Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms. It is essential for the production of gametes, or sex cells, which are necessary for sexual reproduction. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes in the cells is halved, and the resulting gametes are genetically diverse due to a process called crossing over.
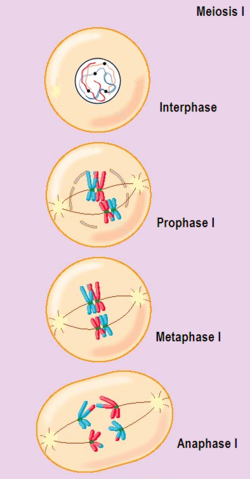
Meiosis begins with a diploid cell, which has two copies of each chromosome, one inherited from each parent. The first step of meiosis is called prophase I, during which the chromosomes become visible and start to condense. The homologous chromosomes, which are pairs of chromosomes that carry genetic information for the same traits, pair up and exchange genetic material. This process is known as crossing over.
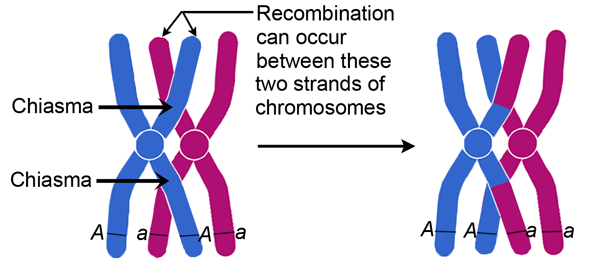
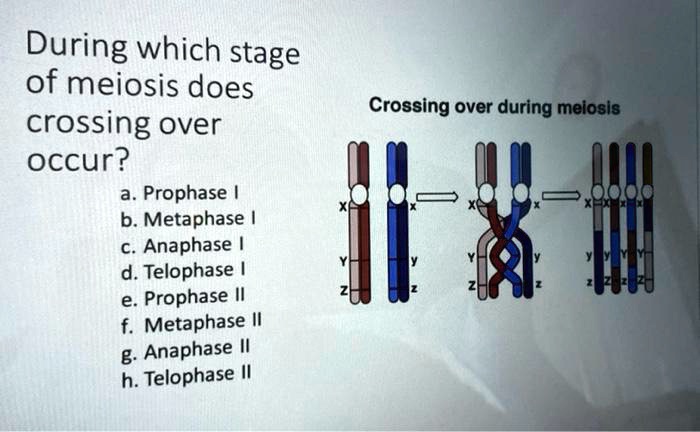
Crossing over occurs when a portion of one chromosome is exchanged with a portion of the other chromosome in the pair. This can result in the production of genetically diverse gametes, as the exchange of genetic material creates new combinations of genes. Cross over occurs during prophase I of meiosis, when the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material.
The crossing over process is initiated by proteins called recombinases, which create a structure called a synaptonemal complex. This complex allows the chromosomes to physically align and exchange genetic material through a process called homologous recombination. Homologous recombination occurs when a sequence of nucleotides on one chromosome is exchanged with a complementary sequence on the other chromosome. This exchange results in new combinations of genes and contributes to the genetic diversity of the offspring.
After crossing over, meiosis continues with metaphase I, during which the homologous chromosomes align at the center of the cell. Anaphase I follows, during which the homologous chromosomes are separated and move to opposite poles of the cell. Finally, during telophase I and cytokinesis, the cell divides, creating two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
Meiosis and crossing over play important roles in sexual reproduction and the production of genetically diverse offspring. Without crossing over, the genetic material of the offspring would be identical to that of the parents, resulting in a lack of genetic diversity within a population. This lack of diversity can lead to problems such as inbreeding and a reduced ability to adapt to changes in the environment. By creating genetically diverse gametes through meiosis and crossing over, sexually reproducing organisms are able to produce offspring with a variety of traits, increasing the adaptability and survival of the population.