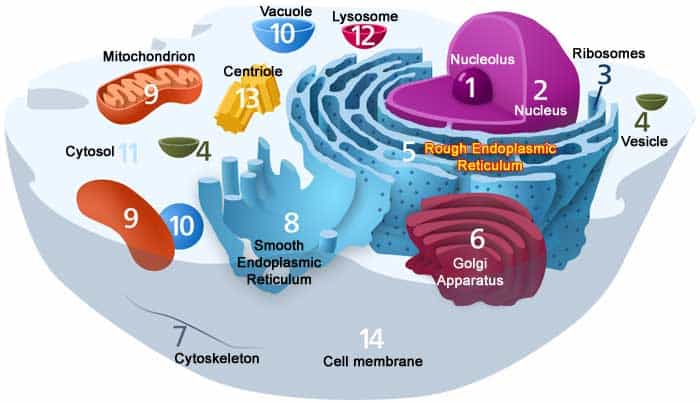
There are many types of organelles, each with a particular function for example, organelles called mitochondrion provides energy to a cell. Complex functions begin to emerge at this level. Complex multicellular organisms have levels of organization that build on each other. The heart is responsible for pumping blood which delivers oxygen to the entire body, while the lungs take in this oxygen. Which is the highest level of organization in the body? Another example of an organ system is the nervous system. The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: Organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere. The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere.
Next
Levels of Organization & Organ Systems in the Human Body

The biological levels of organization of living organisms from the simplest to the most complex are organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere. Groupings of organs that carry out specific functions in an organism are known as organ systems. Living things consume energy. Nam ris s a molestie consequat, ultrices ac magna. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. An organism is a living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life.
Next









