proteins, but not all proteins are enzymes
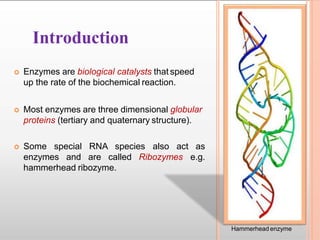
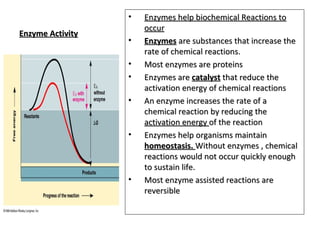
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in chemical reactions within living organisms. They are essential for the proper functioning of cells and play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. Enzymes are found in all forms of life and are responsible for a wide variety of chemical reactions, including digestion, respiration, and metabolism.
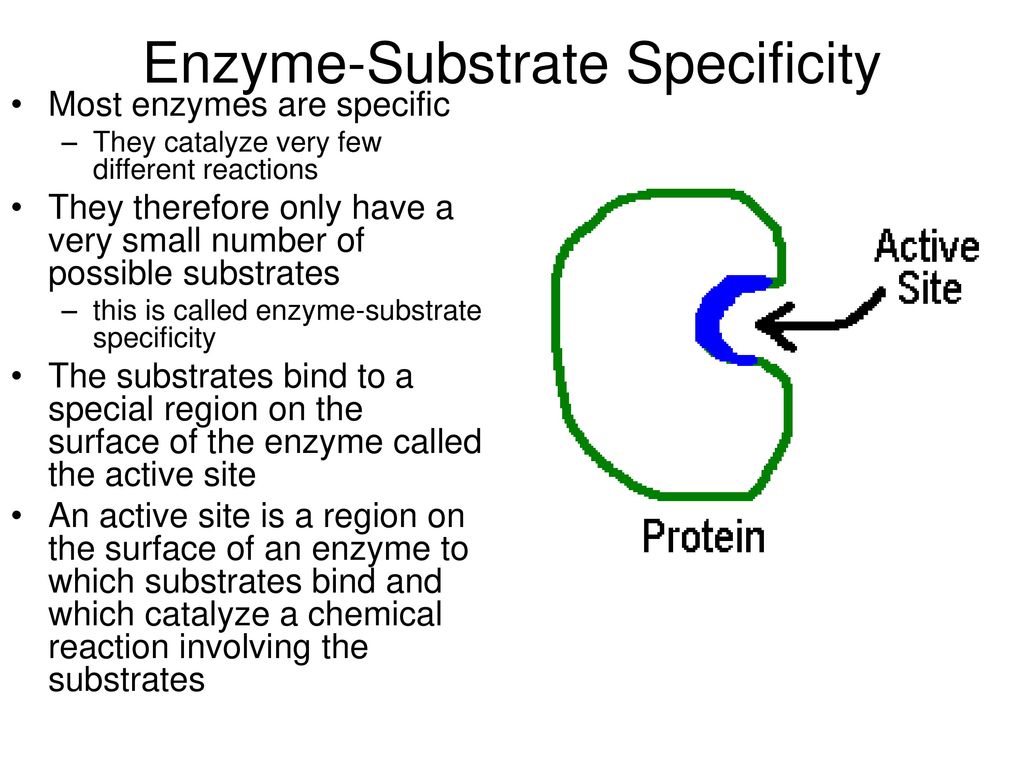
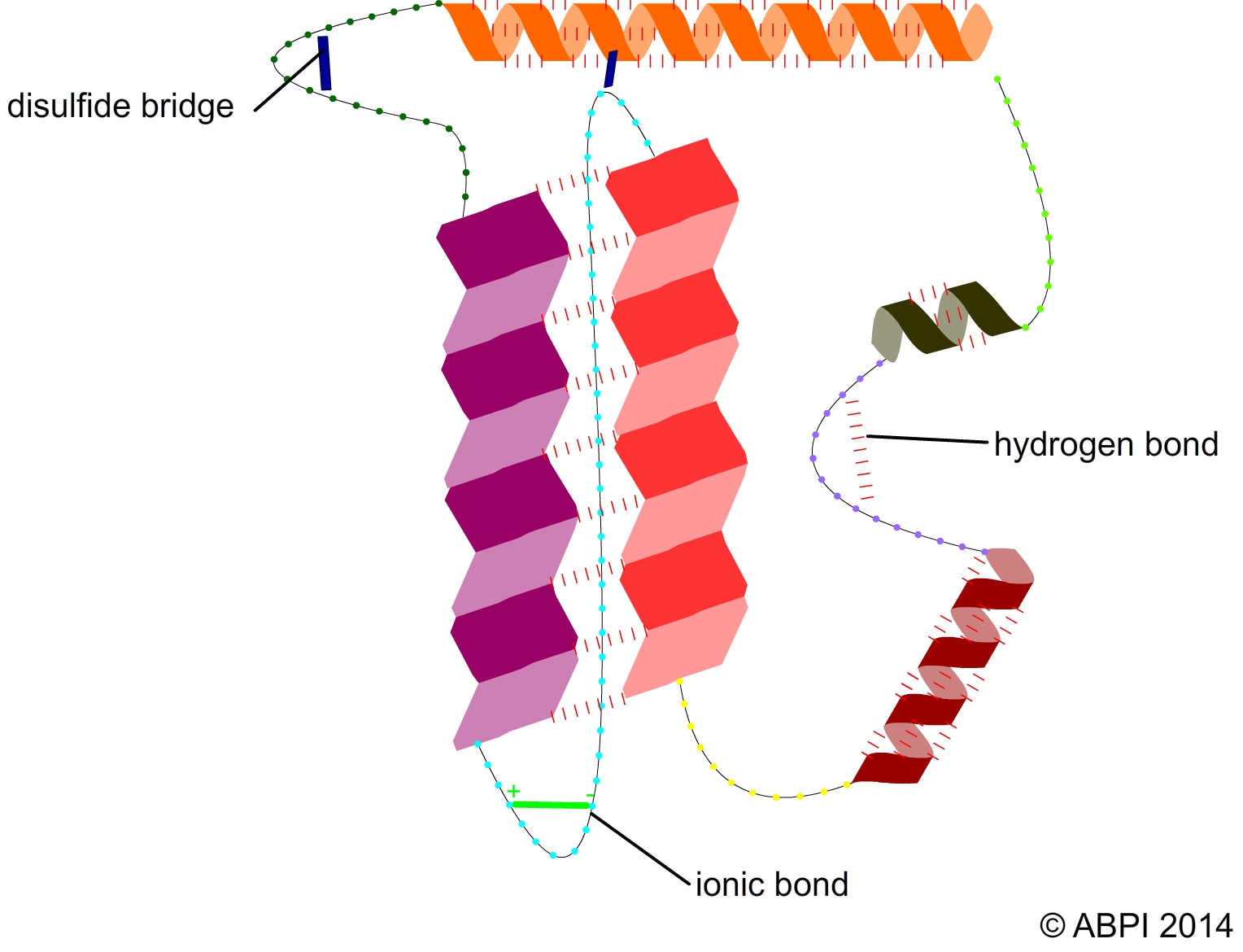
One of the defining characteristics of enzymes is that they are proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules that are made up of chains of amino acids. Enzymes are specifically designed to catalyze specific chemical reactions, and their structure and function are closely related. The specific sequence of amino acids that make up an enzyme determines its unique three-dimensional shape, which in turn determines its function.
While most enzymes are proteins, not all proteins are enzymes. There are many different types of proteins in the body, each with its own specific function. Some proteins, such as structural proteins, play a role in the structure and support of cells and tissues. Others, such as transport proteins, facilitate the movement of molecules across cell membranes. Still others, such as regulatory proteins, play a role in the regulation of cellular processes.
Enzymes are classified into different categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze. There are enzymes that break down large molecules into smaller ones, enzymes that synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones, and enzymes that facilitate the transfer of chemical groups from one molecule to another. Enzymes can be specific to a single reaction, or they can be involved in multiple reactions.
Enzymes are highly efficient catalysts, and they are able to speed up chemical reactions by several orders of magnitude. This is because enzymes lower the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur. Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction, and enzymes lower this energy by providing a specific environment in which the reaction can occur. This allows the reaction to occur more easily and at a faster rate.
In summary, most enzymes are proteins, but not all proteins are enzymes. Enzymes are specialized proteins that act as catalysts in chemical reactions within living organisms. They play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body and are essential for the proper functioning of cells. While there are many different types of proteins in the body, enzymes are specifically designed to catalyze specific chemical reactions and are classified based on the type of reaction they facilitate.