A phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states that a substance can exist in under different conditions of temperature and pressure. The phase diagram for naphthalene, also known as mothballs, is a useful tool for understanding the behavior of this substance under different conditions.
Naphthalene is a white, crystalline solid with a strong, musty odor. It is commonly used as a moth repellent, but it has also been used as a raw material in the production of dyes, plastics, and explosives.
The phase diagram for naphthalene shows that it has a melting point of about 80°C. At temperatures below this point, naphthalene exists in the solid state. As the temperature increases, the solid naphthalene begins to melt and transform into a liquid.
The phase diagram also shows that naphthalene has a boiling point of about 218°C. At temperatures above this point, the liquid naphthalene vaporizes and transforms into a gas.
The phase diagram for naphthalene also shows the effect of pressure on the physical state of the substance. At low pressures, naphthalene exists in the gas phase at temperatures above its boiling point. As the pressure increases, the boiling point of naphthalene increases, and the substance exists in the liquid phase at higher temperatures.
In summary, the phase diagram for naphthalene shows that it exists in the solid state at temperatures below its melting point, in the liquid state at temperatures between its melting and boiling points, and in the gas state at temperatures above its boiling point. The phase diagram also illustrates the effect of pressure on the physical state of naphthalene, with higher pressures causing the substance to exist in the liquid phase at higher temperatures.
3

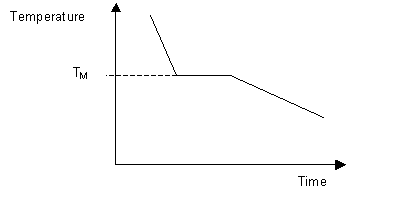
A one-component phase diagram is a plot of the temperature vs. The lines separating the three phases intersect at a single point, the triple point, which is the only combination of temperature and pressure at which all three phases can coexist in equilibrium. Phase Diagram of Naphthalene-Biphenyl Phase diagrams are of considerable practical utility. Look up their emf values in HCP to check the thermocouples. Be prepared to explain the phase diagram with respect to the number of phases, degrees of freedom and the equilibrium that exists in each area. T A and T B are melting points of A and B respectively, and X B is the mole fraction of component B. It was also of interest to study whether CM displays the same anomalous solubility behavior in naphthalene as in hexane, CS 2, and toluene, where the solubility increases with temperature up to a maximum near room temperature and decreases subsequently.
PHASE DIAGRAM OF NAPHTHALENE AND N

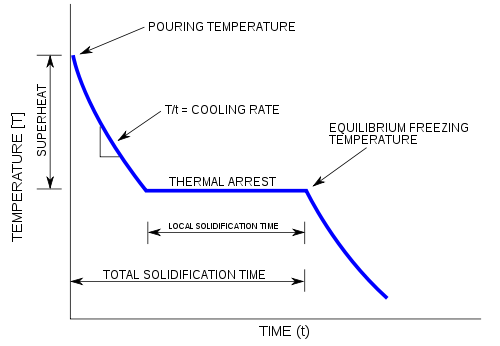
The preparation and the analysis of the phase diagrams can be studied by means of thermal analysis 1. Zimmerman, in Fullerenes: Recent Advances in the Chemistry and Physics of Fullerenes and Related Materials, edited by K. For this to take place the crystal structure of these components should be the same as that of the mixture. A schematic of the thermocouple. MRS Online Proceedings Library 359, 561—566 1994. Organize the data and produce the relevant plots. Ruoff Electrochemical Society Proceedings, 94-24, NJ, 1994 p.
Solid Liquid Phase Diagram Lab blog.sigma-systems.com

There is only one degree of freedom i. Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1993-1994 p. A cooling curve is a graph of the variation of the temperature of a sample with time as it is allowed to cool 1,2. The areas bounded by the curves represent temperature and pressure conditions for which only a single phase exists. At the eutectic temperature, the solution is saturated with respect to both components so that both a and b start to precipitate. Because no more than three phases can ever coexist, a phase diagram can never have more than three lines intersecting at a single point.
EXPERIMENT 2: TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM PHASE DIAGRAM
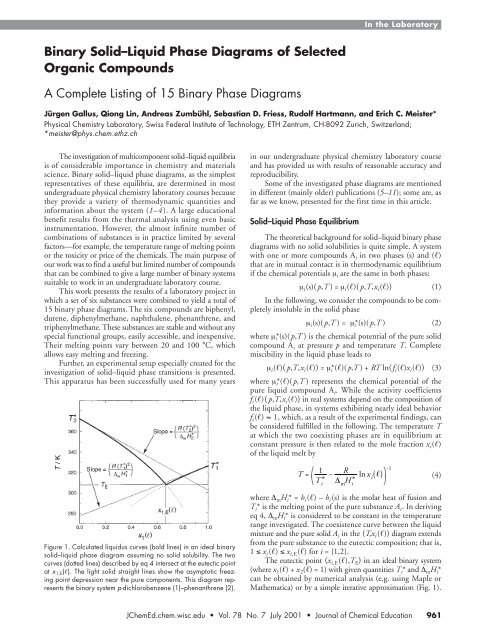
A phase diagram is a diagram from which the physical state of a system may be deduced once the temperature, pressure and composition of the system have been defined. An example of a simple solid-liquid phase diagram of the two components A and B. It is simple to deduce the physical state of a binary system once the temperature and composition of the system have been defined. The theory is found on page 204 of Atkins. Ruoff Electrochemical Society Proceedings, 94-24, NJ, 1994 p. As the tubes cool you should try to pick out temperature halts, super cooling and the formation of the first precipitate.
The Binary Phase Diagram Naphthalene

The two organic compounds that were used to complete this experiment were 1,4- dichlorobenzene and naphthalene, which are shown in the figure below. A binary system consists of two metals that may form an alloy or it could be a mixture of naphthalene-biphenyl which are organic compounds. Recent research indicates that the surface of ice, where the ordered array of water molecules meets the air, consists of one or more layers of almost liquid water. Ruoff Electrochemical Society Proceedings, 94-24, NJ, 1994 p. The letters refer to points discussed in Example 10. Phase Equiliubrium of Naphthalene and Biphenyl Mixture Abstract Thermal analysis of a solid-liquid phase using cooling curves at various compositions is a method used to obtain the eutectic composition and temperature of naphthalene-biphenyl. When all of the liquid solution has disappeared, the number of phases is reduced to 2 and the temperature can again decrease.