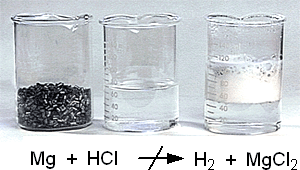
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a silvery-white metal that is lightweight and strong, making it useful in a variety of applications. Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is a strong acid with the formula HCl. It is commonly used in a variety of industrial and laboratory settings, and is known for its corrosive properties.
When magnesium is combined with hydrochloric acid, a chemical reaction occurs that produces hydrogen gas and a salt called magnesium chloride. The reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
Mg + 2HCl -> MgCl2 + H2
In this reaction, the magnesium acts as a reductant, while the hydrochloric acid acts as an oxidant. The magnesium gives up some of its electrons to the hydrochloric acid, and the hydrochloric acid gains those electrons and becomes reduced to hydrogen gas.
The reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid is exothermic, meaning that it releases heat as it proceeds. This can be observed as the reaction mixture becomes warmer as the reaction proceeds.
The reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid has a number of practical applications. One such application is in the production of hydrogen gas, which has a number of uses, including fuel for vehicles and generators. The reaction can also be used to generate electricity, as the hydrogen gas can be burned in a fuel cell to produce electricity.
In addition to its practical applications, the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid is also of interest to chemists and scientists, as it allows for the study of chemical reactions and the properties of different substances. By studying the reaction between these two substances, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the behavior and properties of chemicals, and can use this knowledge to develop new technologies and products.
In conclusion, the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid is a chemical reaction that produces hydrogen gas and a salt called magnesium chloride. The reaction has a number of practical applications, and is also of interest to scientists and chemists who study the properties of different substances.