Long run cost curves are U-shaped because they reflect the relationship between the cost of producing a good or service and the quantity of that good or service produced. In the long run, a firm has the flexibility to change all of its inputs, including the scale of its operations. As a result, long run cost curves take into account the impact of changes in scale on costs.
In the short run, a firm is limited in its ability to change its inputs, and as a result, the relationship between cost and quantity is typically depicted by a straight line. However, in the long run, a firm has the ability to change the scale of its operations, and this can have a significant impact on costs.
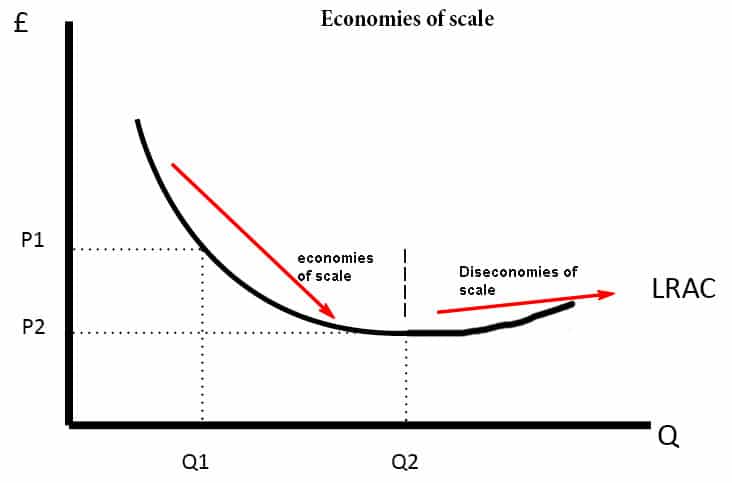
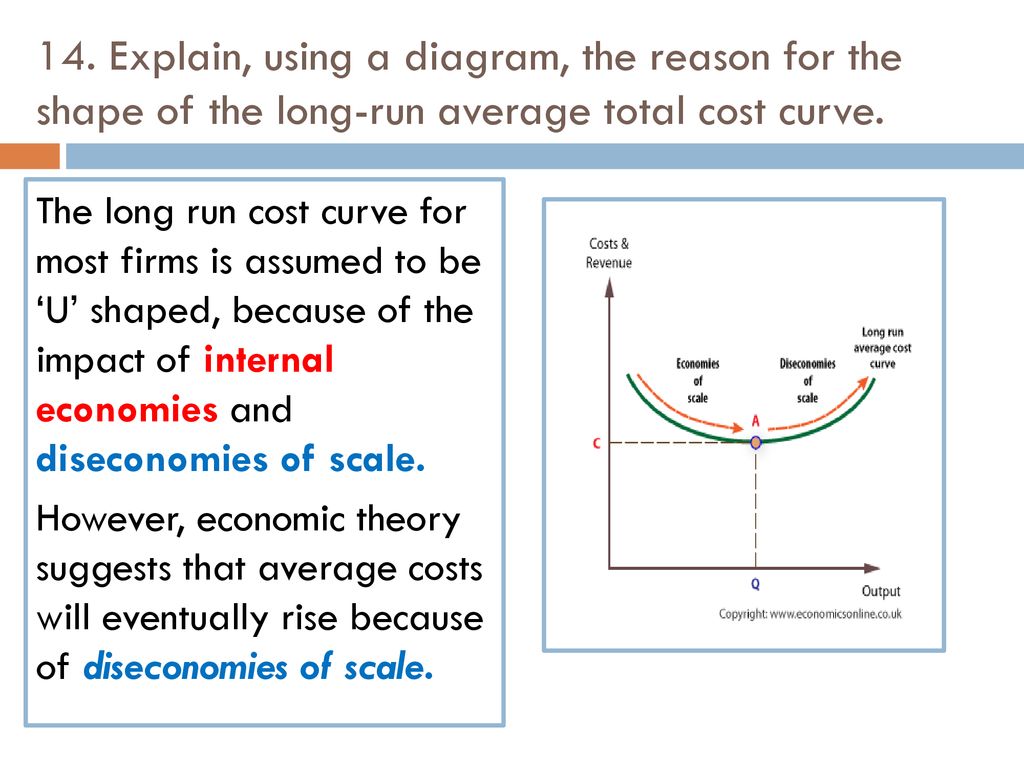
As a firm increases the scale of its operations, it may initially experience economies of scale, which occur when the average cost of production falls as the firm increases production. This is because the firm is able to spread fixed costs, such as the cost of building a factory, over a larger number of units. In addition, the firm may be able to take advantage of specialization and division of labor, which can increase efficiency and reduce costs.
However, as the firm continues to increase production, it may eventually reach a point where the benefits of economies of scale are exhausted and diseconomies of scale begin to occur. Diseconomies of scale occur when the average cost of production begins to rise as the firm increases production. This can occur for a variety of reasons, such as difficulty coordinating and managing a large operation, or the costs associated with maintaining a complex organizational structure.
As a result, the long run cost curve is typically U-shaped, with economies of scale occurring at lower levels of production and diseconomies of scale occurring at higher levels of production. The minimum point on the U-shaped cost curve is known as the minimum efficient scale, which is the level of production at which the firm is able to achieve the lowest possible average cost of production.
In summary, long run cost curves are U-shaped because they reflect the relationship between the cost of producing a good or service and the quantity of that good or service produced, taking into account the impact of changes in scale on costs. The shape of the curve reflects the presence of economies of scale at lower levels of production and diseconomies of scale at higher levels of production, with the minimum efficient scale being the level of production at which the firm is able to achieve the lowest possible average cost of production.