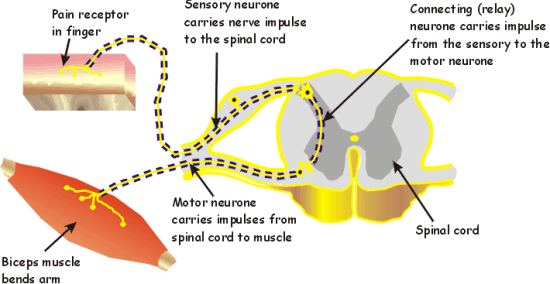
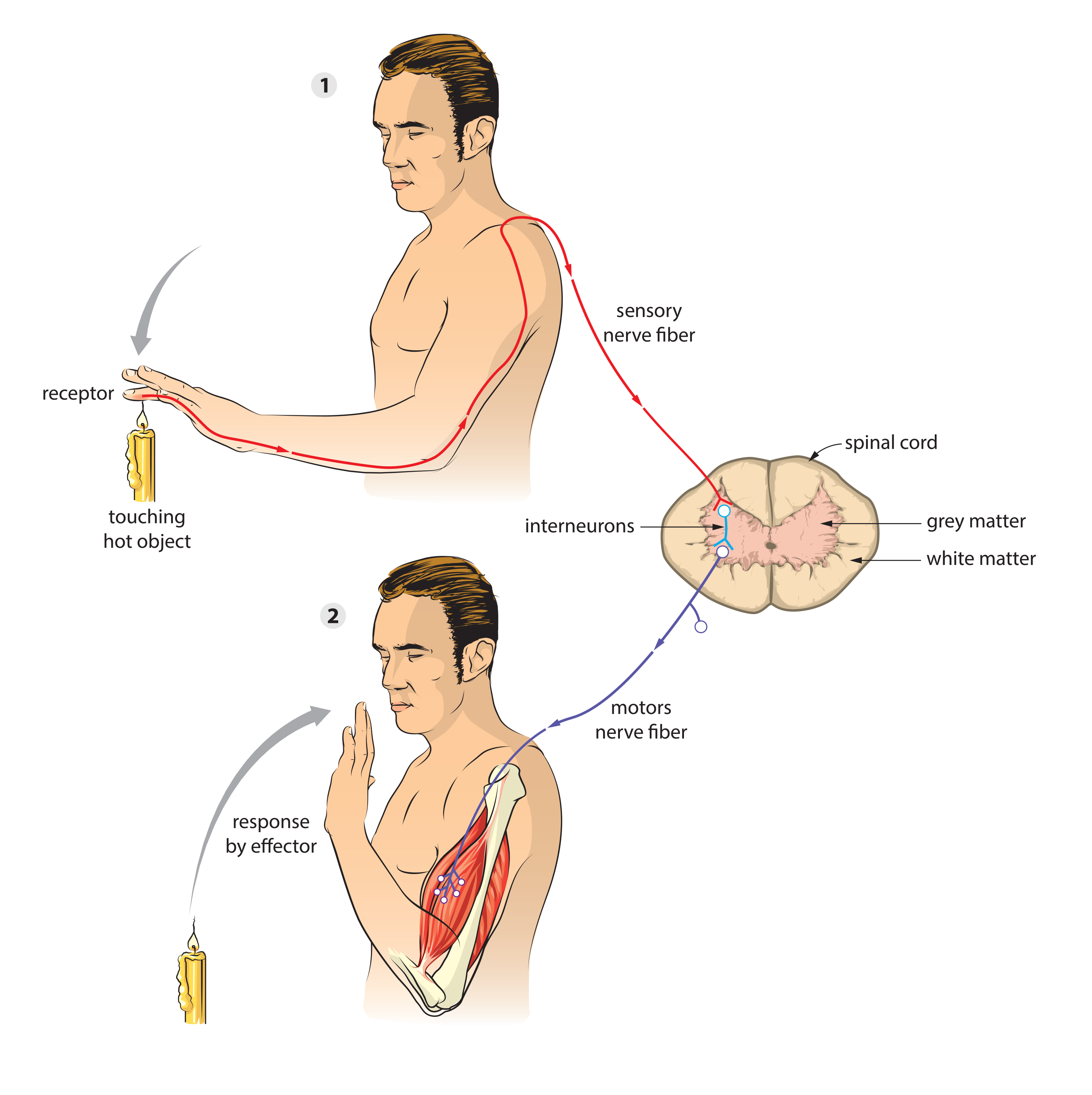
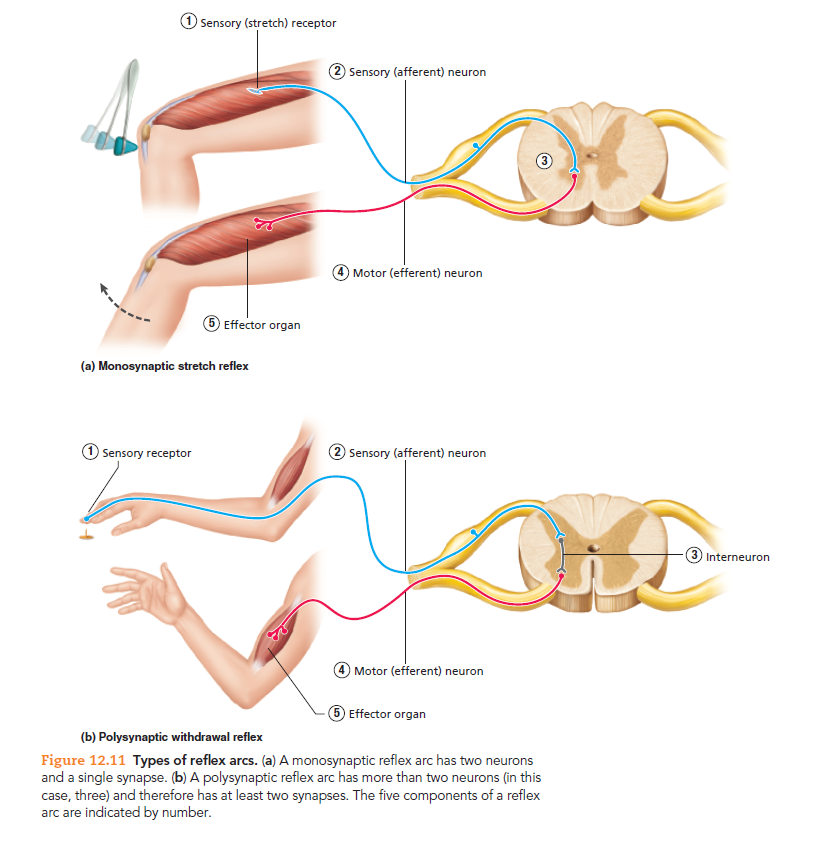
A motor reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflexive action, such as the reflexive withdrawal of a hand from a hot stove. It is a simple, automatic response to a stimulus that does not require conscious thought. The reflex arc involves several components, including a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron.
The sensory neuron is responsible for detecting the stimulus and transmitting a nerve impulse to the spinal cord. For example, when the hand touches a hot stove, sensory receptors in the skin send a signal to the sensory neuron. This neuron then carries the signal through its axon, a long, thin extension of the cell body, to the spinal cord.
The interneuron, also called an integrating neuron, is located within the spinal cord and receives the signal from the sensory neuron. It processes the information and decides whether or not to initiate the reflexive response. If the interneuron determines that the stimulus is harmful, it sends a signal to the motor neuron.
The motor neuron receives the signal from the interneuron and sends it to the appropriate muscles, causing them to contract. In the example of the hand withdrawing from a hot stove, the motor neuron sends a signal to the muscles in the arm, causing the hand to quickly pull away from the stove.
The motor reflex arc allows the body to respond quickly to stimuli without waiting for the brain to process the information and initiate a response. This is important in situations where quick action is necessary to avoid harm. However, reflexive responses can also be inappropriate, such as when a person experiences a reflexive gag response to the sight or smell of certain foods.
In conclusion, the motor reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls reflexive actions in response to stimuli. It involves the interaction of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons to initiate a quick and automatic response. This reflex arc is an important part of the body's defense mechanism, but it can also cause inappropriate responses in certain situations.