Little albert. Mystery solved: We now know what happened to Little Albert 2022-12-24
Little albert
Rating:
6,4/10
1659
reviews
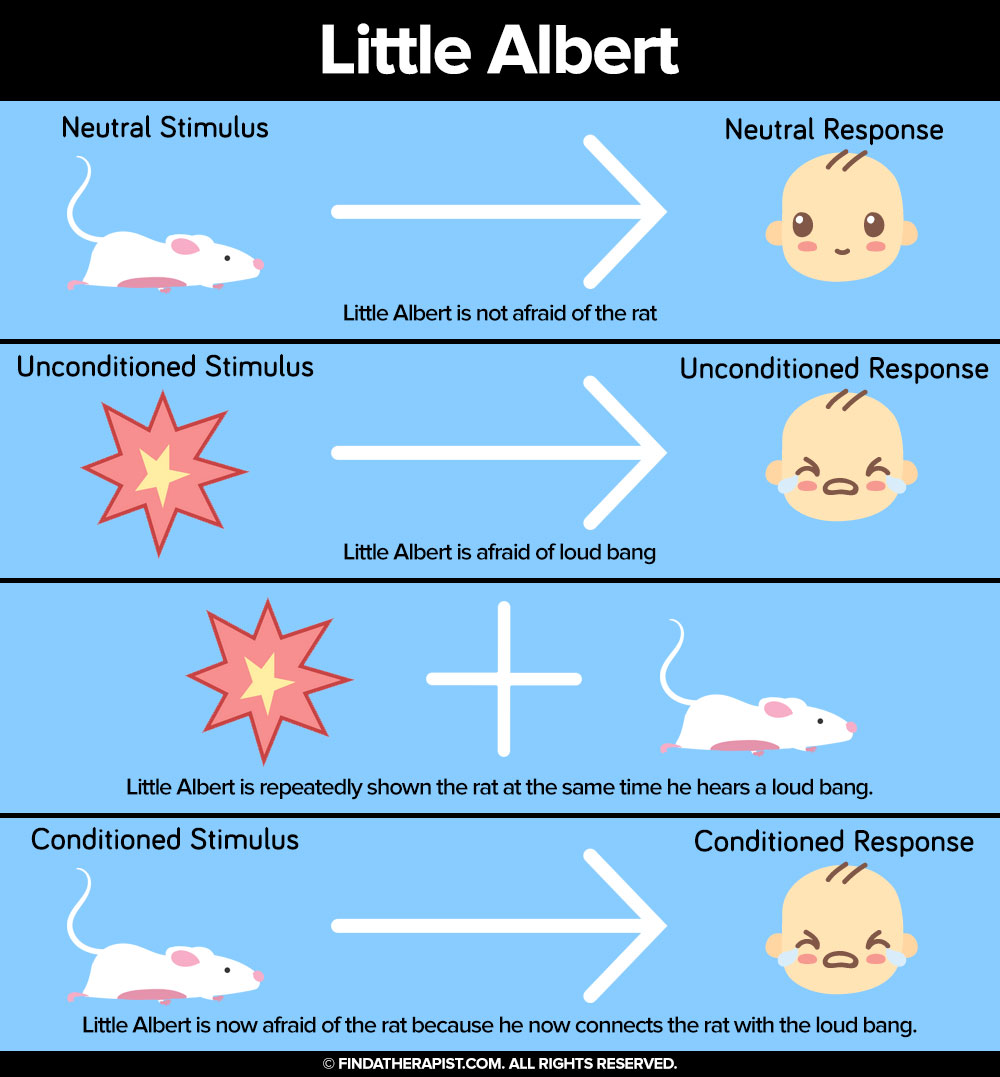
Little Albert was the subject of a famous psychological experiment conducted by behaviorist John B. Watson and graduate student Rosalie Raynor in 1920. The experiment was designed to test Watson's theory of classical conditioning, which proposes that an animal or human can learn to associate a neutral stimulus (such as a white rat) with a fear response (such as a loud noise) through repeated pairings of the two stimuli.
In the experiment, Watson and Raynor presented Little Albert, a 9-month-old baby, with a series of stimuli, including a white rat, a rabbit, a monkey, and various masks. Initially, Little Albert showed no fear towards any of these stimuli. However, when a loud noise was made each time Little Albert was presented with the white rat, he began to cry and show signs of fear whenever he saw the rat. This demonstrated that Little Albert had learned to associate the white rat with the loud noise, and thus, had developed a fear response towards the rat.
The experiment was controversial and sparked much debate in the field of psychology. Some argued that the experiment was unethical because it caused Little Albert to develop a fear that he may not have otherwise experienced. Others argued that the experiment was a valuable contribution to the understanding of classical conditioning and how fear responses can be learned.
Despite the controversy, the Little Albert experiment remains an important milestone in the history of psychology and continues to be studied and discussed in psychology classes and textbooks around the world. It is a prime example of how classical conditioning can shape human behavior and serves as a cautionary tale about the potential risks and ethical considerations of psychological research.
Where Is Little Albert Now? ✔️
Had the opportunity existed, they would have tried several methods: i constantly confronting the child with those stimuli which produced the responses, in the hope that habituation would occur ii trying to "recondition" by showing objects producing fear responses visual while simultaneously stimulating the erogenous zones tactual , first the lips, then the nipples, and, as a last resort, the sexual organs. You may wonder, who is the real little albert? Many people have illogical fears of animals. The study also provides an example. To try and reach some sort of conclusion, in June 2014, researcher Tom Bartlett published a new article in which he concluded that both children had participated in the experiment. This experiment was successful in conditioning the baby to fear the rat by associating - it with a loud, scary noise.
Next
Little Albert

He repeated this many times. Watch a Recap of this experiment in this video: Wow, this entire article is full of inaccuracies. The team, which also included Sharman Levinson, PhD, of The American University in Paris, and Gary Irons, the grandson of Arvilla Merritte, published their findings in the October American Psychologist Vol. The noise distressed Albert. However, he admitted in his research article that the fear he generated was neither strong or lasting.
Next
The Little Albert Experiment

Skinner continued with the search for lawful relationships between the environment and behavior. This developed a fear of the furry things due to the fear the loud sound actually invoked in the 9 month old baby. We may never know if he experienced any long-term negative consequences from his conditioning. Phobias however are real, and for some people quite limiting and potentially damaging. This made the child cry each time he heard the noise. For one, the experiment had only a single subject. It was said that most textbooks "suffer from inaccuracies of various degrees" while referring to Watson and Rayner's study.
Next
What Happened To Little Albert? (Find Out)

Watson filmed his study on Little Albert and the recordings are accessible on Youtube. Who was Little Albert's mother? For seven years, Beck and his associates scoured historical materials, conferred with facial recognition experts, met with relatives of the boy they theorized was Albert. The mask had white hair attached at the top. Why were Little Albert's parents worried? The infant at no time showed any fear. Because of this, both the American Psychological Association and the British Psychological Society would ultimately deem this experiment unethical.
Next
Little Albert Experiment Ethical Issues: All Of Its Controversies

After gaining permission from Albert's mother, the researchers decided to test the process of classical conditioning on a human subject - by inducing a further phobia in the child! Now, while we know now that phobias can be learned from watching others who have a fear, for example our mother being afraid of spiders, known as social learning, Watson used the tools and knowledge he had available to him to investigate the potential causes of them ultimately, one supposes, to develop treatments for phobias. There was only one subject and the experiment lacks any form of control. Albert died in 2007, without ever knowing of his early life in a hospital residence, or of his apparent part in psychology's history. Very quickly Albert was conditioned to expect the frightening noise whenever the white rat was presented to him. Albert described as "on the whole stolid and unemotional" showed no fear of any of these stimuli.
Next
Little Albert experiment

Baby used in notorious fear experiment is lost no more? He had two children with Rayner, who they educated in a strictly behaviorist way. Who was Little Albert's mother? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 98 4 , 381. However, his relatives report that he had an aversion to animals — and they even had to put the family dogs away when he came to visit. Was the Little Albert experiment successful? After that, the loud sound and the rat were simultaneously presented on seven different occasions. When she found out, she took Albert and moved away, letting no one know where they were going. In the study, Watson and graduate.
Next
The Little Albert Experiment And The Chilling Story Behind It

Through the conditioning, the animals and objects that were once a source of joy and curiosity had become a trigger of fear. Unfortunately, Albert's mother withdrew him from the experiment the day the last tests were made, and Watson and Rayner were unable to conduct further experiments to reverse the condition response. He was shown a white rat, a rabbit, a monkey and various masks. After conditioning, it will become the conditioned stimulus. We need to rethink our fears, why are we afraid of certain things, what is it that makes us afraid? Ignoring the role of cognition is problematic, as irrational thinking appears to be a key feature of phobias.
Next
Mystery solved: We now know what happened to Little Albert

And reveal the true identity of little Albert and the experiment that was conducted on him. He rang a bell every time a dog was about to be fed, and after a period of time the dog would salivate to the sound of the bell irrespective of food being presented. Thus, the boy began to associate the sound with the rat, and, after a while, he was afraid when he saw the animal. It went on to become known as the Little Albert Experiment. Thus, they were conditioned to associate the sound of the metronome with food. By tracking down financial records Beck.
Next
The “Little Albert Experiment”, The Most Unethical Experiment Conducted In Psychological History

Other research, however, suggests the true Albert was a little boy named William Albert Barger. You mention that the mask in which Watson wears at the ending of the video would distress any child, but before beginning the experiments, Watson and his crew tested several different stimuli on Albert and marked any emotional responses. . For 7 years, Hall along with a team of colleagues and students did facial matches, met with facial recognition experts and sought out family and relatives of Albert. According to him, little Albert was actually William Albert Barger, a normal child who lived a healthy life and died at the age of 88. At first, the child did not show any fear of the things displayed. Later on, Watson introduced an additional stimulus.
Next








