Newton rings are a type of interference pattern that is formed when light waves reflect off the surface of a lens or other transparent object. They are named after Sir Isaac Newton, who first observed and described them in the 17th century.
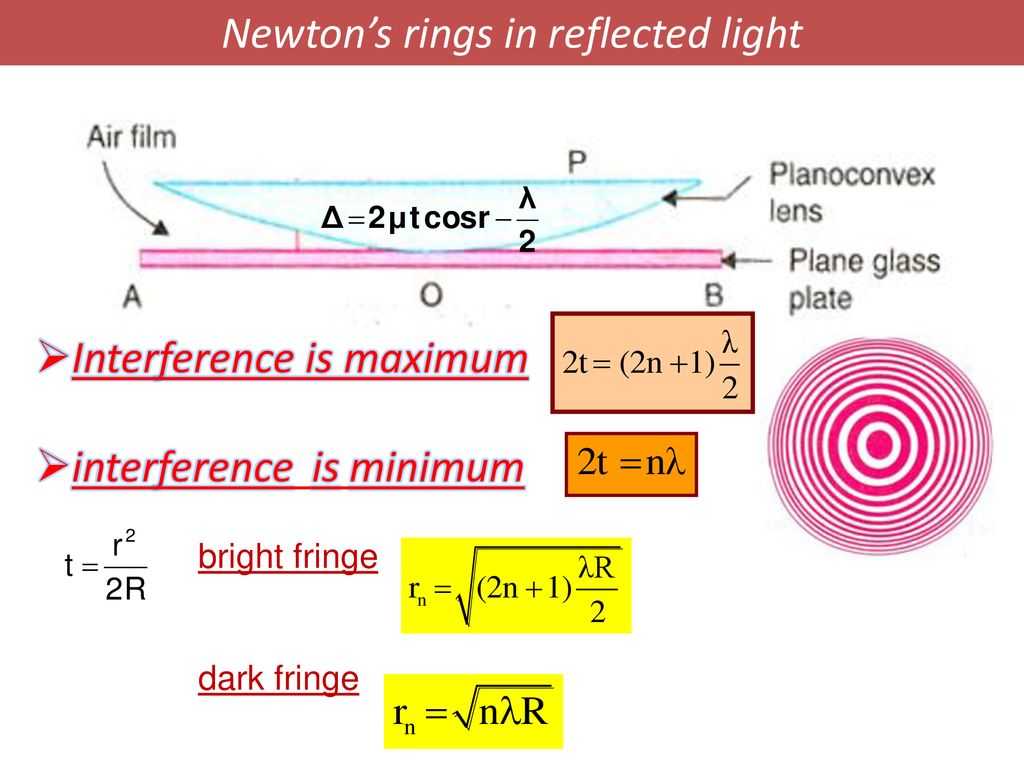
The basic principle behind Newton rings is that when light waves reflect off the surface of a lens, they interfere with one another. This interference can either reinforce or cancel out the waves, depending on the phase difference between the waves. When the phase difference is such that the waves reinforce one another, a bright ring is formed. When the phase difference is such that the waves cancel each other out, a dark ring is formed.
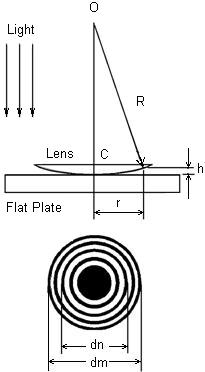
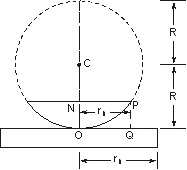
Newton rings are often used in scientific and technical applications to measure the surface flatness of a lens or other transparent object. To do this, a lens is placed on top of a flat surface, and a light source is shone onto the lens from below. The resulting interference pattern can then be used to determine the shape of the lens and any deviations from a perfectly flat surface.
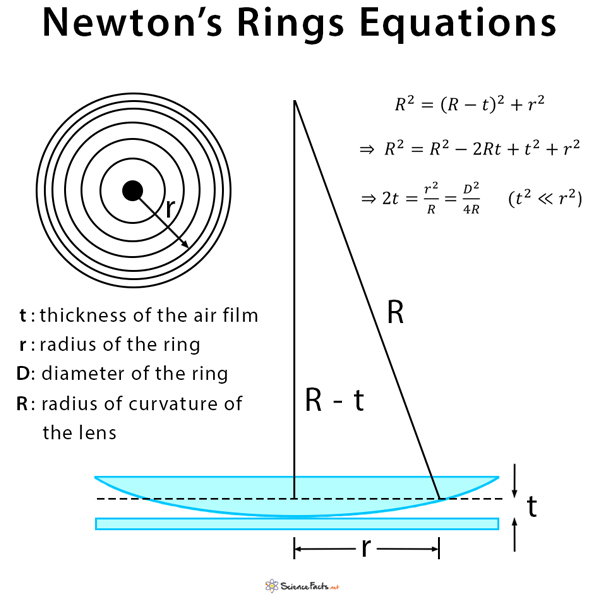
Newton rings can also be used to study the properties of thin films, such as their thickness and refractive index. By measuring the spacing between the rings in the interference pattern, it is possible to determine the thickness of the film. Similarly, the refractive index of the film can be determined by measuring the angles at which the rings appear.
In addition to their practical applications, Newton rings are also a popular subject in demonstrations and demonstrations of optics. They are a simple and visually striking way to demonstrate the principles of wave interference and the nature of light.
In conclusion, Newton rings are an important and versatile tool in the study of optics and light. They have a wide range of practical applications, and are also a popular subject for demonstrating the principles of wave interference and the nature of light.
What are Newton rings and how do I avoid them?

It is said that Newton's Rings are formed by the interference pattern between two surfaces caused by the light reflecting between them. Thanks for the tutoring. I was able to recreate the effect using moisture on a chrome card and an old SGC slab. I shot this one with the PGR. Inspect the resulting image. There are those who believe the case is there to protect the contents, and as long as it is not cracked or severely damaged, not a problem. Ie, either defocus or with a diffuser of some kind? The other things, that's definitely on QC, if we are talking about slabs fresh out of grading to the submitter.
newton rings and book value
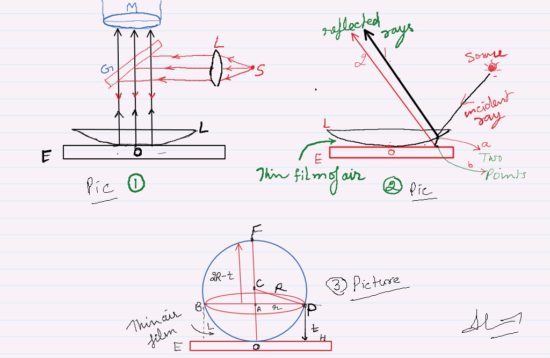
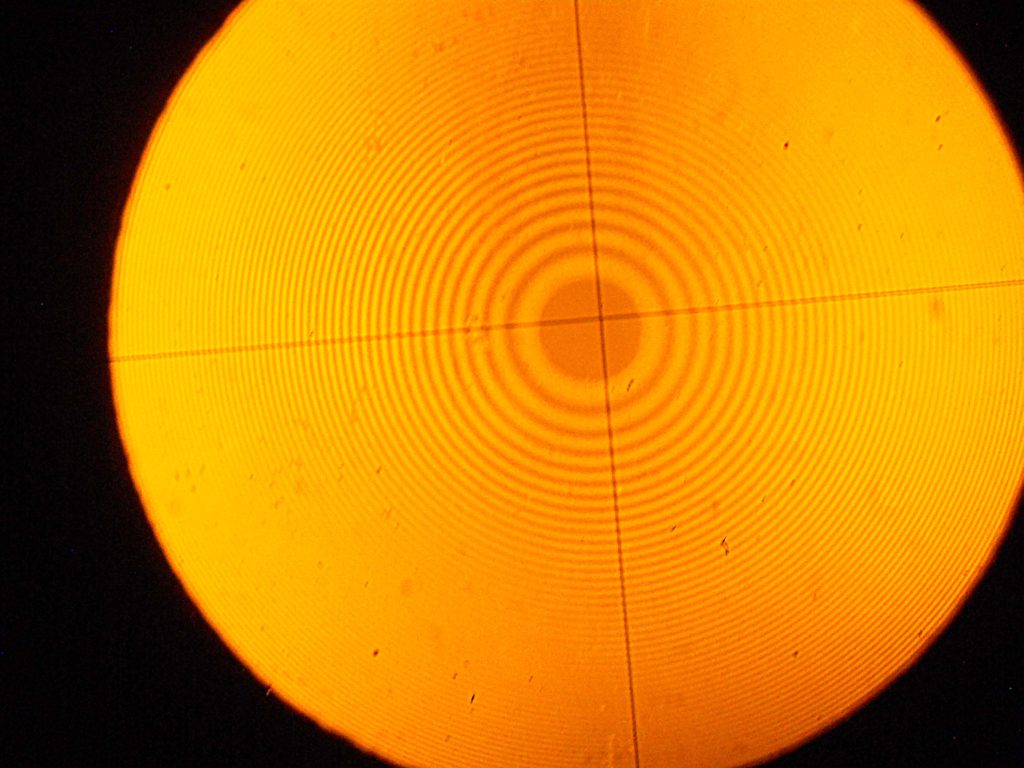
This section will present all the information related to Newton's Ring. If monochromatic light is allowed to fall normally on the lens, and the film is viewed in reflected light, alternate bright and dark concentric rings are seen around the point of contact. Got a personal favorite method that we don't know about? People have pet peeves - don't like date stamps, the wrap has to be perfectly aligned, hate Restored or Qualified, case must be perfect, etc. Drag and select a box around the spikes and hit the delete key to remove the spike. I learned more from this example. Is there a Batch switch on ImageJ? The diameters of the bright rings calculated for transmitted light using the equations above correspond precisely to the diameters of the dark rings in reflection. In the monochromatic example, the source of color is a monochromatic single source of light shining through the top piece and refracting off the bottom and top surfaces.
Newton’s Rings: Definition, Equation, and Applications

If the dealer had offered a discount in the amount it would take to ship and re-holder I might have gone for it. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science. Removing the spike in the FFT will remove that specific frequency component in the actual image, which is what we want. A similar analysis for illumination of the device from below instead of from above shows that in this case the central portion of the pattern is bright, not dark, as shown in Fig. Marty, Should the tilt adapter be directly attached to the camera or attached to the Barlow T2 100mm up the light path? I shot 200 frames yesterday complete with Newtonian rings.