Nike, Inc. is a multinational corporation that is one of the world's largest suppliers of athletic shoes and apparel. In the early 2000s, the company implemented a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system as part of a larger effort to modernize its operations and improve efficiency. However, the implementation of this new system was plagued by a number of problems, leading to what has become known as the "Nike ERP failure."
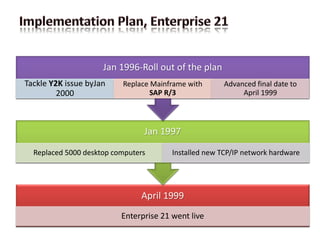
The decision to implement the new ERP system was made in response to a number of challenges faced by Nike at the time. The company was experiencing rapid growth, which had led to disorganization and inefficiencies in its operations. In addition, Nike was relying on a patchwork of legacy systems that were no longer able to support the company's needs. The new ERP system was meant to address these issues by providing a single, integrated platform for managing all of Nike's business processes.
However, the implementation of the ERP system was fraught with difficulties. The project was significantly delayed and over budget, with costs ultimately exceeding $400 million. In addition, the system experienced a number of technical problems, including data integrity issues and performance issues. These problems caused disruptions to Nike's operations and led to delays in the delivery of products to customers.
The ERP failure had a number of negative consequences for Nike. The company's financial performance was negatively impacted, with the ERP project contributing to a decline in profits. In addition, the failure damaged Nike's reputation with customers and stakeholders, as the company was unable to meet demand for its products and experienced delays in fulfilling orders.
One of the key lessons of the Nike ERP failure is the importance of careful planning and execution when implementing new technology systems. In hindsight, it is clear that Nike did not sufficiently consider the complexity and scale of the project, which contributed to its difficulties. In addition, the company did not adequately involve key stakeholders in the planning and implementation process, which likely contributed to the system's performance issues.
Ultimately, the Nike ERP failure serves as a cautionary tale for organizations considering the implementation of new technology systems. While such systems can bring significant benefits, they also come with risks and challenges that must be carefully managed. By learning from the mistakes made by Nike, organizations can avoid similar pitfalls and ensure the successful implementation of their own ERP systems.