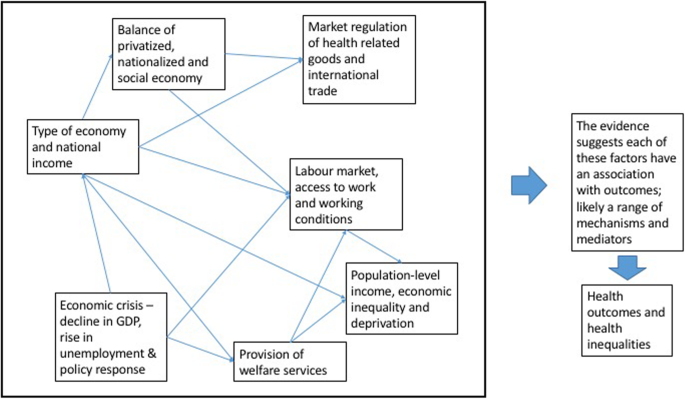
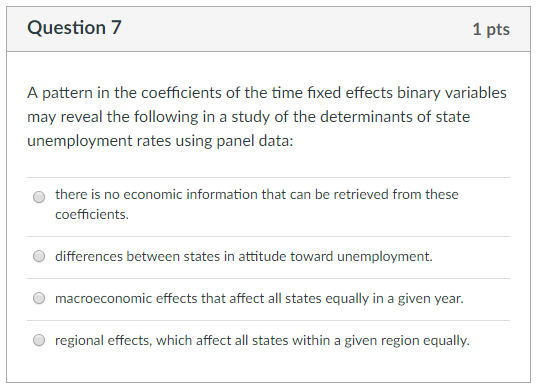
Unemployment is a key indicator of a country's economic health and is affected by a range of macroeconomic factors. In this essay, we will explore some of the main determinants of unemployment and how they can impact the job market.
One of the primary determinants of unemployment is economic growth. When the economy is growing, businesses are more likely to expand and hire new workers. Conversely, when the economy is in a recession, businesses may cut back on hiring or lay off workers in order to reduce costs. This can lead to higher unemployment rates.
Another important determinant of unemployment is the level of productivity in an economy. When workers are productive, they can produce more goods and services, which can lead to higher demand for their labor. On the other hand, if productivity is low, businesses may be less likely to hire new workers or may even lay off existing employees.
The level of wage inflation can also impact unemployment. If wages are rising faster than the rate of productivity, businesses may be less likely to hire new workers due to increased labor costs. On the other hand, if wages are not keeping up with the rate of inflation, workers may be more likely to accept lower-paying jobs in order to remain employed.
The level of government intervention in the economy can also affect unemployment. For example, if the government implements policies that make it easier for businesses to hire and retain workers, such as tax breaks or training programs, unemployment may decrease. On the other hand, if the government imposes regulations that make it more difficult for businesses to operate, such as strict labor laws or high taxes, unemployment may increase.
Finally, global economic conditions can also impact unemployment rates. For example, if a country's major trading partners are experiencing economic downturns, it may lead to reduced demand for the country's exports, which could result in job losses and higher unemployment.
In summary, unemployment is influenced by a range of macroeconomic factors, including economic growth, productivity, wage inflation, government intervention, and global economic conditions. Understanding these determinants can help policymakers and businesses make informed decisions that can help to reduce unemployment and promote economic growth.