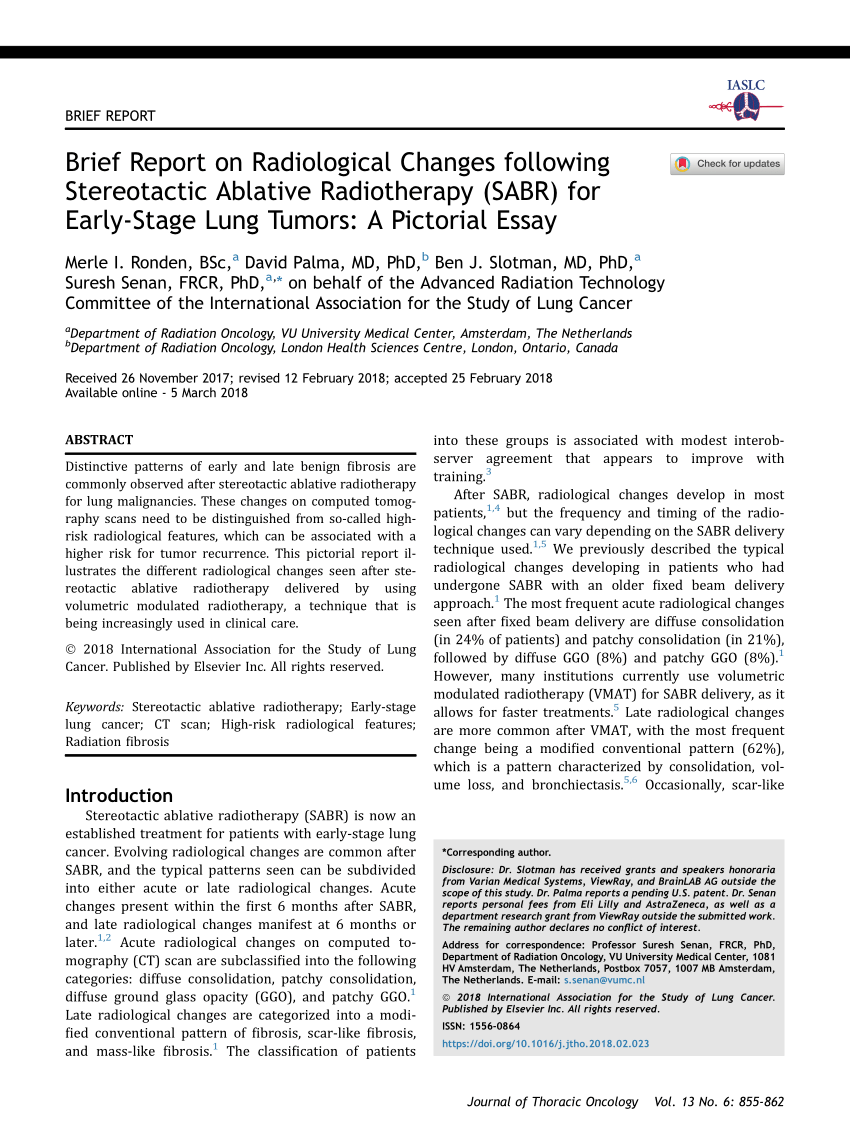
Hobhouse liberalism is a political philosophy that originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, named after the British philosopher and politician Leonard Trelawny Hobhouse. At its core, Hobhouse liberalism advocates for a society in which individuals are free to pursue their own interests and goals, but also recognizes that the state has a role in promoting the common good and protecting the rights and welfare of its citizens.
One of the central ideas of Hobhouse liberalism is the concept of social justice. Hobhouse argued that the state has a responsibility to ensure that all members of society have the opportunity to lead fulfilling and productive lives, regardless of their social or economic status. This includes providing access to education, healthcare, and other essential services, as well as protecting workers' rights and promoting economic equality.
Hobhouse also believed in the importance of individual freedom and autonomy, and argued that the state should not interfere in the personal lives of its citizens unless there is a clear and compelling reason to do so. He argued that the state should protect individual rights and freedoms, such as the right to free speech and freedom of religion, and should not discriminate against certain groups of people based on factors such as race, gender, or sexual orientation.
In addition to social justice and individual freedom, Hobhouse liberalism also emphasizes the importance of democracy and the rule of law. Hobhouse argued that the government should be accountable to the people and should operate transparently and in accordance with the rule of law. He believed that a strong and independent judiciary is essential to upholding the rule of law and protecting the rights and freedoms of citizens.
Overall, Hobhouse liberalism is a political philosophy that seeks to balance the interests of the individual with the needs of society as a whole. It emphasizes the importance of social justice, individual freedom, democracy, and the rule of law, and advocates for a society in which all members have the opportunity to lead fulfilling and productive lives.
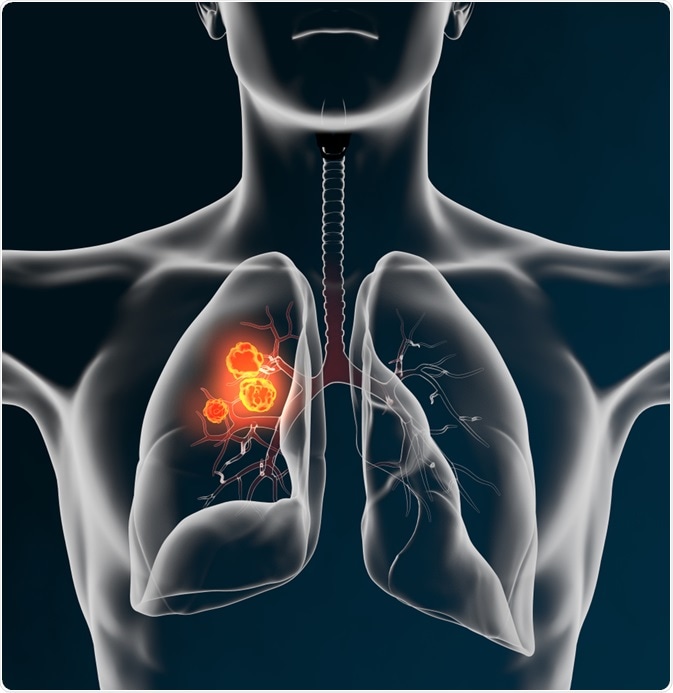
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that affects the lungs, which are a pair of organs located in the chest that are responsible for breathing. It is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and is most commonly caused by tobacco smoke, including cigarettes, cigars, and pipe tobacco. However, other factors such as exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollution, and radiation can also increase the risk of developing lung cancer.
There are two main types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). SCLC is a more aggressive form of lung cancer that typically spreads quickly to other parts of the body. NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer and tends to grow more slowly.
Symptoms of lung cancer can include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, chest pain, and weight loss. These symptoms may not appear until the cancer has advanced, which is why it is important to see a doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Diagnosis of lung cancer typically involves a combination of tests, including a physical examination, chest x-ray, CT scan, and biopsy. Treatment options for lung cancer depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
Preventing lung cancer involves avoiding tobacco smoke and other substances that can cause lung cancer, such as radon and asbestos. It is also important to limit exposure to air pollution and to get vaccinated against the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can cause lung cancer.
Living with lung cancer can be challenging, but there are many resources available to help patients and their families cope with the physical and emotional impact of the disease. Support groups, counseling, and palliative care can all be helpful for those dealing with lung cancer.
In conclusion, lung cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that is caused by a variety of factors, including tobacco smoke and air pollution. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. By avoiding risk factors and seeking medical attention if you experience symptoms, you can take steps to protect yourself from lung cancer.